* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Product-use variables How a group member uses a good
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
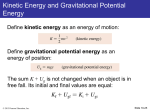
Chapter 12 Understanding Marketing Processes and Consumer Behaviour Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 12-1 Learning Objectives Explain the concept of marketing Explain the purpose of a marketing plan and identify the four components of the marketing mix Explain market segmentation and show how it is used in target marketing Explain the purpose and value of market research Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 12-2 Learning Objectives Describe the key factors that influence the consumer buying process. Describe the international and small business marketing mixes. Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 12-3 Marketing Marketing Planning and executing the development, pricing, promotion, and distribution of ideas, goods, and services Value Relative comparison of a product’s benefits versus its costs Utility Ability of a product to satisfy a human want or need Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 12-4 Goods, Services, and Ideas Consumer goods Products purchased by individuals for their personal use Industrial goods Products purchased by companies to use directly or indirectly to produce other products Services Intangible products, such as time, expertise, or an activity that can be purchased Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 12-5 Relationship Marketing A type of marketing that emphasizes lasting relationships with customers and suppliers Stronger relationships can result in greater long-term customer satisfaction and client retention Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 12-6 The Marketing Mix Marketing mix The combination of product, pricing, promotion, and place (distribution) strategies used in marketing a product Also known as the four P’s of marketing Marketing plan A detailed strategy for gearing the marketing mix to meet consumer needs and wants Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 12-7 Choosing the Marketing Mix Product Price The basic design of the product How much consumer pays Place Where and when the product is + Promotion = Product image and visibility Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education Canada Inc. Customer Satisfaction Business Profitability 12-8 Product Product A good, service, or idea that satisfies the buyers’ needs and demands Product differentiation The creation of a product or product image that differs enough from existing products on the market to attract consumers Mass customization Providing thousands of customers with exactly the products they want Dell Computers Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 12-9 Price Price Choosing the right price to meet the firm’s profit objectives and buyers’ purchasing objectives May be low price strategy (salt) or high price strategy (mink coat) Price must consider all costs operation and administration marketing research advertising Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 12-10 Promotion Choosing the right method of selling the product to the consumer Promotional tools Advertising Personal selling Sales promotions Publicity Public relations Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 12-11 Place (Distribution) The part of the marketing mix concerned with getting products from producer to buyer Physical transportation Choice of sales outlets Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 12-12 Target Market and Segmentation Target market A group of potential customers who have similar wants and needs Segmentation Dividing a consumer market into categories Selecting specific market segment(s) to pursue Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 12-13 Identifying Market Segments • Search for common traits or behaviours that will affect the purchasing decision •Geographic variables •Country, region, neighbourhood •Demographic variables •Age, income, gender, ethnic background, marital •Psychographic variables •Psychological traits that a group has in common (motives, attitudes, activities, opinions) •Product-use variables •How a group member uses a good (athletic, casual) Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 12-14 Geographic Variables Area of residence affects product consumption Rainfall and umbrellas Snowfall and snowmobiles or snow blowers Hot summers and backyard pools Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 12-15 Demographic Variables Age Gender Marital Status Religion Income Family Size Ethnicity Language Education Occupations Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 12-16 Psychographic Variables Psychological traits: Attitudes Interests and hobbies Opinions Motivations Activities Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 12-17 Behavioural Variables Occasion for use Benefits sought Reasons for purchasing Loyalty level Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 12-18 Market Research The systematic study of what buyers need and how best to meet those needs Focuses on the marketing mix elements Leads to more effective marketing Increases the accuracy and effectiveness of market segmentation Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 12-19 The Research Process Study the Current Situation Select a Research Method Collect Data Analyze Data Focus Group Use Secondary Data Prepare Report Survey Use Primary Data Make Recommendations Observation Experimentation Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 12-20 Observation Viewing or monitoring human behaviour Useful for cases where actions occur automatically without thinking Grocery shopping May be human observation or technological Supermarket scanners Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 12-21 Survey Administration of a questionnaire, a list of questions, to prospective buyers Relies on a reliable random sample Administered in person, via phone, mail, or the internet Key issues include choosing appropriate questions and ensuring honest answers Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 12-22 Focus Group A small discussion group of prospective customers or product users Allows in-depth discussion of complex or subjective issues regarding products or services Usually a blind research study where participants do not know who the sponsor of the group is Researchers analyze the results by searching for common themes in participants’ feedback Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 12-23 Experimentation A controlled research design allows the determination of how consumers react to specific situations or appeals The situations can be manipulated to compare responses to such things as shelf placement of products, package colours and design, advertising strategy Very costly Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 12-24 Consumer Behaviour The study of the processes by which customers come to purchase and consume a product or service Influenced by Psychological factors Personal factors Social factors Cultural factors Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 12-25 The Consumer Purchase Process Personal & Environmental Marketing Factors Product Purchase Process Factors Problem Recognition Information Seeking Price Place Promotion Evaluation of Alternatives Purchase Decision PostPurchase Evaluation Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education Canada Inc. Psychological Personal Social Cultural 12-26 International Marketing Mix Products may require substantial change before they can be marketed to different countries Pricing requires consideration of product manufacturing costs, transportation and delivery Promotion must accommodate cultural differences and social traditions Distribution may involve cooperation with other international firms and adherence to foreign packaging and labelling legislation Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 12-27