* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WB Credentials (Nov 09)
Financial crisis wikipedia , lookup
Foreign-exchange reserves wikipedia , lookup
CAMELS rating system wikipedia , lookup
Auction rate security wikipedia , lookup
Futures exchange wikipedia , lookup
Foreign exchange market wikipedia , lookup
Hedge (finance) wikipedia , lookup
Securitization wikipedia , lookup
Fixed exchange-rate system wikipedia , lookup
Commodity market wikipedia , lookup
Financial Crisis Inquiry Commission wikipedia , lookup
Exchange rate wikipedia , lookup
Currency intervention wikipedia , lookup
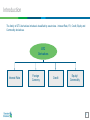
OTC Derivatives: Trading, Reporting & Regulations Udaipur 8th Jan 2011 Introduction The family of OTC derivatives includes is classified by asset class - Interest Rate, FX, Credit, Equity and Commodity derivatives. OTC Derivatives Interest Rate Foreign Currency Credit Equity/ Commodity 2 Background • Includes the gamut of Interest Rate, FX, Credit and Currency Derivatives • Primarily plain vanilla products involving currencies or interest rates • Interest Rate Derivatives is the largest subset with Swaps predominating • A gradual shift from OTC to exchange traded products − Fragmented Markets vs Concentrated Markets • On line Trade reporting for Rupee IRS since 2007 has massively improved transparency and price discovery • Initiatives underway around trade reporting and central clearing of all OTC products 3 Global Context • 20% CAGR from 1995 in the use of Interest Rate and Currency Derivatives • 70% growth in the use of Credit Derivatives since inception • Current Estimated Outstanding • • − $400 Tn in Interest Rate and Currency Derivatives − $ 65 Tn in Credit Derivatives − $ 10 Tn in Equity Derivative Daily Estmated Turnover − $1.7 Tn in Interest Rate Derivatives − $0.3 Tn in Currency Derivatives Credit derivatives - heavily in the news due to the sub-prime crisis 4 Domestic Context • Plain Vanilla IRS introduced in 1999 • Currency Forwards in existence for long, FX Options introduced in 2005 • Credit Derivatives, currently not allowed but in advanced discussion stage • Equity and commodity derivatives due to the nature of their underlying markets have moved to exchanges • Current Outstanding − Rs 46 lac crore in Interest Rate Derivatives − Rs 36 lac crore in Currency Derivatives 5 Products • Interest Rate Derivatives include IRS, FRAs • The IRS dealt include OIS, INBMK, MIFOR • Currency Derivatives include the basic FX forwards, Swaps and Options • Credit Derivatives (CDS) currently disallowed but in the process of being introduced with appropriate safeguards 6 Interest Rate Derivatives • Introduced in 1999 and has seen immense growth and popularity • Gross Outstanding contracts in the region of Rs21 lac cr; however net is much lower • Daily volumes in the region of Rs10,000cr • In recent times has acted as useful hedge for interest rate risk • Key applications include short term asset management and duration management • Participation remains essentially foreign bank skewed • Local banks can play a key role in balancing the market interest and closing the existing arbitrages 7 Interest Rate Derivatives - Benchmarks OIS Overnight inter bank call money rate Most Liquid - Average Daily Volume INR 200 bio MIFOR INBMK Implied rupee interest rate derived from USD vs INR forward rates. Benchmark is the 1 year GOI yield Hedge for Currency swap positions with clients Used primarily for duration management of bond portfolios Liquid Up to 5 years 8 Currency Derivatives • Gradual evolution from forwards to matched swaps to position taking • FX Forwards represent the largest portion of this segment • FX Options allowed in 2005 has tremendously benefited corporate wishing to put on shorter term hedges • Underlying exposure continues to be a key requirement to ensure orderly markets • Latest guidelines issued Dec 28th 9 Key Issues in OTC Derivatives • Established Client need - customized solutions, hedge effectiveness • OTC markets criticized for being opaque, but are the largest component of world financial markets − 3 decades history − Participants are large, professional institutions mostly banks hence regulated − Transparency to regulators versus transparency to all • Capital charge on counterparty exposures and for market risk • Reporting required for MTM, systemic stability, regulatory information • Trade compression, focus on net risk or open interest • Price impact of post-trade dissemination 10 Transparency • • Pre-trade transparency 1. Interbank quotes 2. Single screen offering 3. Composite levels Post-trade transparency 1. Trade repository 2. Confirmations 3. Payment advice 4. Collateral management 5. Valuation 11 Road Ahead for OTC Derivatives • Standardized contracts • Trade repository • Central Clearing • Electronic Trading system, anonymous order matching • Review of Capital charges • Post trade services • New Products (swaptions, caps/ floors) to be introduced in a phased manner 12