* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War I 2015
History of the United Kingdom during the First World War wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War I wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the causes of World War I wikipedia , lookup
American entry into World War I wikipedia , lookup
History of Germany during World War I wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War I wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk wikipedia , lookup
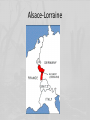
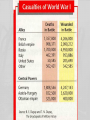
World War I The War to End All Wars…or the Seed of Even Greater Destruction Assassination of Franz Ferdinand Long Term Causes of WWI • Competition/Alliances sparks Militarism – German massive naval build up leads Britain to build up navy & form alliance with France & Russia – All nations on continent begin building up their armies • Entangling Alliances – Triple Entente: Britain, France, Russia (Italy will join later) • Britain vows to protect neutral Belgium – Triple Alliance/Central Powers: Germany, Austria-Hungary, Ottoman Empire (Italy abandoned C. Powers in 1915) • Alsace & Lorraine: Disputed territory b/n Germ. & FR • Imperialism • Nationalism – Intense pride in one’s homeland – Serbs/Slavs push for independence from Austria-Hungary • Serbian/Slavic/Russian ethnic ties Military Alliances: 1914 Alsace-Lorraine The Black Hand & the Assassination of the Archduke • The Black Hand: – Serbian Nationalist Organization • Archdukes assassination is immediate cause of WWI: – Assassin: Gavrilio Princep of Black Hand • Draw Aus.-Hung. into a war with Russia – Why? World War I is Triggered • Austria Declared War on Serbia (a Russian Ally) – German “Blank Check” to Austria-Hungary • Russia Mobilizes against Austria-Hungary • Germany Declares War on Russia, France, Belgium • Great Britain Declares War on Germany as they enter Belgium • How did the alliance system drag these countries into war with each other? – When one country attacked another, all those country’s allies were drawn in… Schlieffen Plan • Germany’s plan for victory in a war in which the German Empire might find itself fighting on two fronts: – France to the west and Russia to the east. – Goal: • Knock France out of the war before it can mobilize • Then use the railroad to quickly mobilize German troops against Russia U.S. Isolationism • Beginning of WWI (1914-April 1917) – Woodrow Wilson issue Proclamation of Neutrality on August 4, 1914. – U.S. follows a policy of isolationism…why? U.S. Inches toward WWI NOTICE! Travelers intending to embark on the Atlantic voyage are reminded that a state of war exists between Germany and her allies and Great Britain and her allies; that the zone of war includes the waters adjacent to the British Isles; that, in accordance with formal notice given by the Imperial German Government, vessels flying the flag of Great Britain, or any of her allies, are liable to destruction in those waters and that travellers sailing in the war zone on ships of Great Britain or her allies do so at their own risk. IMPERIAL GERMAN EMBASSY WASHINGTON, D.C., APRIL 22, 1915. U.S. Inches toward WWI: German Submarine Warfare • German U-Boat sinks Lusitania (May, 1915) – British Ocean Liner – 128 Americans Killed – Enrages Americans, but just first step • German U-Boat attacks pulls U.S. Closer to entering the war v. Germany • Sussex Pledge U.S. Enters WWI: Zimmerman Telegram • Zimmerman Telegram – German telegram to Mexico – Germany tries to encourage Mexico to go to war w/ U.S. – Intercepted/Decoded by British…pass to U.S. • Communist Revolution in Russia begins 1917 • April 2, 1917 – U.S. Declares War on Germany • U.S. buys Virgin Islands in 1917, why? Mobilizing for War John Green: America and WWI Funding the War Making Sacrifices Women in the War U.S. Government Limits Civil Liberties during War • Espionage Act (1917) – Prohibited actions that limited recruitments or promoted insubordination (disobedience) in the military • Sedition Act – Crime to speak against the sale of war bonds – Crime to speak against the government, the US Constitution or the armed forces • Schenck v. United States – Clear and Present Danger Doctrine • Government can limit free speech that poses a “clear & present danger” to national security John Green: America and WWI Selective Service Act: 1917 • • • • 24,000,000 men registered for the draft by the end of 1918. 4,800,000 men served in WW1 (2,000,000 saw active combat). 400,000 African-Americans served in segregated units. 15,000 Native-Americans served as scouts, messengers, and snipers in non-segregated units. The Horrors of War: Life in the Trenches The Horrors of War: Life in the Trenches New Weaponry World War I: The “Great” War • 1914-1918 – – – – 65 million men mobilized for war 37 million casualties (killed, missing, wounded) 9.7 million military deaths 8.8 million civilian casualties • Eastern Front – Communist Revolution in Russia: 1917 – Russia Surrenders to Germany (Oct. 1917)…leads to Treaty of Brest-Litovsk – Civil War in Russia: Rise of Lenin and Communist Party…impact in America? • Western Front: Trench Warfare – Stalemate from 1914-1918 • U.S. Enters War (1917) – Allied Powers • U.S., Britain, France – Why did this help break the stalemate? • 2nd Battle of the Marne (1918) – Turning Point on Western Front The War Ends (11/11/1918) Fourteen Points • Fourteen Points: Woodrow Wilson’s Peace Plan for WWI – Globalization: • Reduce chance of war by creating economic ties/cutting down on armaments – Self Determination: • Break up colonies/grant independence – League of Nations • 1st International Organization Whose Goal Was to Keep Peace (predecessor of United Nations) • How might each of these have prevented future wars? Treaty of Versailles • Treaty of Versailles (June 28, 1919) – Peace Treaty Officially Ending War b/n Germany & Allied Powers • Treaty Establishes the League of Nations, but few of Wilson’s other suggestions. • Treaty Intended to Punish & Weaken Germany – War Guilt Clause • Germany must accept full responsibility for the war – Had to pay massive reparations to the allies • Most of reparations would go to France/Belgium – German military dismantled…why? • Army reduced to 100,000 men • Not allowed to have Tanks or Air Force • Demilitarized Rhineland – Germany suffered major territorial losses • Lose: Alsace & Lorraine, Baltic States (land won from Russia), Poland, & more U.S. Senate Rejects Treaty of Versailles • Senator Henry Cabot Lodge Leads Charge against Treaty of Versailles • U.S. Senate Rejects Treaty of Versailles…Why? – League of Nations…What was their concern? • Influence of George Washington? – Washington’s Farewell Address warns against entangling alliances/getting involved in foreign affairs • Return of U.S. Isolationism Significance of the Treaty of Versailles • How did the Treaty of Versailles help lead to the rise of Adolf Hitler in Germany? – Caused many Germans to want to seek revenge after WWI – Anger combined with economic chaos in Germany during Great Depression, caused Germans to look to nationalistic & militaristic leader like Hitler