* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SuBORDINATE CLAuSES AS MODIFIERS
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
American Sign Language grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Comparison (grammar) wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Relative clause wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sotho parts of speech wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
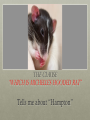
Subordinate Clauses as Modifiers Adapted from Inside English (Chapter 2, Section 1) Adverb Clauses Like single word adverbs, adverb subordinate clauses can modify verbs. For instance… When she ate the mushroom, Alice grew taller. THE CLAUSE “WHEN SHE ATE THE MUSHROOM” ANSWERS THE QUESTION: When did Alice grow taller? Therefore, it is an Adverb clause modifying the verb “grew” [ she ate the mushroom], Alice grew taller. subordinate clause main clause Let’s lo o k at anoth er exa mple: Hampton, which is Michelle’s hooded rat, resides under her bed. The clause “which is Michelle’s Hooded Rat” Tells me about “Hampton” “Hampton” is a noun. THEREFORE, “WHICH IS MICHELLE’S HOODED RAT” IS AN ADJECTIVE CLAUSE MODIFYING “HAMPTON” Hampton, [which is Michelle’s hooded rat], resides under the bed. Main clause Dependent clause Main clause KEY POINTS u Adjective subordinate clauses modify nouns and pronouns just as single-word adjectives do. u Adjective subordinate clauses usually begin with a relative pronoun (that, which, whose, who, and whose). Section one review: Can You Answer? • A clause is a group of words that contains _________________________. • A main clause is a group of words that contains at least one subject and one verb and that ___________________________________________. • A subordinate clause is a group of words that contains at least one subject and one verb but that ________________________________ . • Subordinate clauses begin with ________________________________. • Adverb subordinate clauses usually modify verbs and begin with subordinators that answer ____________________________. • Adjective subordinate clauses modify nouns or pronouns and begin with ____________________________ Section one review: ANSWERS • A clause is a group of words that contains at least one subject and at least one verb. • A main clause is a group of words that contains at least one subject and one verb and that expresses a complete idea. • A subordinate clause is a group of words that contains at least one subject and one verb but that does not express a complete idea. • Subordinate clauses begin with subordinators. • Adverb subordinate clauses usually modify verbs and begin with subordinators that answer when, why, how, to what degree. • Adjective subordinate clauses modify nouns or pronouns and begin with that or which. Exercise 1-C For homework, you were directed to do Exercise 1C on pages 93-94. Before advancing to this slide, be sure you have completed the Exercise as directed and then check your answers with those I have provided. How’d you do? If you are still struggling with these concepts, please go back and review the content from chapter 1 (if necessary) and Chapter 2 Section One before continuing. End show Adapted from Inside English (Form B), by William Salomone and Stephen McDonald Created by Elaine Minamide for English 10 Palomar College Updated Fall 2016