* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 4: Database Management
Expense and cost recovery system (ECRS) wikipedia , lookup
Operational transformation wikipedia , lookup
Data center wikipedia , lookup
Data analysis wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Concurrency control wikipedia , lookup
3D optical data storage wikipedia , lookup
Versant Object Database wikipedia , lookup
Information privacy law wikipedia , lookup
Business intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Data vault modeling wikipedia , lookup
Open data in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
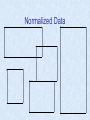
Database Management Chapter 4 Chapter Objectives • Describe why databases have become so important to modern organizations • Describe what database and DBMS are and how they work • Explain four emerging database trends: – Client-server computing – Object-oriented databases – Data mining – Integrating Web applications Database Management for Strategic Advantage • We live in the Information Age • Information used to make organizations more productive and competitive • Databases used to support business operations Databases Before the Use of Computers • Data kept in books, ledgers, card files, folders, and file cabinets • Long response time • Labor-intensive • Often incomplete or inaccurate The Database Approach • Database-management system (DBMS) – Interact with the data in databases • Entity: something you collect data about • Field: one characteristic of an entity • Record: collection of fields that describe one occurrence of an entity • Entities stored in tables – One record per row – One field per column Sample Data Table The Database Approach • DBMS replaced file processing approach – Reduced data redundancy – Reduced program dependence • Databases typically consist of several tables • Tables can be linked together Key Database Issues and Activities • Entering and Querying Data • Creating Database Reports Entering and Querying Data • Use a form for data entry • Use queries to retrieve information – Structured Query Language (SQL) – Query by example (QBE) Preprinted Form Application For Employment Pine Valley Furniture Personal Information Name:Date: Social Security Number: Home Address: City, State, Zip Home Phone:Business Phone: U.S. Citizen?If Not, Give Visa No. & Expiration: Position Applying For Title:Salary Desired: Referred By:Date Available: Education High School (Name, City, State): Graduation Date: Business or Technical School: Dates Attended:Degree, Major: Undergraduate College: Dates Attended:Degree, Major: Graduate School: Dates Attended:Degree, Major: Pine Valley Furniture Computer-Based Form QBE Grid Creating Database Reports • Report – A compilation of data organized and produced in printed format • DBMS packages include a report writer • Graphics can be added • Can be automatically updated by linking to data Sample Quarterly Sales Report Data Structure • Data model – A representation of the entities and their relationships • Primary key – An attribute or combination of attributes – Uniquely identifies each record Data Type • Each field is assigned a type – Text, number, date, etc. • Data types help the DBMS – Organize and sort the data – Do calculations – Allocate space • Data dictionary – A repository of information about the data – Key fields, data types, valid values, etc. Database Management Systems Approaches • Models of the relationship between entities in a database – Hierarchical – Network – Relational The Hierarchical Model • Models entities in a parent-child relationship • One-to-many relationships – Parent entities can have many child records – Each child can have only one parent • Inadequate model for many databases – Not always clear which entity is the parent and which is the child The Hierarchical Model The Network Model • More flexible than the hierarchical model • Many-to-many relationships – Allows multiple children and parents • Complex databases become too cumbersome with this model The Network Model The Relational Model • Views entities as two-dimensional tables – Records are rows – Attributes are columns • Tables can be linked • Supports one-to-many, many-to-many, and one-to-one relationships The Relational Model Normalization • A technique used to make complex databases more efficient • Break one large table into several smaller tables – Eliminates all repeating groups in records – Eliminates redundant data Redundant Data Normalized Data Associations • Relationships among the entities in the data structures • Three types – One-to-one – One-to-many – Many-to-many • Relationships set by placing primary key from one table as foreign key in another – Creates “acceptable” redundancy Recent Developments Affecting Database Design and Use • Databases and Client-Server Computing – Server holds the actual database – Clients hold software to work with the database • Object-Oriented Databases (OODBs) – Treat tables, queries, etc., as reusable objects Client/Server Database Recent Developments Affecting Database Design and Use • Data Mining (On-Line Analytical Processing) – Drill down from summary data to detailed data – Data Warehouses/Data Marts • Integrates many large databases into one repository • Linking Web Site Applications to Organizational Databases – Users have Web view to organizational database – Improves customer contact and service – Adds security as a concern Effective Management of Databases • Database Administrator (DBA) – Responsible for the development and management of an organization’s databases • Works with systems analysts on design • Works with users and managers on managerial and organizational issues • Responsible for implementing security features