* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 7.4 Notes Deformation of the Earth`s Crust *Deformation
Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Great Lakes tectonic zone wikipedia , lookup
Baltic Shield wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
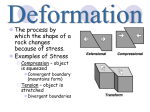
Chapter 7.4 Notes Deformation of the Earth’s Crust *Deformation: any stress (pushing or pulling) on the crust which changes the volume/shape of crust Two types of deformation 1. tension: stress when forces stretch an object 2. compression: stress when an object is squeezed *Folding: bending of rock layers b/c of stress Types of folding 1. anticlines: a fold in rock that bends upward into an arch 2. syncline: a fold in rock that bends downward in the middle 3. monocline: folded rock layers where both ends of the fold are horizontal *Faulting: occur along plate boundaries where rocks break & slide past each other Three types of faults 1. Normal Faults: occur when tectonic forces cause tension that pulls rocks apart & hanging wall slips downward past the footwall 2. Reverse Faults: happen when tectonic forces cause compression that pushes rocks together & hanging wall slides up & over the footwall. 3. Stike-Slip Fault: form when opposing forces cause rock to slip past each other sideways with little up/down motion. Ex. San Andres Fault in CA. *When tectonic plates undergo compression or tension, they form mountains several ways: 1. Folded Mountains: form at convergent boundaries where continents collide. Ex. Appalacian Mts. formed when N. Amer. & Africa collided. 2. Fault-Block Mountains: occur when tension causes large blocks of crust to drop down. Ex. Tetons in Wyoming 3. Volcanic Mountains: located at convergent boundaries where oceanic plates sink at subduction zones & under the sea to sometimes cause islands. Ex. majority of volcanic mts. are formed around rim of Pacific Ocean Ring of Fire. *Two types of vertical movement in the crust: 1. Uplifting of Depressed Rock: -rising of regions of the crust to higher elevations. *Mountains form or areas rise or rebound when weight on it is removed. 2. Subsidence of Cooler Rocks: -sinking of regions of crust to lower elevations. *when lithosphere is hot, it takes up more space at mid-ocean ridge *lithosphere away from ridge is cooler, takes up less space, & is denser, so oceanic lithosphere crust subsides.