* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Power Transmission Elements II: Gears and Bearings
Machine (mechanical) wikipedia , lookup
Semi-automatic transmission wikipedia , lookup
Automatic transmission wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Bearing (mechanical) wikipedia , lookup
Air bearing wikipedia , lookup
Differential (mechanical device) wikipedia , lookup
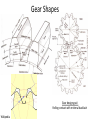
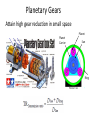
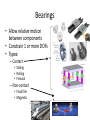
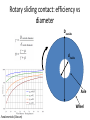
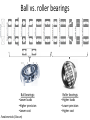
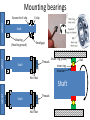
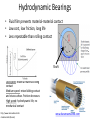
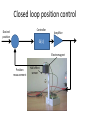
Power Transmission Elements II: Gears and Bearings Lecture 3, Week 4 Announcements • Lab 4 – need to finish by Friday – Friday lab can get started today • Project proposal – Due at 23:59 tonight – Email to us: [email protected], [email protected] • Group project meetings tomorrow • Kinematic couplings due tomorrow Outline • Gears • Bearings • Lab time Gears Rotating elements used to transmit torque or force Common usage – convert motor’s high-speed lowtorque output to low-speed high-torque output Gears in Nature Wikipedia Plant-hopper insect Issus has gear-like mechanism to synchronize legs when it jumps Gear Shapes Gear design goal: Rolling contact with minimal backlash Wikipedia Gear Trains Transmission ratio = #teeth of driving gear # teeth of driven gear What is the transmission ratio here from red to purple? Fundamentals, Slocum Gear Trains Transmission ratio = #teeth of driving gear # teeth of driven gear What is the transmission ratio here from red to purple? High torque Low speed Low torque High speed 9 9 67 1 𝑇𝑅 = ∗ ∗ = 0.065 = 38 67 33 16 Fundamentals, Slocum Important Terminology • Pitch Diameter – diameter of circle where teeth make contact • Module (“mod”) – Pitch diameter (mm) divided by #teeth [mm/tooth] • Pressure Angle – angle teeth make contact at • Pitch – 1/Module [teeth/mm] (“tooth density”) Fundamentals, Slocum How do you choose gear sizes? 1. Choose number and diameter of gears based on reduction ratio required and space constraints 2. Calculate forces at pitch diameter, and size teeth to withstand this force (with some safety factor) 3. Make sure meshing gears have the same module and pressure angle so teeth mesh correctly Buying Gears Mcmaster-carr.com Example – Force on Gear Teeth Is a mod 2, 20-tooth, 20degree pressure angle, 45mm OD, 10mm thick nylon gear adequate to transmit 10 Nm of torque? Example – Force on Gear Teeth Is a mod 2, 20-tooth, 20degree pressure angle, 45mm OD, 10mm thick nylon gear adequate to transmit 10 Nm of torque? 𝐷𝑝𝑖𝑡𝑐ℎ = 𝑚𝑜𝑑 #𝑡𝑒𝑒𝑡ℎ = 2 ∗ 20 = 40𝑚𝑚 Example – Force on Gear Teeth Is a mod 2, 20-tooth, 20degree pressure angle, 45mm OD, 10mm thick nylon gear adequate to transmit 10 Nm of torque? 𝐷𝑝𝑖𝑡𝑐ℎ = 𝑚𝑜𝑑 #𝑡𝑒𝑒𝑡ℎ = 2 ∗ 20 = 40𝑚𝑚 𝐹𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒𝑛𝑡 = 𝑇𝑜𝑟𝑞𝑢𝑒 10𝑁𝑚 = = 500𝑁 𝐷𝑝𝑖𝑡𝑐ℎ /2 20𝑚𝑚 Example – Force on Gear Teeth Is a mod 2, 20-tooth, 20degree pressure angle, 45mm OD, 10mm thick nylon gear adequate to transmit 10 Nm of torque? 𝐷𝑝𝑖𝑡𝑐ℎ = 𝑚𝑜𝑑 #𝑡𝑒𝑒𝑡ℎ = 2 ∗ 20 = 40𝑚𝑚 𝐹𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒𝑛𝑡 = 𝐹𝑛𝑜𝑟𝑚𝑎𝑙 𝑇𝑜𝑟𝑞𝑢𝑒 10𝑁𝑚 = = 500𝑁 𝐷𝑝𝑖𝑡𝑐ℎ /2 20𝑚𝑚 𝐹𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒𝑛𝑡 50𝑁 = = = 530𝑁 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜑 cos(20°) Example – Force on Gear Teeth Is a mod 2, 20-tooth, 20degree pressure angle, 45mm OD, 10mm thick nylon gear adequate to transmit 10 Nm of torque? 𝐷𝑝𝑖𝑡𝑐ℎ = 𝑚𝑜𝑑 #𝑡𝑒𝑒𝑡ℎ = 2 ∗ 20 = 40𝑚𝑚 𝐹𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒𝑛𝑡 = 𝐹𝑛𝑜𝑟𝑚𝑎𝑙 𝑇𝑜𝑟𝑞𝑢𝑒 10𝑁𝑚 = = 500𝑁 𝐷𝑝𝑖𝑡𝑐ℎ /2 20𝑚𝑚 𝐹𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒𝑛𝑡 50𝑁 = = = 530𝑁 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜑 cos(20°) 𝜎𝑡𝑜𝑜𝑡ℎ = 𝐹𝑛𝑜𝑟𝑚𝑎𝑙 530𝑁 = = 10.6𝑀𝑃𝑎 𝐴𝑡𝑜𝑜𝑡ℎ 10𝑚𝑚 ∗ 5𝑚𝑚 Nylon shear strength = 70 MPa Yes – with safety factor 7 Planetary Gears Attain high gear reduction in small space Planet Carrier Planet Sun Ring Planetary gears - animation https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UakeTEJlXGw Other Gears Bevel Gear Rack and Pinion Worm Transmit torque at 90 degree angle Rotary to linear motion Transmit torque at 90 degree angle Directindustry.com Science.howstuffworks.com How is this possible? Regular octahedron Irregular octahedron http://www.thingiverse.com/thing:748202 Differentials • Allows torque transmission to wheels rotating at different speeds https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gIGvhvOhLHU Bearings • Allow relative motion between components • Constrain 1 or more DOFs • Types: – Contact • Sliding • Rolling • Flexural – Non-contact • Fluid film • Magnetic Sliding contact bearings • Better for low/moderate speeds • Use a hard material and a soft material – Lower friction coefficients – Focuses wear on softer part • Examples: – Steel shaft on plastic bushing F • Avoid: – Aluminum on Aluminum friction What do these have in common? Bushings Examples of sliding contact bearings Bushings Friction coefficients Materials Common materials for sliding contact bearings Friction coefficient Material 1 Material 2 Clean and dry Lubricated Silver Silver 1.4 0.55 Aluminum Aluminum 1.05-1.35 0.3 Glass Glass 0.94 0.1-0.6 Rubber Asphalt 0.9 0.25-0.75 Steel Polyethylene 0.2 0.2 Steel Bronze - sintered Steel Teflon 0.05-0.2 Teflon Teflon 0.04 http://www.engineeringtoolbox.com 0.13 0.04 Rotary sliding contact: efficiency vs diameter Doutside dinside Axle Wheel Fundamentals (Slocum) Rolling contact bearings • Lower friction than sliding contact bearings • Less wear • Can achieve high speeds Fundamentals (Slocum) Fradial Radial Tapered roller Faxial Thrust enginemechanics.tpub.com Ball vs. roller bearings Ball bearings: •Lower loads •Higher precision •Lower cost Fundamentals (Slocum) Roller bearings: •Higher loads •Lower precision •Higher cost How to use choose bearings • Calculate the expected forces; decide between a radial vs. thrust bearing • Calculate max RPM • Select shaft diameter Bearing for a 10mm shaft Mounting bearings Wheel Groove for E-clip Shaft Bearing (fixed to ground) Wheel E-clip Small gap Threads Shaft Inner ring Shoulder Nut Nut Wheel Outer ring (fixed) Shaft Threads Shaft Nut Nut Ball Hertz contact: point stresses F p0 F = force δ = deflection p0 = max stress Ee = equivalent elastic modulus Re = equivalent radius of curvature Fundamentals (Slocum) δ Hertz contact: line stresses F F = force δ = deflection p0 = max stress Ee = equivalent elastic modulus Re = equivalent radius of curvature L = contact length Fundamentals (Slocum) p0 δ Non-contact bearings Can achieve very high speeds with very little friction Hydrodynamic • Relies on relative motion to cause hydrodynamic lift • Part glides on thin fluid film Hydrostatic • Parts can be stationary relative to each other • High pressure fluid is pumped through a gap Hydrodynamic Bearings • Fluid film prevents material-material contact • Low cost, low friction, long life • Less repeatable than rolling contact Shaft Low speed: material-material sliding contact Medium speed: mixed sliding contact and viscous shear. Friction decreases High speed: hydrodynamic life; no mechanical contact http://www.marinediesels.info Fundamentals (Slocum) www.duramaxmarine.com Aerostatic and Hydrostatic Bearings • Pressurized air or water flows into an interface • Maintains a gap of 0.005-0.1mm • High accuracy • Need a collection system for water • Pressures: – Air: 10 atm – Water: 40-200 atm F = load capacity η = efficiency (25-40%) P = fluid pressure A = contact area K = stiffness h = air gap Fundamentals (Slocum) The power of air bearings How much air pressure to lift the truck? Assume mass = 2000 kg, contact area = 2 m2 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uRql1fjZQf0 F = load capacity η = efficiency (25-40%) P = fluid pressure A = contact area K = stiffness h = air gap The power of air bearings How much air pressure to lift the truck? P = ~ 4e4 Pa Assume mass = 2000 kg, contact area = 2 m2 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uRql1fjZQf0 F = load capacity η = efficiency (25-40%) P = fluid pressure A = contact area K = stiffness h = air gap Magnetic bearings • Is it possible to stably levitate a permanent magnet with other permanent magnets? ? Magnetic bearings • Is it possible to stably levitate a permanent magnet with other permanent magnets? – Unfortunately, no. Proven by Earnshaw in 1842 • But, levitation is possible using: – Diamagnetic materials, or… – Electromagnets & closed loop control Diamagnetism and paramagnetism • Two types of materials: – Paramagnetic: attracted by magnetic fields (ex: iron) – Diamagnetic: repelled by magnetic fields Diamagnetic levitation of pyrolytic carbon http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diamagnetism Levitation using electromagnets hacknmod.com zeltom.com Closed loop position control Controller Desired position Amplifier G(s) Electromagnet Position measurement Hall effect sensor Japanese magnetic levitation (Maglev) train Magnetic Levitation (Maglev) www.wsj.com Maglev train: propulsion and levitation Propulsion www.dailytech.com Levitation http://www.hk-phy.org Bearing types: rolling or sliding contact • • • • Sliding contact Higher friction Lower cost Lower complexity “Bushings” • • • • Rolling contact Lower friction Higher cost Higher complexity “Ball bearings” • • • • Non-contact Minimal friction Nearly infinite lifetime Lower stiffness Lower repeatability under varying loads How is this possible? Regular octahedron Irregular octahedron http://www.thingiverse.com/thing:748202