* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 20130402094281
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Unified neutral theory of biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Fauna of Africa wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Lake ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
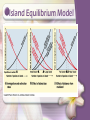
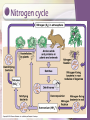
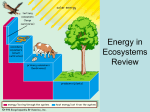
Community Ecology Chapter 54 Interspecific Interactions • Competition --/-• Competitive exclusion • Ecological Niches (Habitat-address; nicheprofession) • Resource partitioning-allows similar species to coexist in a community • Fundamental niche-potential • Realized niche-actual-may be result of interspecific competition Character Displacement • Tendency for characteristics to diverge more in sympatric pop of 2 species than in allopatric pop Predation +/-• Can be animal eating plant tissues • Defensive adaptations – Cryptic coloration Aposematic colorationwarning Batesian mimicry-harmless or palative looks bad Mullerian mimicry • 2 unpalatable species look alike Herbivory +/-Plants have chemical toxins, spines, thorns ex strychnine, nicotine, selenium toxins Herbivores-special adaptations – – – – Insect-chemical sensors Sense of smell Specialized teeth Length of digestive systems Symbiosis • Parasitism +/-• Mutualism +/+ obligate; facultative • Commensalism +/0 Species Diversity • Species richness • Relative abundance Shannon diversity (H) • Index based on species richness and relative abundance Trophic structure • Food Chain Food Webs (Elton 1920s) Limits on length of food chain • Energetic hypothesis-inefficiency of energy transfer -10% rule • Dynamic stability hypothesis-long food chains are less stable than short onespopulation fluctuations at lower trophic levels are magnified at higher levels • Also-carnivores tend to be larger at successive trophic levels-can’t get enough food to meet needs Dominant species • Most abundant-have the highest biomass • Exert a powerful control • Are they are competitively superior in exploiting limited resources? • Are they are most successful at avoiding predation?-would explain effect of invasive species… Invasive pressure • American Chestnut • Before 1910-40% of US trees-fungal diseaseChestnut blight-killed all the trees-oak, hickory replaced; mammals, birds ok, but 7 species of moths and butterflies became extinct Keystone species Foundation species • Ecosystem “engineers” • Affect by causing physical changes in the environment • Ex beavers • Facilitators-may help other species Models of organization • Bottom up VH • NVHP • Top down VH • NVHP Trophic Cascade • Biomanipulation-prevent algal blooms by adding consumers rather than chemicals Disturbance • Influences species diversity and composition • Storms, waves, fires, freezing, drought, • Moderate disturbance can foster greater diversity than low or high levels Ecological succession • Species are replaced by other species • Primary • Secondary • Climax community Island Equilibrium Model Detritivores • Return nutrients to the soil • Law of conservation of mass Aquatic Ecosystem • Light limitation • Nutrient limitation • Eutrophication Biomass-dry mass • Phytoplankton continually replace their biomass at such a rapid rate, they can support a biomass of zooplankton bigger than their own biomass. • Terrestrial herbivores are held in check by a variety of factors. The Green World Hypothesis Transitional Page Productivity • GPP-gross primary production • NPP-net primary production • NPP=GPP – R(autotrophic respiration) • Primary production – in aquatic is mostly affected by light and nutrients-N and P – Eutrophic-nutrient rich – On land-temp and water – evotranspiration Biogeochemical cycles Nitrogen cycle Additional Terms • Bioremediation-use of organisms to detoxify polluted areas • Bioaugmentation-add desirable species such as nitrogen fixers • Biodiversity (3 Levels)-genetic diversity, species diversity and ecosystem diversity • Threats: habitat loss, introduced species, over-harvesting, global change Population conservation • Focuses on: – Population size – Genetic diversity – Critical habitat MVP • Minimum Viable Population • Extinction Vortex Landscape and regional conservation • Habitat fragmentation • Movement corridors • Biodiversity hot spot-small area with an exceptional concentration of endemic species Human Actions • Agriculture-nutrient cycling-take it out of soil or too much in water • Acid precipitation • Biological magnification • Greenhouse effect • Global warming • Ozone layer Elements www.animationfactory.com