* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PIVVIR POWERPOINT!
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
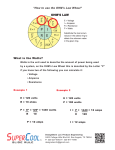
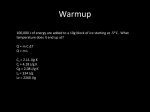
Ohm’s Law And Beyond Let’s Pivver!!! • What’s Pivver? Well, that’s not spelled correctly. The correct spelling is: P=IV and V=IR • First, though, we’ll have to define some terms. Charge • Electrons are negatively charged particles that are responsible for the flow of charge in an electric circuit. • Electrons are so small and so many, that we talk in terms of Coulombs (C). • One coulomb is 6.25x1018 electrons. • One electron has a charge of –1.6x10-19 C. What’s Charge? (Click on the correct answer to this question below) a. Charge is measured in Coulombs (C). b. Electrons transfer charge through wires. c. One C is equal to 6.25x1018 electrons. d. All of the above are true statements. So Sorry, Try Again! Click to try again You’re Right!!!! Keep Going! Current • Current is the flow of electrons through a conductor (like a wire). • The symbol for current is I. • The unit for current is Amperes (Amps, or A). • 1 A = 1 C/s, meaning one coulomb of electrons flows past a point on a wire in one second if there’s an Ampere of current • Current = I = Amps = A = C/s What’s Current? (Click on the correct answer) a. b. c. d. Current Current Current Current = = = = R = ohms = Ω = Js/C2. I = Amps = A = C/s. V = Volts = V = J/C. P = Watts = W = J/s. So Sorry, Try again! Click to try again You’re Right!!!! Keep Going! Voltage • Voltage is the energy (Joules, or J) equivalent to the potential work that could be done by two oppositely charged plates (their attraction could move a mass). • It’s also called potential, or potential difference. The more difference in charge between the two plates, the more work could be done, so the more equivalent energy, the more push or pull, so the more voltage. • The symbol for Voltage is V. • The unit for voltage is Volts (V). • Voltage = V = Volts = V = J/C What’s Voltage? (You know what to do) a. b. c. d. Voltage Voltage Voltage Voltage = = = = R = ohms = Ω = Js/C2. I = Amps = A = C/s. V = Volts = V = J/C. P = Watts = W = J/s. So Sorry, Try again! Click to try again You’re Right!!!! Keep Going! Power • Power is how much energy (J) is used for a period of time (s) when using electrical energy. • The symbol for power is P. • The unit for power is watts (W). • Power = P = Watts = W = J/s. What’s power? a. b. c. d. Power Power Power Power = = = = R = ohms = Ω = Js/C2. I = Amps = A = C/s. V = Volts = V = J/C. P = Watts = W = J/s. So Sorry, Try again! Click to try again You’re Right!!!! Keep Going! Resistance • Resistance is the resistance of a conductor’s (like a wire) resistance to the flow of electrons. • A type of friction, resistance creates heat in a wire, and sometimes even makes the conductor glow (think light bulb or electric stove). • The symbol for resistance is R. • The unit for resistance is ohms (Ω). • Resistance = R = ohms = Ω = Js/C2 What’s resisistance? a. b. c. d. Resistance Resistance Resistance Resistance = = = = R = ohms = Ω = Js/C2. I = Amps = A = C/s. V = Volts = V = J/C. P = Watts = W = J/s. So Sorry, Try again! Click to try again You’re Right!!!! Keep Going! Resistance opposes the push Voltage supplies the push To Recap: • • • • Current = I = Amps = A = C/s Voltage = V = Volts = V = J/C Power = P = Watts = W = J/s Resistance = R = ohms = Ω = Js/C2 Current flow results Power is how much energy is used Now Let’s Pivver!!! Here are the equations you’ll need: P = IV V = IR P = I2R P = V2/R Plus, you can rearrange them for any variable you want! Free of Charge! Let’s Pivver!!! Here’s an example: Your sister is using her 1500W hairdryer to dry your hamster because she dropped it in her piranah fish tank by accident and doesn’t want you to find out. Your house has plugs with 120V. What current does she draw using the dryer? Your sister is using her 1500W hairdryer to dry your hamster because she dropped it in her piranah fish tank by accident and doesn’t want you to find out. Her house has plugs with 120V. What current does she draw using the dryer? 1. Decide which equation you need: P = IV, V = IR, P = I2R, or P = V2/R? I’ll say P = IV because it has all the relevant variables, watts, volts, and amps. 2. Rearrange it for current: I = P/V 3. Then put the given values in: I = 1500W/120V = 12.5A You try one: What’s the resistance of a stove that is using 20A and is plugged into 240V? 20A R=? 240 V What’s the resistance of a stove that is using 20A and is plugged into 240V? a. b. c. d. 120 Ω 12 Ω 60 Ω 6Ω So Sorry, Try again! Click to try again You’re Right!!!! Keep Going! OK, Just One More……… What’s the power of a light bulb on a 120V circuit with 0.625A of current runnung through it? What’s the power of a light bulb on a 120V circuit with 0.625A of current running through it? a. b. c. d. 45W 60W 100W 75W So Sorry, Try again! Click to try again You’re Right!!!! Well, That’s All, Folks!!! Remember, a Pivver a day keeps the short circuits away!