* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy and Electrical Definitions
Indoor air pollution in developing nations wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Renewable portfolio standard (United States) wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Renewable energy debate wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Environmental impact of electricity generation wikipedia , lookup
Renewable energy in Africa wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy applications of nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
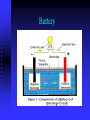
Great Neck South Middle School Technology Energy and Electricity Introduction What is energy? Energy is the ability to do work, or cause change. Energy is literally what makes the world and everything in it go. Energy is the magic stuff stored in the battery that makes the flashlight work. The gasoline in a car’s gas tank contains energy. The car’s engine merely converts the gasoline’s energy into a usable form. While there are many forms and sources of energy, there are only two types: Potential Kinetic Kinetic “energy associated with motion.” When discussing kinetic energy, it’s important to keep in mind that the mass and velocity of an object determine its kinetic energy. We can take a look at kinetic energy by throwing a basketball and a baseball. Potential “The energy something has which is stored and not moving.” “the energy that a piece of matter has because of its position or because of the arrangement of parts” because the matter has the potential, or opportunity, to do work. There are two types of potential energy: elastic potential energy and gravitational potential energy. Water behind a dam has gravitational potential energy. A stretched rubber band has elastic potential Forms of energy Mechanical — the energy of motion Electrical — think lightning or electricity moving through electrical wires Electromagnetic or radiant — energy of magnetism and light Chemical — energy produced by chemical reactions like those that occur in batteries Nuclear — potential energy stored in the nuclei of atoms Sound — the energy of vibrating sound waves Heat – from burning fuel or the earth Energy Conversion Many of the devices we use every day convert energy from one form to another. These devices are called transducers. Transducers Flashlight — converts chemical energy (stored in the battery) to electrical energy to light the bulb. The bulb converts the electrical energy to electromagnetic or radiant energy. Transducers Toaster — converts electrical energy into thermal energy. Car engine — converts the chemical energy stored in the gasoline into mechanical and thermal energy. What do transducers do? Convert one energy type to another. How do we produce electricity? Generators - - - - > Mechanical Batteries - - - - - > Chemicals Photovoltaic Cells - > Light Piezio electric - - > Pressure Generator – A mechanical device that produces electricity by a process of rotating a magnet inside a coil of copper wire. A generator is a transducer that uses rotary mechanical motion to produces electricity. Industrial & Home Electrical Generators Battery Photovoltaic Cells Piezio Electric Renewable Energy Vs. Non Renewable Natural Energy All Renewable Non Consumed when used Solar Wind Water Geothermal Energy Existing in Nature Natural energy sources are ALL RENEWABLE Wind Energy Wind Farm Wind Farm Middlegruden Wind Farm Wind Farm Wind Turbine Generator LIPA wind farm Heat Energy Geothermal – heat from the earth Solar Thermal – heat from the sun Solar Energy Light Heat Solar Energy Light energy -- Electrical energy Uses Photovoltaic Cell Solar Energy Water Energy Water must be Moving •Hydroelectric Power- dams & rivers •Tidal – vertical movement of tides •Wave – using the up/down motion of waves •Thermal-using the temperature difference of oceans Hydroelectric Tidal Wave Oregon State Wave Park A 2.25-megawatt project off the coast of Portugal went on line this fall (2008), becoming the world's first commercial wave-energy development in operation. It can supply 1,500 households with electricity. Ocean Thermal Fuels Fuels Advantages Portable Storable Disadvantages Pollute Energy from Fuels Must Be Burned to Create Steam Pollute Some are : Renewable Non Renewable Renewable Fuels Replaceable in a short period of time Biomass - - - - -> Once alive Plants Trees-Wood Corn, Sugar Cane –Ethanol Alcohol Algae Garbage Biomass as Fuels Non Renewable Fuels Non Renewable Fuels Fossil Fuels Petroleum- Oil Gasoline Heating Oil Plastics Coal Natural Gas Non Renewable Energy Nuclear Fission - split atoms Fusion – combine atoms Energy Conservation Shut off lights Fluorescent/Compact lights Recycle Reduce Reuse What do biomass and fossil fuels have in common? Burnable Pollute Name two advantages to fuels and why we use them. Portable Storable What energy source do you think is the safest, cleanest, easiest to use? Great New York Blackout Hopefully Not The End