* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 4 Powerpoint
Natural computing wikipedia , lookup
Computational complexity theory wikipedia , lookup
Factorization of polynomials over finite fields wikipedia , lookup
Algorithm characterizations wikipedia , lookup
Operational transformation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Lateral computing wikipedia , lookup
Simplex algorithm wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical computer science wikipedia , lookup
Multiple-criteria decision analysis wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Pattern recognition wikipedia , lookup
Planted motif search wikipedia , lookup
Time complexity wikipedia , lookup
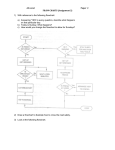
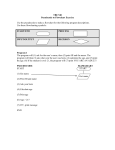
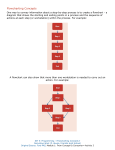
Mathematics for Computing Lecture 4: Algorithms and flowcharts Dr Andrew Purkiss-Trew Cancer Research UK [email protected] Algorithms An algorithm is a step-by-step set of instructions for solving a particular problem We will be using flowcharts to explore simple algorithms Flowchart Graphical representation of an algorithm Show the ‘layout’ of a program Form is a series of symbols linked with arrows Flowchart symbols 1 Terminator Data Entry (or Input/Output) Process Flowchart Symbols 2 Decision Preparation Connector 1 Flowchart example 1 Find the mean of two numbers Start Read X,Y Stop Sum = X+Y Mean = Sum / 2 Print Mean Flowchart example 2:1 Solve a quadratic equation ax2+bx+c = 0 Discriminant, D = b2-4ac, tells us how many real solutions. D <0 means no real solution, D=1 means 1 solution: x = -b/2a D>0 means 2 solns: x = -b ± √(b2 – 4ac) 2a Flowchart example 2:2 1 2 3 X = -B 2xA X1 = -B + √D 2xA X2 = -B - √D 2xA Start Print ‘No real solution Read A,B,C Print ‘solution’, X D = B2-4xAxC negative Sign of D? positive Stop zero 1 2 3 Print X1, X2 Pseudocode Algorithms can also be represented as ‘English language’ instructions. These are then converted to the relevant program code. Variables and Constants Variable Constants Numerical: Integer or exponential Non-numerical: Strings Logical: True or False Flowchart Symbols Terminal Decision Input / Output Connector Process Preparation