* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review Questions for Atmosphere Test (April 2013) Name three ga
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
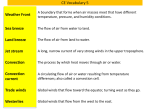
Review Questions for Atmosphere Test (April 2013) 1. Name three gases that are in the atmosphere. Nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide. 2. Why is the atmosphere important? It protects the earth from getting direct UV radiation, and keeps a steady temperature. 3. Why does rain happen? Because water rises from the earth’s surface and as it rises it cools. Then that water vapor condenses into water droplets and forms clouds. When the cloud gets too heavy then it rains and the cloud disappears. 4. What is the relationship between weather and the atmosphere? Weather happens because of the atmosphere. 5. Why is photosynthesis important? Without it, there would be no oxygen circulated. Also, there would be no plants to eat and digest. 6. Why is the atmosphere an important part of human hearing? because sound waves need a medium, like air, to travel though. 7. How is density measured? mass per unit volume or mass over volume 8. What is altitude? it is the height above sea level 9. How is air density and pressure affected by altitude? as the altitude gets higher the air density gets lower , same with air pressure. 10. Which part of the earth receives the most amount of energy from the sun? The equator 11. Is the northern hemisphere tilted towards the sun or away from the sun during winter? Away 12. Why does angle of insolation change throughout the year? - because the earth tilts on it’s axis as it spins throughout the year, so the angle that the sun is hitting a certain spot will change. 13. Approximately what is the angle of insolation during the summer months? 70 degrees 14. Approximately what is the angle of insolation during the winter months? 30 degrees 15. What is a material on earth that is a good reflector? Ice and snow 16. Almost all energy on earth comes from _______________? The sun 17. Define radiation The transfer of energy by waves. 18. Define conduction Transfer of heat between molecules by contact 19. Define convection A transfer of heat by current. 20. What is energy? The ability to do work. 21. Lightly colored materials are better absorbers of light (False) 22. The desert reflects more radiation than a forest (True) 23. Shinier materials make better reflector (True) 24. Why does water heat and cool more slowly than land? Water has a higher heat capacity 25. Define ‘high heat capacity’ It takes a relatively lot of energy to change the temperature of water 26. How does the temperature of an area around one body of water compare to that of another area with no water? The temperature of the area with water would be moderate, would not have large temperature swings, than the one without water. 27. What would Earth be like if there were no atmosphere? The temperature would vary dramatically from extreme heat to extreme cold 28. Which phases of matter allow for convection? liquid and gas. 29. In conduction how is heat transferred? From molecule by contact. 30. Define absorption. When material takes in heat. 31. Define reradiation When material gives off heat. 32. Define Energy? The ability to do work. 33. What are two forms of energy? Heat and light 34. What is radiation? The transfer of energy by waves. 35. Name the three methods by which heat moves through the atmosphere Radiation, Conduction, and Convection. 36. What are the properties of a good absorber? Dark, grainy/rough 37. What are the properties of a good reflector? Light, smooth and shiny, 38. What size of wave lengths have more energy? Shorter wave lengths. 39. List these waves from order from largest to smallest wavelength: Infrared, Ultraviolet, Visible light, Gamma Rays, Radio Radio, Infrared, Visible light, Ultraviolet, Gamma Rays 40. Describe the process of the greenhouse effect. Radiation is absorbed by the greenhouse gases and reradiated in other directions within the atmosphere. 41. Which greenhouse gas is most plentiful? CO2 42. Which isn’t a greenhouse gas: CO2, Ozone, Water vapor, Hydrogen Hydrogen 43. What is good about the greenhouse effect? It allows the earth to be about the same temperature, it moderates wild temperature swings 44. What is bad about the greenhouse effect? Greenhouse gasses at too high concentration will increase temperatures on the earth because of the increased absorption and re-radiation. 45. What have we done to impact the greenhouse effect and the environment because of it? We have created more CO2 that thickens the atmosphere and causes a stronger greenhouse effect which gives a higher average surface temperature on earth, much like the condition on Venus 46. Name three greenhouse gases: Methane, CO2, water vapor, nitrous oxide 47. Which of the following materials absorbs the most radiation? Tar, Snow, Aluminum foil tar 48. Which person’s hair would absorb more radiation? Annemarie’s, Caroline’s, Mr. Rayburn, Minwoo Minwoo 49. What do gasses in the atmosphere do to radiation? Some gasses (greenhouse) absorb and re-radiate infrared radiation 50. UV radiation is harmful to living things. (True) 51. UV rays have highest wavelength frequency. (False) 52. What are the two types of waves? Transverse and longitudinal 53. Which way does each of them move? Transverse waves travel perpendicular to their disturbance and longitudinal waves travel parallel to their disturbance. 54. What is amplitude of a wave? The height from the rest to the crest 55. What is frequency of a wave? How often a wave passes a point 56. What unit of measure is used to describe frequency? Hertz (Hz, which is one per second) 57. What is a wave period? The amount of time it takes for one full wavelength 58. How are wave frequency and period related? They are reciprocals, frequency = 1/period and period = 1/frequency 59. How do you measure wavelength? The length from crest to crest. 60. Draw a transverse wave and label the rest, crest, and trough. crest ^rest is the line trough 61. What atmospheric layer is the ozone layer in? stratosphere 62. What is the importance of the ozone layer? It blocks much of the UV radiation from the sun 63. What changes as altitude increases? Both temperature and pressure 64. What atmospheric layer does weather take place? troposphere 65. Name all the layers of the atmosphere in order of decreasing altitude Thermosphere, mesosphere, stratosphere, troposphere. 66. What causes the layers of the atmosphere to be separate? temperature 67. Why do convection cells occur in the troposphere? Warmer air near the surface of the earth rises because it is less dense than cooler air. Cooler air is more dense so it falls, gets heated up again at the surface and rises, etc. 68. Describe how the temperature changes as you go higher into the atmosphere At first it gets colder, but then in the tropopause it gets warmer and then once it reaches the stratopause it starts to get cold again. Right before you get to the mesopause it gets colder and then it continuously gets colder and colder. 69. What are the three transitional layers of the atmosphere in order of increasing altitude? Tropopause, Stratopause, Mesopause. 70. What is the scientific name for Northern and Southern Lights? Aurora Borealis, Aurora Australis 71. In which layer do the northern and southern lights take place? thermosphere 72. In which layer do meteor showers occur? mesosphere 73. What is temperature inversion? Temperature inversion is when cooler air stays near the ground, temperature does not decrease as you increase altitude. 74. Define Isothermal. (It might help if you break up the work into parts) Same/equal temperature 75. What layer of the atmosphere has very little gravity so that gas molecules sometimes just float off into space? Exosphere 76. Ozone layer is found in the mesosphere (False) 77. Temperature inversions only happen in the troposphere. (False, stratosphere and thermosphere) 78. UV radiation increases as ozone is depleted? (True) 79. What causes monsoons? Sea breezes and seasonal changes in the temperature of land and water cause monsoons. 80. Which continent do the biggest monsoons form? Asia 81. Approximately what percentage of Earth’s surface is covered by water? 70% Approximately what percentage of Earth’s surface is covered by land? 30% 82. Global winds cause what effect? Explain. Global winds cause the Coriolis effect which creates uneven temperature on the planet. Winds would go from north to south but because the Earth is spinning, the temperature goes across diagonally. 83. What are jet streams and what causes them? Jet streams are fast-moving currents of wind in the higher areas of the troposphere. They are caused by the unequal heating from the Coriolis effect. They flow from west to east around the planet. 84. Explain why air moves: Air moves because of differences in heating which causes differences in pressure 85. What is wind: Air moving. 86. Describe a sea breeze: When cooler air from the sea moves towards the land to replace the hot air rising inland. 87. What’s the difference between a sea breeze and a land breeze? A land breeze blows from land to sea during night or winter, while a sea breeze blows from the sea to the land during day or summer. 88. Explain convection currents: Differences in air temperature cause air to rise and fall, making air circle. 89. The _________ _________ is when the rotation of the earth causes winds to move diagonally. Coriolis effect 90. What are global winds? Why do they occur? Winds that go in belts around the planet, caused by unequal heating and pressure 91. ___________ is when a substance takes in radiation. Absorption 92. ___________ is a when a substance gives off heat. Reradiation 93. If you are in the northern hemisphere what way would air currents move? Appear to curve to the right