* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Characteristics of Stars
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
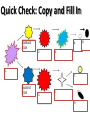
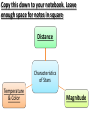
Characteristics of Stars Quick Check: Copy and Fill In 6. AVERAGE STAR 2. 4. 1. 7. MASSIVE STAR 3. 5. 9. 8. Quick Check: Copy and Fill In AVERAGE STAR 2. Red Giant 4. Planetary Nebula 6. White Dwarf 8. Black Dwarf 1. Nebula 7. Neutron Star MASSIVE STAR 3. Red Supergiant 5. Supernova 9. Black Hole Define a star: • A ball of plasma held together by its own gravity • Heat and light planets in a system (like our Sun) Define nuclear fusion: • Process of splitting a large atom into 2 or more atoms • When atom splits, energy is released • Stars turn hydrogen into helium Define main sequence stars: • Major grouping of stars • Form a narrow band from the upper left to the lower right when plotted according to luminosity and surface temperature on the Hertzprung-Russell Diagram Copy this down to your notebook. Leave enough space for notes in square Distance Characteristics of Stars Temperature & Color Magnitude Star Classification: Distance • Distance which a ray of light would travel in one year • Measured in light years (186,000 miles per second) Star Classification: Magnitude • Measurement of brightness • Two Types: – Apparent Magnitude: • How bright stars APPEAR to be from Earth – Absolute Magnitude: • Luminosity • How bright a star actually is Star Classification: Temperature & Color • Blue Star = Hot • Red Star = Cold • As temperature decreases, brightness decreases as well • O,B,A, F,G,K, M [Oh Be a Fine Girl, Kiss Me] Star Classification Chart HOT Bright Decreasing Temp. COLD Dim