* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
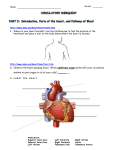
Lab 5 Anatomy of Blood Vessels Dissection of the Blood Vessels of the Cat Examining the Microscopic Structure of Arteries and Veins. Use Text Figure 21-1 Locating Arteries and Veins on a figure or the torso. Use figures in text, Chapter 21 Figures are also available on Canvas. Refer to Lab Exam 1 Review Sheet for arteries and veins. Cat Dissection Directions 1. Getting Ready Clear the lab bench except for one set of directions and the review sheet for the first lab exam. The review sheet lists what you need to know for the exam. Go to the side table and select the following dissection tools: Scissors Forceps Scalpel Several blunt probes Select goggles from the sterilizing cabinet and gloves from the side table. Only students who plan to touch the cat need to wear gloves. You should all wear goggles. Obtain a cat in a sealed plastic bag and a large metal dissecting pan. Cut off a corner of the plastic bag and drain the excess fluid into the bucket near the sink. Remove the cat from the bag and put it on the tray, ventral side up. Discard the bag in the trash. You will be given a new bag to store the cat. 2. Opening the Ventral Cavity Using the sharp point of the scissors, cut into the cat’s skin and underlying musculature starting just above the pubic bone at the midline of the body. See Figure 1. Cut along the midsagittal line to the diaphragm. Make lateral cuts at the point of incision and just below the diaphragm so you can open up the abdominopelvic cavity. Continue the cut up through the thorax, angling toward the right or left to avoid the cat’s sternum. Above the sternum return the cut to the midline. Cut high up into the area under the cat’s jaw. Make lateral cuts just above the diaphragm to open up the thoracic cavity. Figure 1. 3. Initial Organ Identification a. Thoracic Cavity thymus gland – large mass of tissue on the anterior trachea and heart remove this after you have identified it trachea esophagus – deep to the trachea lungs heart diaphragm b. Abdominopelvic Cavity greater omentum – covering the organs of the abdominal cavity. Do NOT remove this, just push it aside. liver – large organ just below the diaphragm stomach – to the left of the liver small intestine – small diameter large intestine – large diameter spleen – large lymphatic system organ usually to the left and a bit below the stomach 4. Blood Vessels of the Cat Note: arteries are injected with pink latex and veins with blue latex on these cats. Using a blunt probe, push aside connective tissue to identify the right and left common carotid arteries running parallel to the trachea. Identify the small internal jugular veins next to the common carotid arteries. This is not present in some cats. Identify the large white vagus nerves that run along the common carotid arteries Remove the pericardium from the heart and identify the aorta and the pulmonary trunk. Follow the aorta and locate the large brachiocephalic artery and the left subclavian artery. Pushing aside connective tissue, locate the three major branches of the brachiocephalic artery: the right subclavian artery and the right and left common carotid arteries. Push the lungs aside on the left and move connective tissue aside to see the aortic arch and the descending thoracic aorta Identify the precava or superior vena cava and post cava or inferior vena cava on the right side of the heart. The post cava travels through the diaphragm into the abdominal cavity. Follow the precava until it branches to form the right and left brachiocephalic veins. Follow a brachiocephalic vein to the branch of the large external jugular vein and the subclavian vein. In the abdominal cavity push aside the intestines and using the blunt probe, dissect out the inferior vena cava and the abdominal aorta. Notice the branches on both carrying blood from and to the viscera. Continue the dissection to reveal the external and internal iliac arteries and the common, external and internal iliac veins. Name____________________________ Lab Section ________________ Review Sheet Please turn in at next lab. 1. What vessel in the cat corresponds to the superior vena cava in humans? 2. What vessel in the cat corresponds to the inferior vena cava in humans? 3. Does the cat have a common iliac artery? _____ common iliac vein? _______ 4. Do humans have a common iliac artery? _____ common iliac vein? _______ 5. Contrast the origin of the common carotid arteries in the cat and the human. 4. Draw an artery and a vein from the slide you observed. Use colored pencils. Use the 10X or 40X lens for your drawing. Label lumen, tunica interna, tunica media, tunica externa. Print at end of leader line, use a ruler. Artery Total Magnification _____X Vein Total Magnification _____X List two differences that helped you to decide which is the artery and which is the vein. a. b. Complete this page before you come to Lab 6 – Blood. 1. Give the normal values of total blood counts (in mm3)for Erythrocytes ________________ Leukocytes ________________ 2. What is the normal range for a hematocrit? Men __________ Women ___________ 3. Give a unique characteristic of each of the blood cell types that can be observed with a microscope and will allow you to clearly distinguish among the cell types. For leukocytes, give the % of each in the leukocyte population. (1 point for each cell type) Neutrophil - % ___________ Unique characteristic______________________________________________ Lymphocyte - % ___________ Size relative to a neutrophil _____________ Unique characteristic______________________________________________ Monocyte - % ___________ Size relative to a neutrophil _____________ Unique characteristic______________________________________________ Eosinophil - % ___________ Size relative to a neutrophil _____________ Unique characteristic – use granules here_______________________________ Basophil - % ___________ Size relative to a neutrophil _____________ Unique characteristic – use granules here_______________________________ Erythrocyte Size relative to a neutrophil _____________ Unique characteristic______________________________________________ For the Lab Exam Identify on figure in text or lab manual: o artery o capillary o capillary network o endothelium o external elastic lamina o internal elastic lamina o lumen o o o o o o Slide of artery and vein: o artery o vein o lumen o tunica interna o tunica media o adventitia Identify the following arteries and veins on torso: o aortic arch o ascending aorta o gonadal vein o brachiocephalic artery o brachiocephalic vein o celiac trunk or artery o common carotid artery o common iliac artery o common iliac vein o descending abdominal aorta o descending thoracic aorta o external iliac artery o external iliac vein o external jugular vein o gonadal artery subendothelial layer tunic intima tunica externa tunica media valve vein o inferior mesenteric artery o inferior vena cava o internal iliac artery o internal iliac vein o internal jugular vein o pulmonary artery o pulmonary trunk o pulmonary vein o renal artery o renal vein o subclavian artery o subclavian vein o superior mesenteric artery o superior vena cava Using Figures in text or lab manual, identify the following arteries: o o o o Abdominal aorta Anterior tibial Arcuate Axillary o o o o Basilar Brachial Brachiocephalic Common carotid o o o o o o o o o o o Common hepatic Common iliac Deep femoral Descending aorta External carotid External iliac Facial Femoral Fibular Gonadal Inferior mesenteric o o o o o o o o o o o Internal carotid Internal iliac Left gastric Radial Renal Right gastric Splenic Subclavian Superior mesenteric Ulnar Vertebral Using Figures in text or lab manual, identify the following veins o o o o o o o o o o o o Anterior tibial Basilic Brachiocephalic Common iliac Dorsal venous arch External iliac External jugular Femoral Fibular Gonadal Great saphenous Inferior vena cava o o o o o o o o o o o Internal iliac Internal jugular Median antebrachial Median cubital Radial Renal Small saphenous Subclavian Superior vena cava Ulnar Vertebral o o o o o o o o o External jugular veins Internal iliac artery Brachiocephalic veins Internal jugular veins Precava Postcava Common iliac vein External iliac veins Internal iliac vein General Cat Dissection and Cat Blood Vessels Identify the following on the cat dissection: o Heart o Lungs o Thymus o Brachiocephalic artery o Subclavian artery o Common carotid arteries o Descending aorta thoracic and abdominal o External iliac arteries