* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transpiration - Don`t Trust Atoms
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
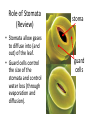
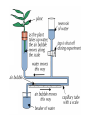
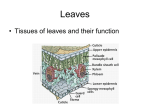
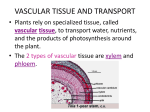
Starter How are the following tissues adapted for their function? Tissue Epidermal Palisade Mesophyll Spongy Mesophyll Function Adaptation Transportation In Plants • The roots, stem, and leaves form a plant organ system for the transport of substances around the plant. Vascular Tissues: Phloem and Xylem Read pg. 85 and make a note of the similarities and differences between xylem and phloem. Phloem Type of Cell Between Cells (Type of End Walls) Materials Transported Direction of Transport Name of transport process Diagram Xylem Phloem Xylem Type of Cell Elongated living cells Between Cells (Type of End Walls) End walls with small pores Dead cells strengthened with lignin No end walls Materials Transported Dissolved food substances (sugars) Both directions Water and minerals translocation Transpiration stream Direction of Transport Name of transport process Diagram Upwards (root to stem and leaves) Transpiration • Transpiration = loss of water from a plant • Transpiration stream = movement of water from the roots to the leaves • Why does this happen? Like sucking liquid through a straw! Water evaporates and diffuses out (mainly through stomata) Creates a shortage of water, more water is drawn up through the xylem More water is drawn up through the roots creating a constant stream Roots • Function: absorption of water (by osmosis) and mineral ions (by active transport). • Adaptations: contain root hair cells that create a larger surface area and speeds up osmosis and active transport. Factors Affecting Transpiration • Explain how each of these factors affect the rate (speed) of transpiration. (pg. 87) – Light intensity – Temperature – Air flow – Humidity Role of Stomata (Review) stoma • Stomata allow gases to diffuse into (and out) of the leaf. • Guard cells control the size of the stomata and control water loss (through evaporation and diffusion). guard cells Investigating Transpiration Rate • A potometer can be used to measure the rate of transpiration. Calculating Rate of Transpiration Rate of transpiration = 𝑑𝑖𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑐𝑒 𝑎𝑖𝑟 𝑏𝑢𝑏𝑏𝑙𝑒 𝑚𝑜𝑣𝑒𝑑 𝑡𝑖𝑚𝑒 Homework • Answer the exam style questions on pg. 93-94.