* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
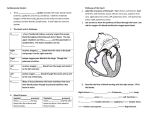
What is the leading cause of death in the US? A. B. C. D. Car Accident Genetic Diseases Cardiovascular Diseases Natural Causes Cardiovascular Diseases • Includes heart attacks, strokes, & high blood pressure What can we do to prevent cardiovascular disease? The Circulatory System The Heart • Near the center of the chest, slightly to the left • Atrium (right & left): upper chambers of the heart • Ventricle (right & left): lower chambers of the heart Body Aorta Superior Vena Cava Left Atrium Right Atrium Through tricuspid valve Pulmonary Vein Through bicuspid (mitral) valve Left Ventricle Right Ventricle Pulmonary Artery Lungs Video Circulatory & Respiratory Systems • Remember that your body’s cells need oxygen to make energy, but they produce carbon dioxide as a waste product. – That’s why we breathe in oxygen & exhale carbon dioxide! • When your blood flows through the body, it drops off O2 to your cells & picks up CO2. • When the blood gets back to the lungs, it drops off the CO2 waste & picks up more O2. Pathway of Blood through the Heart 1. A large vein called the superior vena cava brings the blood from the upper part of the body to the heart, where it enters the right atrium. 2. The blood is pumped out of the right atrium into the right ventricle. 3. Travels through the pulmonary artery to the lungs where it picks up oxygen. Pathway of Blood through the Heart 4. From the lungs, blood travels through the pulmonary veins and returns to the heart, where it enters the left atrium. 5. Finally, the blood is forced from the left ventricle into the aorta which carries it to the tissues of the body. Which 2 chambers of the heart carry oxygenated blood? A. B. C. D. Left & Right Ventricles Left & Right Atriums Left Atrium & Left Ventricle Right Atrium & Right Ventricle When blood flows into the lungs, it drops off CO2 & picks up O2. From the lungs, the blood flows into the left atrium, then to the left ventricle. Hemoglobin is a protein that carries oxygen to the body’s cells. Where is it found? A. B. C. D. Tissues of the Heart Tissues of the Lungs Bone Marrow Blood What’s blood made of? • Red Blood Cells: transport oxygen to the body via hemoglobin • White Blood Cells: part of the immune system • Platelets: involved in blood clotting • Plasma: fluid portion of blood – 90% water, 10% dissolved substances Within a tiny drop of blood, there are… 5 million red blood cells… 300,000 platelets… 10,000 white blood cells! Which type of blood cells play a direct role in the immune system? A. B. C. D. Red Blood Cells White Blood Cells Platelets All of the above 3 Types of Blood Vessels • Veins: blood vessels that return blood to the heart • Arteries: blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to the body tissues • Capillaries: smallest blood vessels, bring nutrients & oxygen to tissues & absorb carbon dioxide & waste products All of the blood vessels in your body measure about 60,000 miles! Which type of blood vessels carry deoxygenated blood (no oxygen)? A. B. C. D. Veins Arteries Capillaries None of the above Which type of blood vessels deliver nutrients from the food you eat to your body’s cells? A. B. C. D. Veins Arteries Capillaries None of the above Pulmonary Vein vs. Pulmonary Artery • The only vein that carries oxygenated blood is the pulmonary vein. • The only artery that carries deoxygenated blood is the pulmonary artery. Remember! Arteries carry blood away from the heart, while veins carry blood to the heart! Blood Clotting • An important process to stop excess bleeding if a blood vessel is injured • Platelets & proteins in the plasma work together to form a blood clot to cover the injury. • Sometimes, clots form in the blood vessels without there being an injury. These can be DANGEROUS! Video from 1:55 What could happen if someone gets a blood clot? • Heart Attack: lack of oxygen to the heart • Stroke: lack of oxygen to the brain • Tissue Damage: due to lack of oxygen