* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Ancient Greek warfare wikipedia , lookup
Direct democracy wikipedia , lookup
Aristotle's biology wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek religion wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek medicine wikipedia , lookup
Ancient economic thought wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek literature wikipedia , lookup
Athenian democracy wikipedia , lookup
History of science in classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
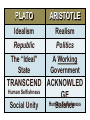
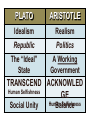
Bell Ringer • How are Greek gods different from gods of other cultures? • Why do you believe what you believe about the world/reality? One of the Tyrants who worked for reform was: DRACO Draco, an Athenian lawgiver of the 7th century B.C. He was the first to codify and write down the laws of Athens, which previously had been interpreted and administered arbitrarily by aristocratic magistrates. His code, written about 621 B.C., became famous for its harshness; death was the penalty for almost all crimes. One advance was in the laws of homicide, which recognized the responsibility of the state, not the victim's family, in punishing a murderer; thus blood feuds were to be avoided. Solon (638?-559? BC) Solon was a statesman who laid the foundation for democracy in the ancient Greek city-state of Athens. Athens was ruled by a few rich, powerful families. They took over land from poor farmers and drove them out of Athens or made them slaves. Solon drew up a clear, simple plan that balanced the rights of the citizens. It had builtin safeguards to keep any one group from oppressing the others. Solon began by passing a law that canceled all debts owed by the poor to rich landowners and forbade that anyone be enslaved for debt in the future. Then he divided the citizens into four classes according to the property they owned, each with a different share in the government. Finally, Solon wrote a code of laws, simpler and less brutal than the existing laws. Cleisthenes Created a new council of five-hundred that oversaw foreign affairs, and made laws that were voted on by the assembly The Assembly came into prominence after his rule helping to shape Athenian Democracy. Greek Philosophers’ Assumptions • The universe (land, sky, sea) is put together in an orderly way and subject to absolute and unchanging laws. • People can understand these laws through logic and reason Philosophers Search for Truth • The Sophists – The word means “the wisest,” so they were proud of their supposed philosophical knowledge. – They claimed they could find the answers to all questions. – They used rhetoric to win arguments. – They often charged fees for teaching their skills and for arguing for others. They might be considered a type of lawyer of the time. – Sophist philosopher Protogoras questions the existence of Greek gods. Socrates’ teaching method Continuous questions Designed to foster deep understandings Encourages critical thinking PLATO ARISTOTLE Idealism Realism Republic Politics The “Ideal” State A Working Government TRANSCEND ACKNOWLED Human Selfishness GE Social Unity Human Selfishness Balance PLATO ARISTOTLE Idealism Realism Republic Politics The “Ideal” State A Working Government TRANSCEND ACKNOWLED Human Selfishness GE Social Unity Human Selfishness Balance Political Science Aristotle was one of the first philosophers to study the science of politics. GOOD Government Should encourage people to do GOOD. FORMS OF GOVERNMENT Aristotle’s Politics Good Version Corrupt Version General Interest Special interest(s) ONE Kingship Tyranny FEW Aristocracy Oligarchy Polity Democracy Government By: MANY Good short review video here: https://youtu.be/GmHAdgDkcCw © Students of History -