* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mauryan India
Dhyāna in Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Sanghyang Adi Buddha wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and violence wikipedia , lookup
Buddhist philosophy wikipedia , lookup
Early Buddhist schools wikipedia , lookup
Enlightenment in Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and psychology wikipedia , lookup
Persecution of Buddhists wikipedia , lookup
Buddhist art wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism in Vietnam wikipedia , lookup
Buddhist ethics wikipedia , lookup
Sanghamitta wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
History of Buddhism in Cambodia wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and sexual orientation wikipedia , lookup
Dalit Buddhist movement wikipedia , lookup
Women in Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Pre-sectarian Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
History of Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism in Myanmar wikipedia , lookup
Triratna Buddhist Community wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and Western philosophy wikipedia , lookup
Decline of Buddhism in the Indian subcontinent wikipedia , lookup
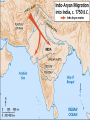
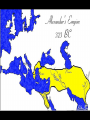
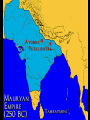
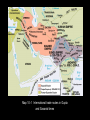
Imperial India Decentralization under the IndoAryans • Kshatriya kingdoms • Decentralized form of government: feudalism • Peasants (sudras) had hard lives; princes (Rajas) lived in luxury • Constant warfare Invasion by Alexander the Great • 326 – cataclysmic invasion of Indus valley area • Troops turned back • Small-pox • Inspired the Maghada • ruler create an empire The Mauryan Empire • King of Magadha conquered other nearby kingdoms and became a Maharaja • Spies, soldiers, and bureaucrats numbered over 1 million (combined) Economy • Took large tax – 25 – 50% of all output • Built massive capital at Pataliputra Imperial Organization • Divided into districts reflecting existing tribal boundaries • Each district run by close relative or friend of Chandragupta Maurya • Gigantic Army Chandragupta’s end • 301 BCE – stepped down to become a monk (!) • Son Bindusara took rule • Bindusara’s son ASHOKA more famous Ashoka Ashoka (r. 269-232) • First eight years typical • Invaded frontier area of Kalinga; bloodiest war of era • Renounced violence & became Buddhist • Ruled according to Buddhist principles, tried to spread Buddhism The Buddha Ashoka (cont) • Laid out “edicts” on 18 rocks and 30 pillars across the empire • Sent out Buddhist missionaries to Central Asia, SE Asia, Parthia (Greeks in Afghanistan) Ashoka (cont) • • • • Pilgrimages, roads with shade trees Vegetarianism Hosted Great Council of Buddhism Created 84,000 Buddhist stupas around India Gupta Rule • Established Hinduism as religion of state • Heavily influenced by caste system, e.g. who got which govt jobs (ksyatriya as warriors, Brahmans as bureaucrats) Map 10–1 International trade routes in Gupta and Sasanid times • Code of Manu codified Hindu beliefs into detailed rules • Hinduism absorbed Buddhism (the Buddha as avatar of Vishnu) • Refocus on devotion to one of the gods, ritual Vishnu • Preferred diplomacy to war, esp. intermarriage • Did not have a welldeveloped bureaucracy • Ultimately fell to the Huns