* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ATP: The Main energy carrier
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
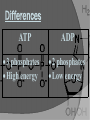
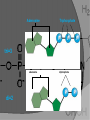
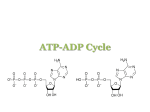
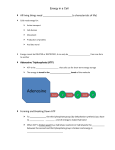
Macromolecule: Nucleic Acid Organelle: Mitochondria Main Function: Energy: Carries chemical energy that calls can use. Comes from: Breakdown of food molecules. Structure: Made up of adenine, ribose, and three phosphates Adenine Ribose 3 Phosphates •Third bond is very weak. When removed, energy is released and becomes ADP. Adenosine Diphosphate. Differences ATP 3 phosphates High energy ADP 2 phosphates Low energy Adenosine Triphosphate tri=3 adenosine di=2 diphosphate How do we get back to ATP?_________ phosphate removed Fats store the most energy. – 80 percent of the energy in your body – about 146 ATP from a triglyceride • Proteins are least likely to be broken down to make ATP. – amino acids not usually needed for energy – about the same amount of energy as a carbohydrate Carbohydrates are the molecules most commonly broken down to make ATP. – not stored in large amounts – up to 36 ATP from one glucose molecule What if there isn’t any sunlight? Of course it all starts with photosynthesis, and then organisms take it in via cellular respiration. Chemosynthesis: Process by which some organisms use chemical energy, instead of light energy, to make their own food. Where does this occur? In the deep sea of course, near hydrothermal vents!