* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
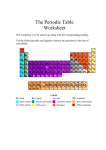
Download Periodic Table
Alkali metal wikipedia , lookup
Boron group wikipedia , lookup
Group 12 element wikipedia , lookup
Alkaline earth metal wikipedia , lookup
Group 3 element wikipedia , lookup
Dmitri Mendeleev wikipedia , lookup
Period 3 element wikipedia , lookup
Period 6 element wikipedia , lookup
The Periodic Table History of the Periodic Table Dmitri Mendeleev organized elements according to their increasing atomic mass and their physical properties Lother Moseley arranged the periodic table according to the atomic number Dmitri Mendeleev’s Table Reading the Squares Each square on the periodic table represents one atom In each square it tells the following information about each element Atomic Number Atomic Mass Element Name Element Symbol Reading the Periodic Table Each horizontal row of elements (from left to right) is called a period Elements follow a repeating pattern as you move across the period Each period moves from metals to nonmetals Horizontal row is the period Reading the Periodic Table Each column of elements (top to bottom) are called a group Elements in the same group have similar physical and chemical properties Sometimes groups are called families Vertical column is the group Properties Determined by the number of electrons in the outer energy level of the atom Same number in the outer shell will be in same group sodium lithium potassium oxygen K oxygen Corrode Na Reading the Periodic Table Elements are classified as metals, nonmetals and metalloids The zigzag line on the periodic table helps you to recognize which elements are metals, nonmetals and metalloids The color of the element symbol tells whether it is a solid, liquid or gas Color your table as metals, metalloids, and non-metals. Metals Metals are to the LEFT of the zigzag line Most elements are metal Most metals are solid at room temperature Exception to the rule: Hg (mercury) is liquid at room temperature Metals Three or fewer electrons in the outer shell Good conductor of heat and electricity Shiny luster Malleable Nonmetals Nonmetals are to the RIGHT of the zigzag line Found as a solid and a gas Exception: (Br) Bromine only liquid non metal. Nonmetals Five or more electrons in the outer shell Lack luster Does not conduct heat or electricity Not malleable Metalloids Elements that border the zigzag line Metalloids have some properties of metals and some properties of nonmetals Metalloid Has properties of both Found along the zigzag line Example: (Te)Tellurium