* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Science TAKS Review
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Living things in culture wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Incomplete Nature wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Soil food web wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
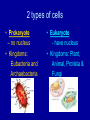
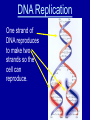
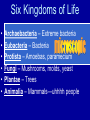
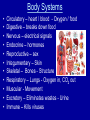
Science TAKS Review I want plants to grow faster • Independent Variable – – the thing I change • Water plants different amounts • Control / constant – • Do not change- all plants in same location, get same amount of dirt and sunlight. Etc… • Dependent Variable – • Did the plants grow any faster with change in water 2 types of cells • Prokaryote – no nucleus • Kingdoms: Eubacteria and Archaebacteria • Eukaryote - have nucleus • Kingdoms: Plant, Animal, Protista & Fungi Cell Structures and Functions • • • • • • Cell Membrane - barrier Nucleus – DNA Cytoplasm- “blood” of cell Ribosome- protein maker Mitochondria- energy maker Chloroplast- make sugar and O2 Cellular Processes • Homeostasis – balance or same –Water –temperature –blood pressure Permeability • Diffusion - movement from high concentration to low concentration • Osmosis – movement of water Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Nitrogen bases (Thymine, Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine) determines the inherited traits. AT GC DNA Replication One strand of DNA reproduces to make two strands so the cell can reproduce. Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) 11th • Transcription A U GC Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) 11th • Translation Amino acids are linked together to make a protein. 3 bases needed for 1 codon Six Kingdoms of Life • • • • • • Archaebacteria – Extreme bacteria Eubacteria – Bacteria Protista – Amoebas, paramecium Fungi – Mushrooms, molds, yeast Plantae – Trees Animalia – Mammals—uhhhh people Single cell • Bacteria • Protista – little guys you look at under microscope vs. Multi-cell • Fungi – mushroom • Plant • Animal Heterotroph vs. -eat something Autotroph -make own food • Animalia • Fungi • Plantae BOTH Bacteria Protista Body Systems • • • • • • • • • • • Circulatory – heart / blood - Oxygen / food Digestive – breaks down food Nervous – electrical signals Endocrine – hormones Reproductive – sex Integumentary – Skin Skeletal – Bones - Structure Respiratory – Lungs - Oxygen in, CO2 out Muscular - Movement Excretory – Eliminates wastes - Urine Immune – Kills viruses Viruses and Bacteria • Viruses are not alive, Bacteria are alive Viruses (not alive) • Viruses – cause disease – ANTIBIOTICS DO NOT CURE THEM – ONLY IMMUNE SYSTEM • AIDS, the common cold, small pox, influenza, and warts Bacteria (alive) • Harmful - get antibiotics – Strep Throat – Staph Infections • Helpful – decomposers – septic tanks, rotting meat – mutualism : intestines – cheese, yogurt Evolution • Mutations • Reproductions Natural Selection- environment decides who lives… only tall trees- giraffes happy Who would survive? Symbiosis • Symbiosis – relationship between two organisms • Mutualism – both species benefit • Predation – one species (predator) benefits, other (prey) is eaten • Parasitism – one species benefits, the other is harmed • Competition – two species want same thing • Commensalism – one species benefits, one is not affected • Remora fish eat shark’s scraps; shark is not affected Food chain & food web – who eats what Arrows show flow of energy Trophic levels • Producer - green plant - photosynthesis • Consumer – Must eat • Decomposer breaks down dead and waste Types of matter Elements Fe H O Au Compounds FeCl3 H2O CO2 Density D = M V More dense liquids sink! Water density = 1g/ml Viscosity Resistance to flow more viscous– the slower the flow Buoyancy Chemical Change • • • • Change of temperature Production of light Production of a gas New thing formed Physical change • Change in size and shape • Making a solution • Change in state Conservation of Mass 6CO2 + 6H20 --> C6H12O6 +6O2 Matter is never created or destroyed Solutions • Solute- salt • Solvent – water • Soluble- salt can be dissolved • Force - a push or a pull on an object F = ma Force is measured in NEWTONS (N) • Work - force causes an object to move W=Fd Work -JOULES (J) • Power – How fast you get work done • P=W/t • Power - WATTS (W) Kinetic Energy - motion Potential Energy - energy stored Click on the slide! Energy • Conduction - heat transfer from one object to another by direct contact …solids • Convection - heat carried from one place to another in a liquid or gas as molecules move in currents caused by density differences…liquids & gases • Radiation - the transfer of heat energy through empty space • (heat from sun)….infrared Soooooo……..Heat moves by- Waves • Transverse wave moves up and down as the energy travels right to left. Perpendicular • example: light, ocean • Longitudinal wave – moves back and forth as the energy travels right to left. Parallel • Example: sound REFLECTION Refraction Electricity- 10th • Series Circuit - a circuit in which the current has only one path • Parallel Circuit - a circuit in which the current can take more than one path READ!!! READ!!! READ!!! Remember • Use your Equation Sheet • Use your Calculator • Use your Periodic Table • YOU need at least 41 correct to pass….. DO YOU HAVE THAT?