* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download L5 Heart anatomy
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
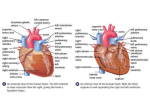
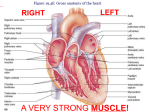
The Heart: L5 44 Very muscular organ about the size of your fist The major portion of the heart is called the myocardium It is mostly composed of cardiac muscle L5 The Heart 45 Epithelial and fibrous tissue called pericardium covers the heart This tissue forms the pericardial sac. the heart is located within this sac and contains lubricating liquid L5 The Heart 46 Think of it as two separate pumps: One(on the right side of the heart) pumps blood to the lungs The other (on the left side of the heart) pumps blood to the rest of the body The left and right side of the heart is divided by the septum L5 The Heart 47 On each side are two chambers. The smaller one, located on the top, is called the atrium (atria) The larger one, on the bottom, is called the ventricle. The left ventricle is considerably larger than the right ventricle because while the right ventricle only pumps blood to the lungs, the left ventricle must pump to the rest of the body L5 The Heart 48 There are valves between the atria and ventricle, collectively referred to as atrioventricular valves and prevent backflow A heart murmur is caused by faulty valves in your heart! L5 The Heart 49 a tricuspid valve with *3 flaps or cusps * on the right side. L5 The Heart 50 and a bicuspid valve (or mitral valve) that *has two cusps* on the left side L5 The Heart 51 Chordae Tendinae Very strong, fibrous strings that support the valves and prevent them from inverting L5 The Heart 52 Each ventricle also has a semi-lunar valve between it and its attached blood vessels. It prevents backflow 53 AV Valve AV Valve Semilunar Valve Semilunar Valve L5 The Path of Blood Through the Heart 54 1.) Blood enters the right atrium through the superior (top) and inferior(bottom) venae cavae=the bodies largest veins 2.) the right atrium contracts, forcing the blood into the right ventricle L5 The Path of Blood Through the Heart 55 3.) The right ventricle contracts sending the blood to the lungs through the pulmonary artery. 4.) At the lungs the blood is now oxygenated 5.) blood returns via pulmonary veins to the left atrium L5 The Path of Blood Through the Heart 57 6.) The left atrium contracts, forcing the blood into the left ventricle. 7.) the left ventricle contracts, forcing the blood into the aorta= the body s largest artery Blood Flow Animation http://www.sciencelearn.org.nz/Contexts/Seethrough-Body/Sci-Media/Animations-andInteractives/Label-the-heart