* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Scientech 2138A AT Manual
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
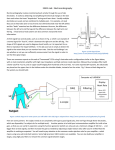
ECG Cum Heart Rate Monitor Scientech 2351 Product Tutorial Ver. 1.1 Designed & Manufactured byAn ISO 9001:2008 company Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 94, Electronic Complex, Pardesipura, Indore - 452 010 India, + 91-731 4211100, : [email protected] , : www.ScientechWorld.com Scientech 2351 ECG cum Heart Rate Monitor Scientech 2351 Table of Contents 1. Safety Instructions 3 2. Introduction 4 3. Features 5 4. Technical Specifications 6 5. Panel Controls and Indicators 7 6. Block Diagram of ECG cum Heart Rate Monitor 8 7. Explanation of the Block Diagram 9 8. Human Cardiovascular System 11 9. Electrocardiogram (EKG, ECG) 16 10. Heart Rate Monitor 19 11. Glossary of Human Cardiovascular System Terms 20 12. Operating Instructions 21 13. Real Time ECG Analysis Software 22 14. Experiments • Experiment 1 To observe ECG waveforms of subject (Human body) using Lead I of standard bipolar lead configuration 25 • Experiment 2 To observe ECG waveforms of subject (Human body) using Lead II of standard Bipolar lead configuration 26 • Experiment 3 To observe ECG waveforms of subject (Human body) using Lead III of standard Bipolar lead configuration 27 • Experiment 4 To measure the Heart-Rate of subject (Human body) 28 • Experiment 5 To study the abnormalities (Tachycardia, Bradycardia) occur in Human Cardio-Vascular system 30 15. Frequently Asked Questions 32 16. Warranty 39 17. List of Accessories 39 Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 2 Scientech 2351 Safety Instructions Read the following safety instructions carefully before operating the product. To avoid any personal injury, or damage to the product, or any products connected to it; Do not operate the instrument if you suspect any damage within. The instrument should be serviced by qualified personnel only. For your Safety: Use proper Mains cord : Use only the mains cord designed for this product. Ensure that the mains cord is suitable for your country. Ground the Instrument : This product is grounded through the protective earth conductor of the mains cord. To avoid electric shock the grounding conductor must be connected to the earth ground. Before making connections to the input terminals, ensure that the instrument is properly grounded. Observe Terminal Ratings : To avoid fire or shock hazards, observe all ratings and marks on the instrument. Use only the proper Fuse : Use the fuse type and rating specified for this product. Use in proper Atmosphere : Please refer to operating conditions given in the manual. Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 1. Do not operate in wet / damp conditions. 2. Do not operate in an explosive atmosphere. 3. Keep the product dust free, clean and dry. 3 Scientech 2351 Introduction Scientech TechBooks are compact and user friendly learning platforms to provide a modern, portable, comprehensive and practical way to learn Technology. Each TechBook is provided with detailed Multimedia learning material which covers basic theory, step by step procedure to conduct the experiment and other useful information. Heart-rate monitor cum ECG Scientech TechBook 2351 provides in-depth study of Electrocardiogram, ECG standard leads configuration, and the measurement of heartrate i.e. number of ECG pulses (heartbeats) per minute. Scientech TechBook 2351 enables the Electrocardiogram observation by affixing Biomedical Electrodes to the human body in standard bipolar leads configuration. The Heart-rate monitor receives each ECG observation (heartbeat) i.e. detects the electrical action executed by the heart of a subject (human body) and displays the heart-rate as number of heartbeats per minute. Scientech TechBook 2351 also monitors the abnormalities occur in human cardiovascular system which is Tachycardia (faster heart-rate) and Bradycardia (slower heart-rate) using visible controls. It also facilitates real time acquisition of raw data (ECG) and their corresponding measurements by its real time Analysis Software. Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 4 Scientech 2351 Features • Self contained and easy to operate • 16x2 LCD display of heartbeats per minute • On board both visible (LED) and audible (buzzer) heartbeat event indicator • Separate test-points to observe ECG waveform after each block (in simulation mode (SM) pre-amplifier and filter are not in the function because data coming from the simulator is already filtered and amplified data, while in real time mode all the blocks will be in the function) • In built Data Acquisition module with USB interface for Real time analysis • On board one minute indicator • User Selectable Heart-rate, Bradycardia limit, Tachycardia limit display • On board Bradycardia and Tachycardia Indicator • On board Bradycardia limit, Tachycardia limit adjustment • User selectable buzzer for heartbeat indication • On board Reset for display and One minute Timer reset Real time ECG Analysis Software • ECG can be analyzed in real time during acquisition • Review and analysis of recorded ECG file • Horizontal and vertical analysis of ECG data on graph, using Grid Scale • Heart-rate display with QRS detection by visual indication Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 5 Scientech 2351 Technical Specifications Measuring Range : 30-300 heartbeats per minute Accuracy : ±2 heartbeats/ minute Heart-rate Display : 16x2 LCD Display Tachycardia limit Range : 0-255 heartbeats per minute Bradycardia limit Range : 0-255 heartbeats per minute ECG Acquisition module : Real time ECG acquisition with 200 samples/ sec 8-bit A/D Converter with USB interface Electrodes : Surface or clamp (Ag-AgCl) electrodes Test Point : 7 nos. Dimensions (mm) : W 326 x D 252 x H 52 Power supply : 110V - 260V AC, 50/60Hz Weight : 1.5 Kg. (approximately) Test Point : 7 nos. Operating Condition : 0-400 C, 85% RH Product Tutorial : Online (Theory, procedure, reference results, etc). Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 6 Scientech 2351 Panel Controls and Indicators • Power ‘On’/ ‘Off’: Rocker switch for supplying power to the instrument • Heartbeat Event Indicator: LED indication for each heartbeat event executed by heart of human body. • Tachycardia Limit Adjust: Knob used to adjust the tachycardia limit. • Bradycardia Limit Adjust: Knob used to adjust the tachycardia limit. • 16x2 LCD Display: 16x2 LCD used to display Heart-rate, Tachycardia limit and Bradycardia limit depending upon their selection. • Tachycardia Indicator: Tachycardia LED indication when Heart-rate is greater than the set Tachycardia limit. • Bradycardia Indicator: Bradycardia LED indication when Heart-rate is less than the set Bradycardia limit. • Mode Selection Switch: This push switch is used to select Heart-rate, Tachycardia limit, Bradycardia limit. • Mode Selection for Real Time or Simulation Mode: This switch is used for selecting the mode of working, if you are using 12 Lead ECG Simulator Scientech 2352A then this switch must be in simulation mode (SM) and for real time measurement switch must be in real time mode (RTM). • On board Reset/Count Selection: Switch used to select either the Count mode or the Reset mode. Count mode starts the counting of heartbeats of the subject (human body) and simultaneously starts the timer for one minute duration. Reset mode resets the Heart beats counting to zero and also resets the one minute timer. • One Minute Timer: Timer which gives one minute indication by glowing LED • USB Interface: Allow transferring ECG data to PC by inbuilt Data Acquisition Module Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 7 Scientech 2351 Block Diagram of ECG cum Heart Rate Monitor Block diagram of the Heart-Rate monitor Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 8 Scientech 2351 Explanation of the Block Diagram 1. Input from Electrodes: The voltage generated by the pumping action of the heart is actually a vector whose magnitude, as well as spatial orientation, changes with time. Because the ECG signal is measured from electrodes applied to the surface of the body, the waveform of this signal is very dependent on the placement of electrodes. To observe the ECG pattern of a subject (human body) it is necessary to apply ECG metal (clamp) electrodes to the patient's limbs in special formats called leads. Bipolar leads are preferably used along with our heart-rate monitor. 2. Pre-Amplifier and Filter: The signal coming from the sensor is very less and consists of noise, so it must be amplified by operational amplifier and filtered by second order low pass filter to get the ECG signal. But in simulation mode data coming from the Scientech 2352A is already amplified and filtered, so in simulation mode these two blocks are not in the function while rest of the circuit will work properly and you can see waveforms at the test points after the blocks. 3. Main Amplifier: The filtered signal has amplitude of some mV, hence it is amplified using main amplifier with variable gain from 800 to 2000. To reduce the DC offset A.C. amplifiers are used in this section. Output from the main amplifier is also given to the inbuilt data acquisition module to transfer the raw data (ECG) to PC RS232 interface. 4. Threshold Detector: A comparator circuit used to detect the heartbeat event executed by the heart of subject (Human body) and generates a pulse with every heartbeat. 5. Synchronous Pulse Generator: The resulted pulse from the threshold detector is given to the non-retriggerable monostable multi-vibrator, which generates a large duration pulse of around 500ms and eliminates chances of triggering of multi-vibrator due to noise and artefacts. This circuit finally generates synchronized pulse to represent every heartbeat event executed by the heart of subject (human body) which is given to F-V converter section. 6. Frequency to Voltage Converter: The pulse coming from the synchronous pulse generator is averaged to produce DC voltage level proportional to the total heartbeat event, which is then calibrated to show as the heart-rate on the digital panel meter. Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 9 Scientech 2351 7. Tachycardia Comparator: The DC voltage coming from frequency to voltage converter is compared with a preset tachycardia limit value to trigger the abnormality indicator block whenever the heart rate goes higher than the preset value. 8. Bradycardia Comparator: The DC voltage coming from frequency to voltage converter is compared with a preset Bradycardia limit value to trigger the abnormality indicator block whenever the heart rate goes lower than the preset value. 9. LCD Display: LCD is used to display either heart rate as number of heart beats per minute or tachycardia limit or bradycardia limit depending upon their selection. 10. Abnormality Indicator: This circuit indicates the abnormalities present in the subject (Human body) by Audio and Visible controls. This section triggers when either heart-rate goes more than the tachycardia limit value or heart-rate goes less than the bradycardia limit value. Tachycardia and Bradycardia conditions are indicated by Tachycardia LED and Bradycardia LED. Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 10 Scientech 2351 Human Cardio-Vascular System The Anatomy of the Human Heart: The heart is basically a hollow muscular pump, which pushes the blood through out the body via the blood vessels. It is located between the lungs and slightly to the left of centre. The heart is an involuntary muscle that has approximately seventy to ninety contractions per minute during a restful state. It begins to pump early in the life of a foetus and will continue unceasingly until death. Heart Walls: The heart walls are divided into three layers: • Pericardium • Myocardium • Endocardium Chambers: The heart is divided by a partition or septum into two halves. The halves are in turn divided into chambers. The upper two chambers of the heart are called atria and the lower two chambers are called ventricles. Valves allow blood to flow in one direction between the chambers of the heart. The heart has four distinct chambers. 1. Right atrium is the thin-walled area that receives the venous or "used" blood returning to the body by the veins. 2. Right ventricle is the "pump" area of the heart's right side. The atrium dumps the blood into the ventricle where it is then pumped out the pulmonary arteries and to the lungs. 3. Left atrium receives the oxygenated blood returning from the lungs. 4. Left ventricle has the thickest walls of all. It is from this chamber the blood is pumped out of the heart, into the aorta and out to the rest of the body. Heart Valves: 1. Tricuspid valve is the one located at the entrance of the right ventricle. It prevents the blood from washing back into the right atrium. 2. Pulmonary semi lunar valve is located between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery. 3. Mitral valve is made of very heavy cusps and is located at the entrance of the left ventricle. This is a powerful valve that closes as the left ventricle begins each of its contractions to ensure the oxygenated blood doesn't re-enter the left atrium. 4. Aortic valve is located, as its name would imply, between the left ventricle's exit and the aorta itself. Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 11 Scientech 2351 Even though the heart splits up into two distinct halves, these two must work together to function properly. Human Heart Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 12 Scientech 2351 Heart as a Pump: Blood from the body that enters the right side of the heart contains carbon dioxide, a gaseous waste the cells produce in creating energy. Blood enters the right atrium through the superior vena cava and inferior vena cava. The atrium fills with blood and then contracts, squeezing the blood through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle. After the ventricle is filled, pressure forces the tricuspid valve to close and the pulmonic valve, leading to the pulmonary artery, to open. The ventricle contracts and the blood rush through the pulmonary artery and into the lungs. In the lungs, carbon dioxide is removed from the blood and oxygen is added. The oxygenated blood then flows through the pulmonary veins to the left side of the heart. Oxygenated blood from the lungs enters and fills the left atrium. The atrium then contracts, which squeezes the blood through the mitral valve into the left ventricle. After blood fills the ventricle, the mitral valve is closed and the aortic valve is opened. Blood pours into the aorta and flows through arteries to the body tissues. Heart as a Pump Both sides of the heart pumps blood at the same time. As the right ventricle contracts and sends blood to the lungs, the left ventricle contracts and squeezes blood out to the body. The heart's cycle of activity has two periods viz. systole and diastole. Systole occurs when the ventricles contract, and diastole when they relax. One complete contraction and relaxation of the heart muscle makes up one heartbeat. The heart-rate is a rate at which the heart beats per minute. Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 13 Scientech 2351 The Heart's Conduction System: There are four basic components to the heart's conduction system. 1. Sinoatrial node (SA node) 2. Inter-nodal fibre bundles 3. Atrioventricular node (AV node) 4. Atrioventricular bundle At the right top corner of the heart there is a special group of excitable cells called Natural Pacemaker or Sinoatrial Node. This natural pacemaker generates electrical impulses spontaneously. At the lower part of the right atrium there is another mass of specialized group of cells called atrioventricular node. From the atrioventricular node a bundle of conducting fibers called Bundle of His, passes down to interventricular septum. A natural pacemaker generates electrical impulses at regular rate. To initiate the heartbeat the action potentials generated by the natural pacemaker or S.A. node gets propagated in all directions along the surface of both atria and Atrioventricular Node. This spreads throughout the right and left atrium, their wall tissues and results into contraction of atria. Now the waveform reaches to the A.V. node through special nerve fibers which provide the delay in propagation so as to have proper timing between the pumping action of atrium and ventricles. During the delay time the atria completes their contraction forcing blood into ventricles in order to complete their filling. At this point A.V. node initiates an impulse that gets propagated into the ventricles throughout Bundles of His then into left and right bundle branch and further into purkinje fibres causing contraction of both the ventricles and forcing blood into lungs and the whole body. During the contraction of ventricles the atria complete their filling and to initiate the next heart beat a pacemaker generates another electrical impulse. With the natural pacemaker providing the impulse, the rate of contraction of the heart is maintains and controlled. Normally this action occurs for 60-100 times in a minute, when additional blood is required, the flow must be increased. This is achieved by generating the impulse at faster rate by natural pacemaker. Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 14 Scientech 2351 Heart Conduction System Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 15 Scientech 2351 Electrocardiogram (EKG, ECG) As the heart undergoes depolarization and repolarization, the electrical currents that are generated spread not only within the heart, but also throughout the body. This electrical activity generated by the heart can be measured by an array of electrodes placed on the body surface. The recorded tracing is called an Electrocardiogram (ECG, or EKG). A "typical" ECG tracing is shown below. The different waves that comprise the ECG represent the sequence of depolarization and repolarization of the Atria and Ventricles. The P wave represents the wave of depolarization that spreads from the SA node throughout the atria, and is usually 0.08 to 0.1 seconds (80-100 ms) in duration. ECG Wave The QRS complex represents ventricular depolarization. The duration of the QRS complex is normally 0.06 to 0.1 seconds. This relatively short duration indicates that ventricular depolarization normally occurs very rapidly. The T wave represents ventricular repolarization and is longer in duration than depolarization (i.e., conduction of the repolarization wave is slower than the wave of depolarization). Typically the total time required for one complete cycle of the heart electrical activity ranges from approximately 0.4 to 0.6 second. A healthy ECG shows a normal sinus rhythm. This is when each depolarization of the cardiac conduction system creates a P wave, followed by a QRS complex, followed by a T wave. During a normal sinus rhythm, the atria are contracting first (around the time of the P wave), and the ventricles contract second (around the time of the QRS complex). Ventricular relaxation occurs around the time of the T wave. Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 16 Scientech 2351 ECG Electrodes and Standards ECG Leads: The Bio Electric signal generated on the surface of body is picked up by using the electrodes. The electrodes make electrical conduction, which is necessary for making measurements. There are two types of electrodes used in practices: 1. Surface electrodes or disc electrodes 2. Deep seated electrodes or needle electrodes The surface electrodes picked up potentials from the surface when placed over it without damaging the tissues whereas deep-seated electrode senses the potential difference arising inside the live tissue or cell. There are three types of electrodes used for the ECG recording 1. Limb electrode 2. Floating electrodes 3. Suction cup electrodes The most common types of electrodes routinely used for ECG recording are circular or rectangular surface electrodes. An electrode conductive jelly is applied between the body and the electrode to reduce contact impedance. Floating are suitable and effective for long term monitoring they consists of AgAgcl3 metal electrode and flat plastic washer which does not allow metal to make contact with the body directly. This arrangement reduces the effect of motion artefacts. Floating electrodes are placed on the chest with electrodes conductive jelly and fix using sticking plastics. The voltage generated by the pumping action of the heart is actually a vector whose magnitude, as well as spatial orientation, changes with time. Because the ECG signal is measured from electrodes applied to the surface of the body, the waveform of this signal is very dependent on the placement of electrodes. To record the ECG pattern of a subject (human body) it is necessary to apply ECG metal electrodes to the patient's limbs in special formats called leads, on each arm and leg, and six electrodes are placed at defined locations on the chest. These electrode leads are connected to a device that measures potential differences between selected electrodes to produce the characteristic electro-cardio-graphic tracings. • Limb Leads (Bipolar) • Augmented Limb Leads (Unipolar) • Chest Leads (Unipolar) Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 17 Scientech 2351 Limb Leads (Bipolar): Sr. No. Lead symbol Lead Name 1. I 2. 3. Electrode location and polarity Positive (Yellow) Negative (Red) Ref. (Black) Lead I Left Arm Right Arm Right Leg II Lead II Left Leg Right Arm Right Leg III Lead III Left Leg Left Arm Right Leg Electrodes arrangement in bipolar lead configuration Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 18 Scientech 2351 Heart-Rate Monitor: Heart-rate conduction is the rate at which the heart conducts electrical impulses. Cardiac muscle cells contract spontaneously and are coordinated by nodal tissue, specifically the sino-atrial node. There are other factors that influence heart rate as well. These include endocrine hormones, body temperature and exercise. With contraction of the heart, the blood in the left ventricle flows out to the arteries. This blood flow causes the walls of the arteries to throb and produces a wave, which get propagates all over the body via arteries. This is represented by QRS waveforms of ECG complex or a heartbeat. The Heart-rate is a rate at which the heart beats per minute. It is controlled by the frequency at which the natural pacemaker generates electrical pulses. However cardiac and vagus nerves of the sympathetic systems and parasympathetic systems causes the heart-rate to increase or decrease respectively according to body requirements. When measured using heart-sounds or ECG it is called heart-rate. A person's size largely determines a person's resting heart rate. The bigger a person is, the slower the heart rate. A newborn baby's heart beats about 120 times per minute. The typical rate for adults is 72 beats per minute. But doctors consider resting rates from 60 to 100 beats per minute within the normal range normal sinus rhythm. A slower rate than normal sinus rhythm this is called Bradycardia A higher rate than normal sinus rhythm this is called Tachycardia Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 19 Scientech 2351 Glossary of Human Cardiovascular System Terms Artery: A muscular blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart Arrhythmia: Pronounced uh RIHTH mee uh, is an abnormal heart rhythm Atrium: One of the chambers of the heart that receives blood directly from a vein Bradycardia: When the heart-rate less than the normal heart-rate rhythm Circulatory System: The system of the body responsible for internal transport Composed of the heart, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, lymph, and the blood Cardiology: Is the branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of disorder of the heart Diastole: Pronounced dy AS tuh lee, is the period of heart activity when the ventricles relax Diastolic Pressure: The decreased pressure due to the relaxation of the ventricles is called diastolic pressure Electrocardiograph (ECG): It is an instrument used to detect heart damage or diagnose heart disorders Heart: The muscular organ composed of cardiac muscle that is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body Normal Sinus Rhythm: Normal pumping action of heart generates 60 -100 heartbeats per minute Septum: The wall dividing the two ventricles Systole: It is the period of heart activity when the ventricles contract Systolic Pressure: The increased pressure due to the contraction of the ventricles is called systolic pressure Tachycardia: When the heart-rate exceeds than the normal heart-rate rhythm Ventricle: One of the muscular chambers of the heart that is responsible for pumping blood from the heart into the arteries Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 20 Scientech 2351 Operating Instructions 1. Select the mode of working using mode selection switch for the selection of the Simulation Mode (SM) or Real time mode (RTM) of the operation. 2. In real time mode Electrodes must be placed carefully along with ECG GEL so that the ECG pulses can be obtained without noise. 3. Connect the electrodes cable to the instrument only after placing the electrodes properly on patient's predefined places, to reduce the false pulses generated during placing the electrodes. 4. Before monitoring the Heart-rate of human body, initially the Count/Reset switch should be in Reset mode to allow the Heart-rate Monitor to start measuring from beginning (Reset value) and to reset the one minute timer. 5. For calculating the Heart-rate select Heart-rate mode with the help of mode selection switch and Count/Reset switch should be in Count Mode. 6. For adjusting the Tachycardia limit should select Tachycardia limit mode with the help of mode selection switch. 7. For adjusting the Bradycardia limit select Bradycardia limit mode with the help of mode selection switch. 8. During monitoring the patient should be completely in rest position otherwise the displayed values will be incorrect. 9. Properly connect the USB cable with PC and kit when using the Real Time ECG analysis software. Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 21 Scientech 2351 Real Time ECG Analysis Software Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 22 Scientech 2351 This Software Contains Three Modules (windows): 1. Display Block 2. Control Block 3. Measurement Block 1. Display Block : 2. 3. • Displays the selected Lead Real Time ECG signals. • Used for setting the threshold value. • Helps to measure the time-period of ECG signals by setting their beginning and end point. • Direct display of X and Y axis measurement, QRS complex, Heart Rate, final result of ECG measurement. Control Block: User interface for • Start/Stop the Display • Contains check hardware and Reset button • Allow to perform Threshold settings • Allows setting Tachycardia and Bradycardia Limit adjustments • One minute timer control for Heart rate calculation Measurement Block • Displays Heart-rate, Bradycardia, Tachycardia results, direct measurement of QRS Complex voltage. • Contains ‘Cursor 1’ and ‘Cursor 2’ for X-axis and Y-axis measurement respectively. System Requirements: O/S : Windows 98/2000/Me/Xp RAM : 128 MB or more Space Required : 10 MB Screen Resolution : 1024 × 768 pixels Software language used : Visual Basic 6.0 Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 23 Scientech 2351 About Copyright This software is protected by copyright law and international treaties .Unauthorized reproduction or distribution of this software or any portion may result in severe civil and criminal penalties and will prosecute to the maximum extent possible under law. Instructions for installing the Real Time ECG Analysis Software • Insert the Real time ECG Analysis Software CD into CD drive. • Now open the CD ROM drive and run .exe file. It will install the Scientech 2351 software. • The installing location is set to C:/program files by default, although it can be changed during installation. Instruction for installing the Drivers for the software • Execute the Real time ECG Analysis Software Application from start menu/ Real-time ECG Analysis Software/RTECG.exe • Click on the File on the top left corner of the window • Click on the Install/ Reinstall Drivers • Follow the procedure shown and the drivers will be installed • Now the software is ready to use Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 24 Scientech 2351 Experiment 1 Objective: To observe ECG waveforms of subject (Human body) using Lead I of standard bipolar leads configuration. (In Real Time Mode) Equipments needed: 1. ECG cum Heart Rate Monitor Scientech 2351 2. ECG electrodes (clamp electrode) 3. ECG Connector cable 4. DSO ( RIGOL DS 1102C 100MHz 400 MSa/s or equivalent) 5. Real Time ECG Analysis Software 6. USB Cable (male to male A type) Procedure: 1. Connect one end of the Power Supply to ECG cum Heart Rate Monitor Scientech 2351, while other end to mains Power Supply 2. Switch ON the Mains Power Supply, then Scientech 2351 TechBook 3. Now place the electrodes in Lead I of standard Bipolar lead configuration Positive electrode (yellow) in left arm of subject, negative electrodes (Red) in right arm, and common (reference) electrode (Black) in the right leg of subject properly with ECG Gel and connect the cables to the kit 4. Observe the ECG waveform in Lead I configuration at test-point Amplifier block (TP3) of TechBook. Or Make a USB Connection between USB port on Training kit and USB port on PC. And observe the waveforms and analyze them with Real time ECG Analysis Software 5. Then observe ECG waveforms at outputs of the different blocks of ECG cum Heart Rate Monitor Scientech 2351 Conclusions: 1. Lead I configuration wave form is coming properly in appropriate shape 2. Amplitude of the wave is varying according to the adjustment of gain 3. Shape of Lead I wave form is same in hard ware and software Questions: 1. What are the different wave amplitudes (P,Q,R,S,T) in Lead I 2. Why Lead I is called as Bipolar Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 25 Scientech 2351 Experiment 2 Objective: To observe ECG waveforms of subject (Human body) using Lead II of standards bipolar lead configurations. (In Real Time Mode) Equipments needed: 1. ECG cum Heart Rate Monitor Scientech 2351 2. ECG electrodes (clamp electrode) 3. ECG connector cable 4. DSO ( RIGOL DS 1102C 100MHz 400 MSa/s or equivalent) 5. Real Time ECG Analysis Software 6. USB Cable (male to male A type) Procedure: 1. Connect one end of the Power Supply to ECG cum Heart Rate Monitor Scientech 2351, while other end to mains Power Supply 2. Switch ON the Mains Power Supply, then Scientech 2351 TechBook 3. Now place the electrodes in Lead II of standard bipolar leads configuration i.e. positive electrode (Yellow) in Left Leg of subject, negative electrode (Red) in Right Arm, and common (reference) electrode (Black) in the Right Leg of subject properly with ECG gel and connect the cables to the kit. 4. Observe the ECG waveform in Lead II configuration at test-point after Amplifier block of TechBook. Or Make a USB Connection between USB port on Training kit and USB port on PC. And observe the waveforms and analyze them with Real time ECG Analysis Software. 5. Observe ECG waveforms at outputs of the different blocks of Heart-rate. Monitor cum ECG TechBook Scientech 2351. Conclusions: 1. Lead II configuration wave form is coming properly in appropriate shape 2. Amplitude of the wave is varying according to the adjustment of gain 3. Shape of Lead II wave form is same in hard ware and software Questions: 1. Why Lead II is called Standard Lead in ECG measurement? 2. What is the peak to peak voltage of QRS complex in Lead II? Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 26 Scientech 2351 Experiment 3 Objective: To observe ECG waveforms of subject (Human body) using Lead III of standard bipolar leads configuration. (In Real Time Mode) Equipments needed: 1. ECG cum Heart Rate Monitor Scientech 2351 2. ECG electrodes (clamp electrode) 3. ECG connector cable 4. DSO ( RIGOL DS 1102C 100MHz 400 MSa/s or equivalent) 5. Real Time ECG Analysis Software 6. USB Cable (male to male A type) Procedure: 1. Connect one end of the Power Supply to ECG cum Heart Rate Monitor Scientech 2351, while other end to mains Power Supply 2. Switch ON the Mains Power Supply, then Scientech 2351 TechBook 3. Now place the electrodes in Lead III of standard bipolar leads configuration i.e. positive electrode (Yellow) in Left Leg of subject, negative electrode (RED) in Left Arm, and common (reference) electrode (BLACK) in the Right Leg of subject (human body) properly with ECG gel and connect the cables to the kit 4. Observe the ECG waveform in Lead III configuration at test-point after Amplifier block of TechBook. Or Make a USB Connection between USB port on Training kit and USB port on PC. And observe the Waveforms and analyze them with Real time ECG Analysis Software 5. Then observe ECG waveforms at outputs of the different blocks of ECG cum Heart Rate Monitor Scientech 2351 Conclusions: 1. Lead III configuration wave form is coming properly in appropriate shape 2. Amplitude of the wave is varying according to the adjustment of gain 3. Shape of Lead III wave form is same in hard ware and software Questions: 1. What is the peak to peak Voltage of QRS complex in Lead III? 2. Why peak to peak voltage of Lead III is small in comparison with Lead I & II? Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 27 Scientech 2351 Experiment 4 Objective: To measure the Heart-Rate of subject (Human body) in Real Time Mode Equipments needed: 1. ECG cum Heart Rate Monitor Scientech 2351 2. ECG electrodes 3. ECG connector cable 4. DSO ( RIGOL DS 1102C 100MHz 400 MSa/s or equivalent) 5. Real Time ECG Analysis Software 6. USB Cable (male to male A type) Procedure: 1. Connect one end of the Power Supply to ECG cum Heart Rate Monitor Scientech 2351, while other end to mains Power Supply 2. Switch ON the Mains Power Supply, then Scientech 2351 TechBook 3. Before monitoring the heart-rate of human body the Count/Reset selection switch should be in Reset mode to allow the Heart-rate Monitor to start measuring from beginning (Reset value) and to reset the one minute timer 4. The Display mode provided at front panel displays either Heart-rate or Tachycardia limit or Bradycardia limit depending up on their selection. Initially in case of Heart-rate it will give Reset value indication, and if Tachycardia limit or Bradycardia limit is selected then it will display their present value 5. Now place the Electrodes in any of the standard Bipolar leads configuration (Lead I, Lead II or Lead III, it is recommended to use Lead II for better accuracy) properly with ECG gel and connect the cables to the kit 6. Select Count Mode using Count/Reset selection switch and observe each heartbeat event executed by the subject (human body) on heartbeat event indicator with in one minute duration. One minute duration is indicated by one minute timer LED Now observes the Heart rate displayed on the LCD Or Make a USB Connection between USB port on kit and USB port on PC and observe the Waveforms and analyze them with Real time ECG Analysis Software 7. Select Reset mode, before counting Heart-rate of any other subject (human body) in Count Mode Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 28 Scientech 2351 Conclusions: 1. Selected Lead configuration wave form is coming properly in appropriate shape 2. Amplitude of the wave is varying according to the adjustment of gain 3. Heart rate is shown by the software is accurate 4. Hardware and software showing same result of Heart rate Questions: 1. What are the normal heart rate values of Adult male and female? 2. What are the different parameters over which heart rate depends? Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 29 Scientech 2351 Experiment 5 Objective: To study the abnormalities (Tachycardia, Bradycardia) present in human cardiovascular system using ECG Simulator Scientech 2352A. (In Simulation Mode) Equipments needed: 1. ECG cum Heart Rate Monitor Scientech 2351 2. 12 lead ECG Simulator Scientech 2352A 3. DSO ( RIGOL DS 1102C 100MHz 400 MSa/s or equivalent) 4. ECG connector cable 5. Real Time ECG Analysis Software 6. USB Cable (male to male A type) Procedure: 1. Connect one end of the Power Supply to ECG cum Heart Rate Monitor Scientech 2351, while other end to mains Power Supply 2. Switch ON the Mains Power Supply, then Scientech 2351 TechBook 3. Before monitoring the Heart-rate of human body the Count/Reset selection switch on Scientech 2351 should be in Reset mode to allow the Heart-rate Monitor to start measuring from beginning (Reset value) and to reset the one minute timer 4. The Display mode provided at front panel of Scientech 2351 displays either Heart rate or Tachycardia limit or Bradycardia limit depending upon their selection. Initially in case of Heart-rate it will give Reset value indication, and if Tachycardia limit or Bradycardia limit is selected then it will display their present value 5. Now make connections as in any of the standard bipolar leads configuration (Lead I, Lead II, and Lead III, it is recommended to use Lead II for better accuracy) properly on Scientech 2352A and connect the cables to the kit. 6. Select Count Mode using Count/Reset selection switch and observe each heartbeat executed by the subject (human body) with in one minute duration. One minute duration is indicated by one minute timer LED 7. Observe the Heart-rate displayed on the LCD 8. To test the Tachycardia conditions, select the Tachycardia limit mode using mode selection switch so that the display mode comes to display current Tachycardia limit with LED indication 9. Set the Tachycardia limit by adjusting the Limit adjustment potentiometer (preferable to set 100 heartbeats per minute) 10. Set the Bradycardia limit by adjusting the Limit adjustment potentiometer (preferable to set 40 heartbeats per minute) and then returns to Heart-rate mode by selecting it Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 30 Scientech 2351 11. Select Reset mode, before counting current Heart-rate in Count Mode 12. Rotate ECG Pulse-rate adjustment control on ECG Simulator Scientech 2352A to vary the pulse rate, Whenever the rate exceeds than the current Tachycardia limit, or less than the current Bradycardia limit, the out of control visible indications are given by Tachycardia LED and Bradycardia LED Conclusions: 1. Selected Lead configuration wave form is coming properly in appropriate shape 2. Tachycardia and Bradycardia results shown by hardware and software is same 3. As we are changing the values of tachycardia and bradycardia limits, the result is shown by the TechBook kit changing according to the set value Questions: 1. What are the standard values of Tachycardia and bradycardia in adult male? 2. What is Atrial Flutter and Fibrillation? Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 31 Scientech 2351 Frequently Asked Questions 1. What is the Anatomy of the human heart? The heart is basically a hollow muscular pump, which pushes the blood through out the body via the blood vessels. It is located between the lungs and slightly to the left of centre. 2. How many contractions heart have? The heart is an involuntary muscle that has approximately seventy to ninety contractions per minute during a restful state. It begins to pump early in the life of a fetus and will continue unceasingly until death. 3. In how many layers heart wall is divided, name them? The heart wall is divided into three layers: 4. • Pericardium • Myocardium • Endocardium How chamber is sub divided? The heart is divided by a partition or septum into two halves. The halves are in turn divided into chambers. The upper two chambers of the heart are called atria and the lower two chambers are called ventricles. 5. How many chambers does heart have? The heart has four distinct chambers. 1. Right atrium is the thin-walled area that receives the venous or "used" blood returning to the body by the veins. 2. Right ventricle is the "pump" area of the heart's right side. The atrium dumps the blood into the ventricle where it is then pumped out the pulmonary arteries and to the lungs. 3. Left atrium receives the oxygenated blood returning from the lungs. 4. Left ventricle has the thickest walls of all. It is from this chamber the blood is pumped out of the heart, into the aorta and out to the rest of the body. 6. How many types of heart valves are there? There are four types of heart valves which are as follows: a. Tricuspid Valve: is the one located at the entrance of the right ventricle. It prevents the blood from washing back into the right atrium. b. Pulmonary Semi Lunar Valve: is located between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery. Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 32 Scientech 2351 7. c. Mitral Valve: is made of very heavy cusps and is located at the entrance of the left ventricle. This is a powerful valve that closes as the left ventricle begins each of its contractions to ensure the oxygenated blood doesn't re-enter the left atrium. d. Aortic Valve: is located, as its name would imply, between the left ventricle's exit and the aorta itself. How right ventricle and left ventricle works? As the right ventricle contracts and sends blood to the lungs, the left ventricle contracts and squeezes blood out to the body. 8. What is systole and diastole? Systole occurs when the ventricles contract, and diastole when they relax. One complete contraction and relaxation of the heart muscle makes up one heartbeat. 9. How many components heart conduction system have? There are four basic components to the heart's conduction system. 10. i. Sinoatrial node (SA node) ii. Inter-nodal fibre bundles iii. Atrioventricular node (AV node) iv. Atrioventricular bundle What is the function of natural pacemaker? A natural pacemaker generates electrical impulses at regular rate. To initiate the heartbeat the action potentials generated by the natural pacemaker or S.A. node gets propagated in all directions along the surface of both atria and atrioventriculer node. 11. What is the full form of ECG? Electrocardiogram 12. How the electrical activity of heart can be sensed? This electrical activity generated by the heart can be measured by an array of electrodes placed on the body surface. 13. What P wave represents? The P wave represents the wave of depolarization that spreads from the SA node throughout the atria, and is usually 0.08 to 0.1 seconds (80-100 ms) in duration. 14. What QRS complex represents? The QRS complex represents ventricular depolarization. The duration of the QRS complex is normally 0.06 to 0.1 seconds. This relatively short duration indicates that ventricular depolarization normally occurs very rapidly. 15. What T wave represents? Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 33 Scientech 2351 The T wave represents ventricular repolarization and is longer in duration than depolarization (i.e., conduction of the repolarization wave is slower than the wave of depolarization). 16. How much time period is required to complete one cycle by the heart? The total time required for one complete cycle of the heart electrical activity ranges from approximately 0.4 to 0.6 second. 17. Define heart rate? The Heart-rate is a rate at which the heart beats per minute. 18. How the heart rate is controlled? It is controlled by the frequency at which the natural pacemaker generates electrical pulses. 19. What is the heart rate for various human beings? The bigger a person is, the slower the heart rate. A newborn baby's heart beats about 120 times per minute. The typical rate for adults is 72 beats per minute. But doctors consider resting rates from 60 to 100 beats per minute within the normal range. 20. To measure the ECG signals where the electrodes are placed on human body? To record the ECG pattern of a subject (human body) it is necessary to apply ECG metal electrodes to the patient's limbs in special formats called leads, on each arm and leg, and six electrodes are placed at defined locations on the chest. 21. How electrical signals are generated through the heart? As the heart undergoes depolarization and repolarization, the electrical currents that are generated and spread not only within the heart, but also through out the body. 22. How the electrical current is measured from the heart? The electrical activity generated by the heart can be measured by an array of electrodes placed on the body surface. 23. How different waves are generated? The different waves that comprise the ECG represent the sequence of depolarization and repolarization of the atria and ventricles. 24. What ‘P’ wave represent? The ‘P’ wave represents the wave of depolarization that spreads from the SA node throughout the atria. 25. What is the duration of ‘P’ wave? The duration is usually of 0.08 to 0.1 seconds (80-100 ms). 26. What ‘QRS’ complex represents? Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 34 Scientech 2351 The QRS complex represents ventricular depolarization. 27. What is the duration of ‘QRS’ wave? The duration of the QRS complex is normally 0.06 to 0.1 seconds. 28. What short duration indicates in ‘QRS’ wave? The relative short duration indicates that ventricular depolarization normally occurs very rapidly. 29. What ‘T’ wave represents? The T wave represents ventricular repolarization and is longer in duration than depolarization 30. What is the duration of ‘T’ wave? Typically the total time required for one complete cycle of the heart electrical activity ranges from approximately 0.4 to 0.6 second. 31. What is the standard value of one complete cycle for ‘T’ wave? 0.8 seconds is the standard value of one complete heart cycle. 32. What ‘T’ wave represents? This U wave represents the state of heart when all four chambers of heart receive the blood generally this wave is not present in the normal ECG graph. 33. Which type of activity is held during ‘P’,’QRS’ and ‘T’ wave? During a normal sinus rhythm, the atria are contracting first (around the time of the P wave), and the ventricles contract second (around the time of the QRS complex). Ventricular relaxation occurs around the time of the T wave. 34. What heart's electrical axis refers? The heart's electrical axis refers to the general direction of the heart's depolarization wave front (or mean electrical vector) in the frontal plane. 35. What is the orientation of heart's electrical axis? It is usually oriented in a right shoulder to left Leg direction, which corresponds to the left inferior quadrant of the hex axial reference system, although -30o to +90o is considered to be normal. 36. What the electric axis of the heart usually denotes? The concept of the electric axis of the heart usually denotes the average direction of the electric activity throughout ventricular (or sometimes atrial) activation. 37. What is the range of electric axis? The normal range of the electric axis lies between +30° and -110° in the frontal plane and between +30° and -30° in the transverse plane. The direction of the electric axis may be approximated from the 12-Lead ECG by finding the Lead in Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 35 Scientech 2351 the frontal plane, where the QRS-complex has largest positive deflection. The direction of the electric axis is in the direction of this Lead vector. The result can be checked by observing that the QRS-complex is symmetrically biphasic in the Lead that is normal to the electric axis. 38. What the deviation of the electric axis to the right indicates? Deviation of the electric axis to the right is an indication of increased electric activity in the right ventricle due to increased right ventricular mass. 39. Due to which types of diseases the deviation of the electric axis to the right occurs? This is usually a consequence of chronic obstructive lung disease, pulmonary emboli, certain types of congenital heart disease, or other disorders causing severe pulmonary hypertension and corpulmonale. 40. What the deviation of the electric axis to the left indicates? Deviation of the electric axis to the left is an indication of increased electric activity in the left ventricle due to increased left ventricular mass. 41. Due to which types of diseases the deviation of the electric axis to the left occurs? This is usually a consequence of hypertension, aortic Stenosis, ischemic heart disease, or some interventricular conduction defect. 42. What is the amplitude of ‘P’ wave? Amplitude 43. : 0.25mV What should be the dimensions of ‘P’ wave? The P wave in general should not be more than 1 box wide or 1 box tall. If it exceeds these, it generally means that either or both atria is enlarged (hypertrophied). 44. What are the characteristics of ‘P’ wave? Positive deflection of P wave greater than 1 box wide or 1 box in height indicates right atrial hypertrophy Negative deflection of P wave greater than 1 box wide or 1 box in depth indicates left atrial hypertrophy. 45. What is the duration of PR-Interval? Duration: 180-220 m sec The distance from the beginning of the P wave to the beginning of Q wave is PR interval. It’s a period from the beginning of atria depolarization to the beginning of ventricular depolarization. 46. What is PR-segment? It is the distance from end of the P wave and beginning of Q wave. 47. What is the duration of PR-segment? Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 36 Scientech 2351 Duration: 0.01 sec (approximately) 48. What is the amplitude of Q wave? Amplitude 49. : 0.2 mV What normal Q wave represents? Normal Q waves are small, less than 1 mm deep or wide and one fourth the height of their R wave. 50. When Q wave Develops? Pathological Q waves usually develop when ST segments are elevated and appear several hours or days after the clinical manifestations of the Myocardial Infarction. 51. What abnormal Q wave represents? Abnormal Q must be one Small Square (0.04 sec) wide and greater than onethird of QRS height in Lead III. Myocardial infarction causes pathological Q waves over the affected area of the ventricle. The age of the infection can be determined. If only Q wave is present without elevated ST segment then it indicates old infarction while if ST segment is there (with or without T wave inversion) then it indicates acute infraction. Q waves with inverted T waves may indicate undetermined age. 52. What is the amplitude of ‘R’ Wave? Amplitude 53. : 1mV What ‘R’ wave represents? R wave is the largest wave of the ECG graph and it is always above iso electric line, No such thing as a "negative R-wave" exists. 54. What is the amplitude of ‘S’ Wave? Amplitude 55. 0.4 - 0.5 mV What is the amplitude of ‘QRS’ Complex? Amplitude 56. : : 1.5mv What is the duration of ST-Segment? Short segment from end of S wave to beginning of T wave and has duration of about 0.07 sec. 57. What is the amplitude of ‘T’ Wave? Amplitude : 0.1 - 0.5 m sec Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 37 Scientech 2351 58. What normal ‘T’ waves represents? Normal T waves are in the same direction as their complex, wave is asymmetrical and it peaks toward the end, instead of the middle. Normal T wave in frontal plan is about 5 mm and in precordial plane 10 mm tall. 59. What is the duration of ST-Interval? Period from end of S wave to end of T wave and has the duration of about 0.20 0.27 m sec. 60. What QT-Interval represents? It is the interval from beginning of Q wave to end of T wave, or we can say this is the period from beginning of ventricular depolarization to the end of repolarization. 61. What is the duration of QT-Interval? It has the duration of about 0.26 - 0.49 m sec. 62. What RR-Interval represents? This is the distance between QRS-complexes. Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 38 Scientech 2351 Warranty 1. We guarantee this product against all manufacturing defects for 24 months from the date of sale by us or through our dealers. 2. The guarantee will become void, if a. The product is not operated as per the instruction given in the Learning Material. b. The agreed payment terms and other conditions of sale are not followed. c. The customer resells the instrument to another party. d. Any attempt is made to service and modify the instrument. 3. The non-working of the product is to be communicated to us immediately giving full details of the complaints and defects noticed specifically mentioning the type, serial number of the product and date of purchase etc. 4. The repair work will be carried out, provided the product is dispatched securely packed and insured. The transportation charges shall be borne by the customer. Hope you enjoyed the Scientech Experience. List of Accessories Quantity ● ECG Electrodes (Clamp type)......................................................................5 ● ECG electrode Gel........................................................................................1 ● 5 Pin din to 3 Banana Cable (2mm)..............................................................1 ● USB Cable (male to male)............................................................................1 ● Power Supply................................................................................................1 Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 39