* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download History Study Guide Ch_ 4 _ 5 blank
Survey
Document related concepts
Thebes, Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Joseph's Granaries wikipedia , lookup
Plagues of Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Art of ancient Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Index of Egypt-related articles wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian medicine wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian race controversy wikipedia , lookup
Middle Kingdom of Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Prehistoric Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Egypt (Roman province) wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
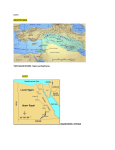
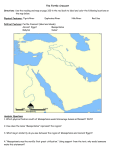
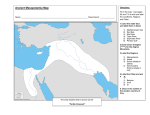
Chapters 4 & 5 Study Guide 1. silt 2. irrigation 3. surplus 4. city-state 5.polytheism 6. ziggurat 7. cuneiform 8. scribe 9. epic 10. empire 11. tribute 12. province 13. caravan 14. astronomer 15. cataract 16. delta 17. shadoof 18. papyrus 19. hieroglyphics 20. dynasty 21. theocracy 22. pharaoh 23. bureaucrat 24. embalming 25. pyramid 26. incense 27. envoy 28. savanna 29. textile 30. In Mesopotamia, floods deposited silt, which made the soil 31. Which of the following groups belonged to the Sumerian middle class? 32. Sumerians developed a 12-month calendar by recording the... 33. Who developed the first empire in Mesopotamia? 34. What did Assyrians often demand from the people they conquered? 35. The astronomers of Babylon mapped... 36. What did the delta of the Nile River provide Egyptians? 37. Who was responsible for uniting and governing Egypt? 38. Egyptians built pyramids because they... 39. The largest group in Egyptian society was made up of... 40. What was the main focus of Queen Hatshepsut's rule? 41. How were Kushites different from the Egyptians? True and False: Write out the whole word Mesopotamia means "the land between two rivers" in Greek Mesopotamia began between the Euphrates and Nile river The farmers in Mesopotamia did not know when the Tigris and Euphrates rivers would flood or dry out. Mesopotamia is often referred to as "the cradle of civilization" The Sumerians were the first people to use the wheel The Sumerians developed the 180 degree circle Hammurabi's code demanded "an eye for an eye and a tooth for a tooth" Babylon's Hanging Gardens were once considered one of the seven wonders of the Ancient world. The Nile is the world's second longest river Narmer was the first King to unify Egypt The word Pharaoh originally meant "great house" Osiris was the god of the afterlife in Egypt Two important gods in Egypt were Re and Hapi Pyramids were used for storing grains in case of a famine People in Egypt could not move up in social classes even if they worked hard Egypt's history is broken into the Old Kingdom, Middle Kingdom and New Kingdom Ramses II was the most successful of all the Pharaohs King Tut became the youngest Pharaoh at the age of 19 Queen Hatshepsut was one of the few women to rule Egypt Diagram: Using a Venn Diagram, Compare and Contrast the following: Compare and Contrast the influences of the Nile River in Egypt with the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers in Mesopotamia Compare and Contrast the Sumerian and Egyptian Civilizati