* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Preposition Notes
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
American Sign Language grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Udmurt grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
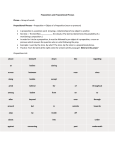
Preposition Notes Preposition-A preposition sits before a noun (or a pronoun) to show the noun's relationship to another word in the sentence. Hint: Anywhere something/someone can go Ex: above, below, upon, toward, with, without, near of, in, etc. Prepositional Phrase- A prepositional phrase is a group of words that begins with a preposition and ends with a noun or a pronoun. This noun or pronoun is called the “object of the preposition.” Ex: The boy looked at a magazine. (The preposition is at and the phrase is at a magazine) Infinitive- to + verb The word "to" is not a preposition in this case Ex: The maid wanted to clean the room. (The predicate/verb in this sentence is wanted and the (to clean) is the infinitive. Verb Phrase- consists of a helping verb + a main verb Ex: Their parents are golfing after breakfast. (The helping verb is are and the main verb is golfing. The verb phrase is are golfing Not (n’t) is never a verb. Do not underline it as part of a verb phrase. Ex: The acrobat has not performed for the audience. (The verb phrase in this sentence is has performed since not should never be considered a verb.) Conjunction- Conjunctions join words or group of word together. The most common ones are and, or and but. Ex: For lunch Laura had a sandwich and a juice box. (The conjunction in this sentence is and) Compound Object: a preposition may have more than one object. Ex: An oak tree is beside a shed and a corral. (The compound objects in this sentence are shed and corral.) Compound Subjects. The subject tells who or what the sentence is about. Sometimes there are two or more subjects in a sentence. This is called a compound subject. Ex: A boy and his friend played in the woods. (The compound subjects in this sentence are boy and friend) Compound Verb: A verb tells what is (was) or what happens (happened). Sometimes more than one verb appears in the sentence. This is called a compound verb. Ex: You must sit and read for a few minutes. (The compound verbs are must sit and read) Imperative Sentences- (You) is the subject of an imperative sentence. Read (You) as you understood. Ex: Please finish your homework within the next hour. (The implied subject is You) Prepositions versus Adverb: A preposition must be followed by a noun or pronoun called an object of the preposition. If there is not an object of the preposition, the word is not a preposition. (It serves as an adverb.) Ex: Janet went inside with her pets. (The preposition inside stands alone, it is not followed by a noun or pronoun so it is the adverb in this sentence.) Symbols: Subject Predicate/Verb Phrase Preposition Prepositional Phrase (Infinitive) Conjunction Imperative (You) ADV. Adverb