* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transition Metals
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Sol–gel process wikipedia , lookup
Cluster chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Metal carbonyl wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Stability constants of complexes wikipedia , lookup
Jahn–Teller effect wikipedia , lookup
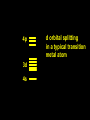
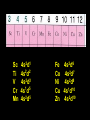
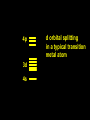
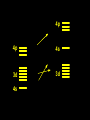
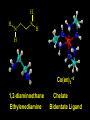
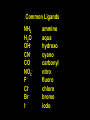
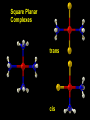
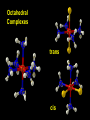
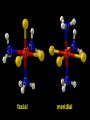
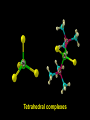
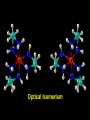
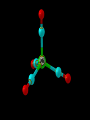
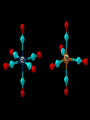
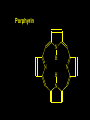
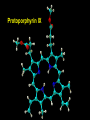
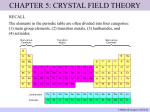
Transition Metal Chemistry 4p 3d 4s d orbital splitting in a typical transition metal atom Sc Ti V Cr Mn 4s2d1 4s2d2 4s2d3 4s1d5 4s2d5 Fe 4s2d6 Co 4s2d7 Ni 4s2d8 Cu 4s1d10 Zn 4s2d10 4p 3d 4s d orbital splitting in a typical transition metal atom The 4s an 4p orbitals is much more diffuse in space than are the 3d orbitals. They have a higher quantum number n and the have fewer nodes (0 or 1) versus 2 for the d orbitals. This means that when a transition metal atom bonds to other atoms, the most significant interactions are with the s and p orbitals, not the d orbitals. 4p 4p 3d 4p 4s 4s 3d 4s 3d The 3d orbitals are not as important for bonding as are the 4s and 4p, but the details of what happens to the 3d orbitals determine the properties of transition metal complexes. 3d Coordination Compounds NH3 Base - electron pair donor Ligand Co(NH3)6+3 H H N N H H Co(en)3+3 1,2-diaminoethane Ethylenediamine Chelate Bidentate Ligand Common Ligands NH3 H 2O OHCNCO NO2FClBrI- ammine aqua hydroxo cyano carbonyl nitro fluoro chloro bromo iodo Square Planar Complexes trans cis Octahedral Complexes trans cis facial meridial Tetrahedral complexes Optical Isomerism Porphyrin N H N N H N Protoporphyrin IX