* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mesopotamia
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
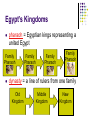
Mesopotamia FOCUS QUESTION Why did early civilizations tend to develop in river valleys? Civilization Begins Between 6000 and 500 B.C., huntersgatherers began settling on the flat grassy regions between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. Easy to grow crops, good farming, easy to feed many people. Civilization Begins (cont’d) social class = a group of people who hold a similar position or rank in society agricultural surpluses specialization was possible class structure in society The Fertile Crescent Mesopotamia = “the land between 2 rivers” Tigris River & Euphrates River Rivers often flooded, leaving rich soil for farming. PROBLEM the flooding was VERY unpredictable irrigation = a way of controlling water and bringing water to crops Summary The first civilizations arose in river valleys. They produced agricultural surpluses, which led to the development of specialization and class system. The earliest known civilization developed in Mesopotamia, which was in the eastern part of the Fertile Crescent between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. Sumer FOCUS QUESTION What are some of the lasting achievements of the Sumerians? City-States Sumer was a region in southern Mesopotamia. Regions in Sumer were isolated. Separate city-states formed, each with their own government. Sumerians believed in many gods. Gods had power over natural force or human activity. polytheism = belief in many gods ziggurats = temples Sumerian Daily Life Upper Class kings, priests, & government Middle Class Artisans, merchants, farmers & fishers Lower Class Enslaved people MEN head of household and could go to school WOMEN couldn’t be head of household couldn’t go to school could buy/sell property could run businesses Sumerian Daily Life (cont’d) Many great inventions - WRITING Sumerians developed a system of writing to keep track of business deals and other events. cuneiform = system of symbols used for writing scribes = a record keeper (mainly boys & men) Mesopotamian Technology Wagons (wheel), boats, and the plow Mathematics Number system based on 60 (60 minutes, 60 seconds, 360-degree circle) Astronomy Developed 12-month calendar Summary The Sumerians believed in many gods and built temples called ziggurats in which to worship them. Sumerian society was divided into three classes ruled over by a king. Their achievements included the development of a the oldest known system of writing, which they used to keep many kinds of records. The Sumerians’ technological advances and inventions allow us to learn about their history and way of life. United Lands FOCUS QUESTION What caused the Mesopotamian and Sumerian civilizations to rise and fall? The Akkadians government city-state FIGHTING government city-state There was a struggle for land in the Fertile Crescent. Sargon - king of the Akkadians (2300 BC) Established Ashur as the capital city. “The Land of Ashur” would become Assyria. Babylonia and Assyria Babylon was south of Ashur King Hammurabi established control of the Euphrates River for Babylon. Hammurabi’s Laws Set laws and established punishements “an eye for an eye” About 1,000 years after Hammurabi, Assyria took control of the rest of Mesopotamia. Very fierce warriors with better weapons A New Way to Govern Assyrian kings divided the empire into political districts/regions. Assyria treated its people cruelly. People rebelled Assyria crumbled Babylon soon became the world’s largest and richest city. Soon, Babylon weakened and the Persians attacked. Summary The Akkadians took control of Sumer and created an empire. The city of Ashur became known as Assyria. The Babylonian ruler Hammurabi developed one of the first codes of law. The Assyrians eventually took over Mesopotamia. Assyrian people rebelled and the Assyrian Empire came to an end. They rebuilt the city of Babylon as the center of their empire. In 539 B.C., Babylon fell to the Persians. The Nile Valley FOCUS QUESTION Why did Egyptian civilization begin in the Nile Valley? A Fertile Valley Nile Delta The Nile River Lower Egypt Upper Egypt River was used for dayto-day purposes Flows 4,000 miles to the north into the Mediterranean Sea Begins as 2 rivers, then connect into 1 river Ships can only travel up the river for 650 miles Very important for farming Natural Barriers delta = an area of fertile soil at the mouth of the river that fan out There was desert to the east and to the west (Sahara Desert is in the west). Transportation and trade along the Nile River and the Red Sea to the east. Dependable and gentle floods were useful. Farming was very successful. A System of Writing papyrus = a reed plant that grew along the shores of the Nile, became a useful resource. Papyrus was used for making sandals, baskets, rafts, and paper. Egyptians developed their own system of writing. hieroglyphics = system of writing made up of hundreds of picture symbols Summary The Egyptians depended on the Nile for many of their basic needs. The Nile flows north, separating two great deserts. The Egyptians developed a system of writing known as hieroglyphics. Egypt’s Old Kingdom FOCUS QUESTION How was Egyptian society organized? Early Egyptian Society Successful Agriculture Craft Advancement THERE WAS A NEED FOR GOVERNMENT Lower Egypt Increase in Trading Upper UNITED Egypt Narmer, A.K.A. Menes, was the first pharaoh Egypt’s Kingdoms pharaoh = Egyptian kings representing a united Egypt Family Pharaoh Family Pharaoh Family Pharaoh Family Pharaoh dynasty = a line of rulers from one family Old Kingdom Middle Kingdom New Kingdom Egypt’s Social Classes pharaoh Priests Nobles Government Officials Business Owners Craft Owners FARMERS *largest social class* Unskilled Workers/Slaves Summary Narmer, known also as Menes, was the first pharaoh and united Upper and Lower Egypt. Egyptians obeyed the pharaoh because they believed the well-being of society depended on it.