* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2nd Semester Final Exam Review 2016
Survey
Document related concepts
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Induced pluripotent stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
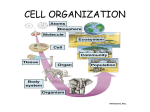
Name: ______________________________ Date: ______________ Class: __________ 2016 7th Grade Science Spring Final Exam Review My Test is on: _______________________________ Geotropism & Turgor Pressure: 1. Define tropism. The movement by the plant in response to a stimulus 2. How can you tell that a plant has a decreased turgor pressure? It begins to wilt 3. What is the first sign of seed emergence? Absorption of water 4. Describe the force of the vacuole and cell wall in a plant with high turgor pressure. The force of the vacuole will be GREATER than the force of the cell wall in high turgor pressure 5. What is an example of positive stimulus? A plant bending towards light, roots growing downward in the direction of gravity 6. Define xylem and explain the direction of water flow. Xylem conducts the flow of water from the roots to the leaves and stems. (Clue: Xy- goes high.) 7. Which plant structure transports glucose? Phloem Cells, Microscopes, and Classification 8. What is a limitation to a model? Size of structures, proportions, spacing, and shapes. 9. How do prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ? The DNA in a prokaryotic cell is not inside a membrane bound nucleus. The DNA in a eukaryotic cell in is a membrane bound nucleus. 10. Name 3 differences between plant and animal cells including the shape. Plant – more rectangular: animal – circular or oval, Plants have one or two large vacuoles; animals have many small vacuoles, and plant cells have a cell wall and chloroplasts 11. Which organic compound do ribosomes make? Create proteins 12. List the three components of the cell theory. a. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living organisms b. All organisms are made of cells c. Cells only come from other cells 13. Which objective of a microscope do you use first? Low power objective lens 1 14. If a microscope has an eyepiece with a power of 10x and the objective power is turned to 40x, what is its total magnification? 400x 15. What is the function of the diaphragm? Controls the amount of light emitted 16. Which cell organelle is responsible for getting rid of wastes? lysosomes 17. Define dichotomous key and know how to use one. A tool used the identify organisms based on observable characteristics 18. What cell organelle must an organisms have to be an autotroph? Chloroplast Genetics, Heredity, Reproduction, Natural Selection, and Selective Breeding 19. Who is the Father of Genetics and what did he study? Gregor Mendel studied pea plants 20. Write the definitions of the following terms: a. DNA - the hereditary code contained in the chromosomes in the nucleus of a cell b. Haploid - Haploid contain single set of chromosomes (half the number of diploid cells, example: sex cells such as sperm and egg) c. Diploid - Diploid cells contain pairs of chromosomes (cells throughout the body EXCEPT sex cells) d. Regeneration - the process that uses cell division to regrow body parts e. Hybrid - genotype with different alleles for a trait from each parent 21. Define Genetics – The study of how traits are inherited 22. Define Heredity – When traits are passed on from one generation to the next 23. How many PAIRS of chromosomes do cells in your body have (including skin cells, lung cells, muscle cells, etc)? 23 24. What are the two sex cells AND how many chromosomes do they have? The two sex cells are the egg and sperm. Sex cells have 23 single chromosomes; no pairs. 25. What is a similarity between asexual and sexual reproduction? They are both a way for species to continue. 26. What are the three types of asexual reproduction and give an example of each. a. Fission Example – Bacteria b. Budding Example – Yeast c. Regeneration Example – Starfish 2 27. Using the letter “R”, write the genotype for the following OR define: 1. Homozygous dominant - RR 2. Homozygous recessive - rr 3. Heterozygous dominant - Rr 4. Genotype - RR, Rr, rr 5. Phenotype - description of the trait (ex: short or tall) 28. Create a punnett square to answer the following question. In dogs, floppy ears are a recessive trait while pointy ears are the dominant trait. If a mama dog has floppy ears and a daddy dog is homozygous for his pointy ears, what is the percent chance their puppy will have pointy ears? r r Rr Rr Rr 100% Rr 29. What is the end result of mitosis? Two diploid cells 30. Which scientist developed the theory of Natural Selection and what does it mean? Charles Darwin Natural Selection means organisms that do not adapt to changes in their environment will not survive and the ones that do adapt will pass on that trait to the next generation. 31. Define selective breeding. When you select what species will breed to try to achieve a specific trait. 32. Give an example of selective breeding. You have two different kinds of roses. One is prettier than the other while the second smells better. You cross the two flowers hoping for a flower that is both beautiful and smells pretty. 33. Define natural selection. The process by which organisms better adapted to the environment survive while those that have not adapted do not survive. 34. Give an example of natural selection. The Galapagos finches whose beaks had adapted to various sizes and shapes in order to better obtain the type of food that was available on their respective islands were equipped to survive and reproduce over those who did not have adapted beaks. 3 35. Give an example of a species that has adapted to its environment - Frogs and salamanders which live in caves have no skin pigment and no eyes since caves have no light. Human Body Systems Levels of Organization 36. List the 5 levels of organization in order. Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism 37. What is the smallest unit of life? A cell 38. Define tissue. A group of cells that have a similar job 39. What makes up organs? A group of tissues 40. What is homeostasis? The ability for an organism to maintain steady conditions inside no matter what happens outside. 41. When the skeletal and muscular systems work together they help you to _move_? 42. How does the skeletal system help maintain homeostasis? (HINT: think about what your marrow makes!) Replace blood cells as they die Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems 43. Give three examples of moveable joints. Knee, Elbow, Wrist 44. Give 2 examples of hinge joints. Elbow and Knee 45. Skeletal muscles always work in _pairs_. 46. _Tendons_ attach muscle to bone. 47. What is the tissue at the ends of your bones which allows you to move without experiencing pain? Cartilage 48. What are the 5 functions of your skin? a. Protection b. Sensory Response c. Formation of Vitamin D d. Regulation of Body Temperature e. Ridding the body of wastes 4 49. How does the integumentary system help you maintain homeostasis when you get cold? Forms goosebumps to keep heat in Nervous System 50. What are the two components of the central nervous system? Brain and spinal cord 51. What is controlled by the somatic nervous system? Body movement, voluntary activities 52. What body system is at work when the body feels pain? Nervous system 53. A message carried by a neuron is called a _impulse_. 54. How do drugs (such as caffeine and alcohol) affect the nervous system? Speed up or slow down the activities of the central nervous system Endocrine and Reproductive Systems 55. Which glands make up the endocrine system? Thyroid, Parathyroid, Pituitary gland, and Adrenal glands 56. Describe how the endocrine system helps your body maintain homeostasis. It keeps your body regulated by giving negative feedback (Think of an air condition in your home turning on and off by thermostat readings.) 57. What are the organs of the male and female human reproductive system? Male: testicles, accessory glands, duct system, and penis Female: vagina, uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries Circulatory and Immune (Lymphatic) Systems 58. Label the following diagram: A – Right Atrium B – Superior Vena Cava C – Aorta D – Pulmonary Artery E – Left Atrium F – Left Ventricle G – Right Ventricle H – Inferior Vena Cava 5 59. Which chambers of the heart hold oxygenated blood? E and F – Left Atrium and Left Ventricle 60. How many chambers does the human heart have? 4 61. What are the 4 main functions of blood? Carries oxygen, carries wastes, transports nutrients, helps fight infections 62. How do arteries and veins differ? Arteries carry blood away from the heart while veins bring blood back to the heart 63. What are the four components of blood? Plasma, White Blood Cells, Red Blood Cells, and Platelets 64. Describe the functions of each item in question #63 above. Plasma: the liquid part of the blood that carries nutrients to the cells White blood cells: fights bacteria and other pathogens Red blood cells: carries oxygen, carbon dioxide and other materials to and away from cells Platelets: clots the blood Respiratory System 65. Your lungs give oxygen to your capillaries through which structures? alveoli 66. Which part of your respiratory system moistens and warms the air as it enters your body? Nasal cavity 67. Which muscles contracts and relaxes allowing you to breathe? Diaphragm Digestion and Excretion 68. List the organs that food passes through in order as it passes through your digestive tract. Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small Intestine Large Intestine Rectum Anus 69. List the accessory organs in the digestive system (there are 6 of them). Liver, Gallbladder, Pancreas, Teeth, Tongue, Salivary Glands 70. Define the following: a. vitamins - organic nutrients needed for growth, regulating body functions, and preventing disease b. peristalsis - wave of muscle contractions in esophagus that moves food along digestive system c. minerals - inorganic nutrients that regulate chemical reactions d. esophagus - muscular tube which food passes through to move from the mouth to the stomach 71. When your stomach mixes food while hydrochloric acid breaks it down, both _chemical_ and _physical_ changes have occurred. 72. How much blood passes through the kidneys each day? All of it 6 73. What other systems, besides the excretory systems, help in excreting wastes? Skin (Integumentary) and Lungs (Respiratory) 74. Label the following diagram: A. B. C. D. E. F. Aorta Kidney Renal Artery Ureters Bladder Urethra 75. Know the function of the following systems a. Nervous - control body actions b. Skeletal – helps provide movement and shape and support c. Respiratory – takes in oxygen and releases carbon dioxide d. Digestive – breaks down food e. Circulatory – transports materials throughout the body STUDY HARD AND GOOD LUCK! HAPPY SUMMER 7