* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AS lab 4
List of vacuum tubes wikipedia , lookup
Standing wave ratio wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
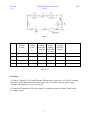
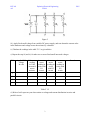
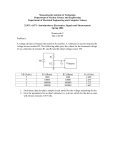
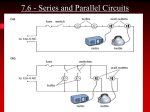
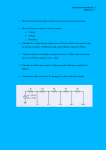
ECE 101 AS Exploring Electrical Engineering LAB 4 PSU ECE 101 Lab 4 Take 3 resistors of different sizes, with resistance ratios of about 1:10:100. Then measure for some fixed, small, constant voltage the voltage division (AKA voltage drops) across the 3 resistors, when all 3 are in series. Do the same, with all 3 in parallel, and measure the 3 divided currents. Summarize findings and conclude in a brief report. For the measurements of A and V you may use V-meters and A-meters, or an oscilloscope. Objectives: i) To conduct experiment to measure voltage across 3 resistors having resistance values in the ratio of 1:10:100. in a series circuit. ii) To conduct experiment to measure 3 branch currents in a parallel circuit having 3 parallel resistors having value of 1: 10: 100 iii) To write a summary report on the above two circuits and to explain the voltage and current distribution in the series and parallel circuit. Equipment: i) 3 resistors having different resistance values (R1, R2, and R3) in the ratio of 1: 10:100. ii) Variable DC Voltage source iii) DC Ammeters in mA range and Voltmeters (0-10volts) range or Multimeter. Procedure: i) Connect 3 resistors R1, R2 and R3 having different values in the ratio 1:10:100 (for example 100 Ohms, 1000 Ohms and 10,000 ohms) respectively in series with a DC power supply and an ammeter as shown in figure 1. ii) Connect DC voltmeter (0 to 10 volts range) across each resistors iii) Switch on the DC power supply and apply fixed small voltage from variable DC power supply, and note down the current value in the ammeter and voltages across each resistor by voltmeter. iv) Tabulate the readings in the table T1.1 as given below. v) Repeat the step iii) and iv) for other two or more fixed small voltages. 1 ECE 101 AS Exploring Electrical Engineering LAB 4 PSU figure 1 Sl.No Applied DC voltage In volts Ammeter reading in mA Volt meter Volt reading meter across R1 reading in volts across R2 in volts Volt meter reading across R3 in volts Remark 1 2 3 4 Table T 1.1 Procedure: i) Connect 3 resistors R1, R2 and R3 having different values in the ratio 1:10:100 (for example 100 Ohms, 1000 Ohms and 10,000 ohms) respectively in parallel with a DC power supply, voltmeter and ammeters as shown in figure 2. ii) Connect DC ammeters (of few mA range) in 3 branches as shown in figure. Switch on the DC supply voltage. 2 ECE 101 AS Exploring Electrical Engineering LAB 4 PSU Figure 2 iii) Apply fixed small voltage from variable DC power supply, and note down the current value in the ammeters and voltage across the resistors by voltmeter. iv) Tabulate the readings in the table T 1.2 as given below. v) Repeat the step iii) and iv) for other two or more fixed small increased voltages. Sl.No Applied DC voltage In volts Volt meter reading in Volts measured across resistors. Ammeter meter reading in series with R1 in mA Ammeter meter reading in series with R2 in mA Ammeter meter reading in series with R3 in mA Remark 1 2 3 4 Table T 1.2 vi) Write a brief report on your observation on voltage and current distribution in series and parallel circuits. 3