* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evidence of Evolution - Get a Clue with Mrs. Perdue
Survey
Document related concepts
Deception in animals wikipedia , lookup
Comparative foot morphology wikipedia , lookup
Life history theory wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
History of zoology (through 1859) wikipedia , lookup
Anatomical terminology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
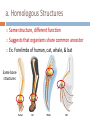
Evidence of Evolution Evidence Supporting Evolution 1. Fossil Record Shows change over time 2. Anatomical Record Comparing body structures Homologous & vestigial structures Embryology & development 3. Molecular Record Comparing DNA & protein sequences 4. Artificial Selection Humans cause evolution 1. Fossil Record Layers of rock contain fossils new layers cover older ones creates a fossils record over time show detailed structural changes in plants and animals over time Fossils tell a story… the Earth is old Life is old Life on Earth has changed 2. Anatomical Record • Analyzing similarities in structures from different organisms to show a common ancestor a. Homologous Structures Same structure, different function Suggests that organisms share common ancestor Ex. Forelimbs of human, cat, whale, & bat Same bone structures b. Analogous Structures Different structures, same function Suggests that organisms do not share common ancestor Ex. Hawk, butterfly, & bat can all fly but have different wing structure c. Vestigial Structures Structures on modern animals that have no function Remains of structures that were functional in ancestors evidence of change over time Ex. Eyes on blind cave fish Some snakes & whales have pelvis bones & leg bones d. Comparative Embryology Analyzing embryos with similar structures to show common ancestor 3. Molecular Record Comparing DNA & protein structure in different organisms Every living organism has a genetic code = DNA Human Macaque Dog Bird Frog Lamprey 32 45 67 125 compare common genes compare common proteins Cladogram shows number of amino acids different from human hemoglobin 8 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110120 4. Artificial Selection Humans choosing which organisms reproduce & survive = “Evolution by human selection” Ex. Designer breeds of dogs Artificial Selection Two chickens at 8 weeks old: one artificially selected & one naturally selected • Artificially inseminated to produce chicken with more meat mass CAMOUFLAGE AND MIMICRY Structural adaptations 1. Camouflage Any color, pattern, shape or behavior that enables an animal to blend in with its surroundings Short Videos: • Cuttlefish, master of camouflage • Walking stick Tasseled Scorpion Fish Frog Owl Scorpion Fish Leaf-tailed Gecko Crocodile Caterpillar Wolf 2. Mimicry Appearing or behaving like another species which protects one or both Coral Snake (venomous) King Snake (nonvenomous) This tropical lo moth, once a caterpillar with an honest signal now sports eyespots on its hind wings, which it displays when threatened. Munching on a plant stem in Costa Rica's Monteverde Cloud Forest Reserve, this Xylophanes caterpillar has such tiny eyes that you would need a hand lens to see them. The red "eyes" and pointed "stinger" are both fake. Viceroy butterfly (nonvenomous) Monarch butterfly (venomous) In the lowland rain forest of the Peruvian Amazon, a "bird dropping" on a leaf turns out to be a caterpillar.