* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
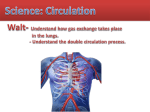
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Study Guide: 1.) List 4-5 components of a good experiment? Question/ or problem Hypothesis (if, then because) One Independent and dependent variables Constants (things that stay the same through whole experiment) Large sample size Control 2.) Difference between Qualitative (quality) and Quantitative (quantity) data? Qualitative data – description or can be observed (red flower, blue sky) QuaNtitative – N= number (the flower is 5 inches tall, we did 3mins of exercise in feel the beat) 3.) Using Feel the beat identify the IV, DV and Constants In the feel beat exp. independent variable- was the exercise dependent variable- was pulse rate constant – amount time you did the exercise for the exercise sample size/number of trials location of pulse fingers used to check pulse 4.) Main ideas/results from Dr. Goldbergers exp on pellagra Nutritional Deficiency. Their diet was lacking in vitamins which lead them to become sick with pellagra. (poor diet) ** developed a good experimental method to test his ideas 5.) Function of sensory neurons Neurons that gather (sense) information from the environment around you You touch a hot stove, sensory neurons send the signal of “hot” to your brain(interneurons) and then motor neurons move your hand away from the stove 6.) Four main functions of skeletal system Bone marrow produces red/white blood cells, stores minerals Protection (protects your soft and squishy organs) Support (gives you shape- no skeleton = blob) Movement- allows you to walk etc… 7.) Compare/contrast ligaments and tendons Tendon- muscle to bone Ligament –bone to bone 8.) 3 types of muscles Smooth- found in organs (involuntary) Cardiac-found only in heart (involuntary) Skeletal – moves us (arms, legs) biceps/triceps 9.) Main function of circulatory system To transport oxygen (nutrients) around body and pick up carbon dioxide (waste) to be exhaled. Heart pumps blood around body. An important FUNCTION IS TO TRANSPORT NUTRIENTS TO OTHER PARTS OF YOUR BODY. The heart is like two separate pumps bc the right side pumps deoxygenated blood out to the lungs and the left side pumps oxygen rich blood through body….. Right side to lungs (co2 Left side To body (O2) 10.) 3 types of blood vessels Arteries carry blood Away from heart Veins – blood back IN to heart Capillaries- smallest blood vessels, where gas exchange takes place. 11.) List the Organs in respiratory system Nose/ mouth Trachea (wind pipe) lungs Bronchi tubes Bronchioles Alveoli (capillaries wrapped around) 12.) Gas exchange in respiratory system… Breathe in air (oxygen) goes down trachea to lungs into alveoli where it diffuses into the capillaries so oxygen can get into the blood then the heart pumps the oxygen rich blood around the body. Blood picks up co2 (waste) and it diffuses back across capillaries and you breathe it out. 13 & 14.) What is the order of organs in digestive system and chemical/ mechanical breakdown Mouth (chemical: saliva and mechanical -teeth breakdown), down esophagus (muscles= mechanical), Stomach (chemical –acid, mechanical-muscles squeeze), small intestine (absorbs nutrients-chemical), large intestine (remove water to produce solid wastemechanical), rectum, anus extra (liver- chemical, pancreas- chemical) 15.) Order of organization in human body Organelle---cell--- tissue---organ--- organ system--- organism 16.) what is pulse? How does it change during exercise? Pulse is the number of times your heart beats in a period of time (BPM’s). When you exercise your muscles need/use more oxygen (and to remove more co2) so your heart beats faster and you breath increases to help send oxygen around your body. 17.) trade off with microscopes As you increase magnification you have more detail BUT you can only see a smaller area of the object and it may be harder to find microbes 18.) Four common organelles Nucleus: Control center of cell, contains DNA or genetic information Mitochondria: power house of cell, makes energy using cellular respiration Cell wall: found only in plant cells, provides support for cell (square shape) Cell membrane: selectively permeable, controls what goes in and out of cell Cytoplasm; holds organelles in place –jelly like 19.) compare and contrast animals vs bacteria Animal: Eukaryotes (have a nucleus and organelles) Round/ irregular shape, more complex , specialized cells, unicellular or multicellular bacteria : prokaryotes, no nucleus, free floating dna simple, small, individualized cells * unicellular only asexually reproduce both: have cell membranes and cytoplasm 20.) single cell vs multi cell Single : bacteria, amoeba, yeast- shorter life, independent (don’t need any other cells to do their job), simpler, small Multi cell: human, plant, animals- larger, more complex, live longer, dependent on other cells to complete function, ** review old study guides!!