* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide sem título - World Bank Group
Financial literacy wikipedia , lookup
Private equity secondary market wikipedia , lookup
Private equity in the 2000s wikipedia , lookup
Shadow banking system wikipedia , lookup
Interbank lending market wikipedia , lookup
Public finance wikipedia , lookup
Systemically important financial institution wikipedia , lookup
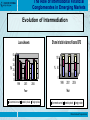
The Role of International Financial Conglomerates in Emerging Markets Banco Central do Brasil The Role of International Financial Conglomerates in Emerging Markets June/2005 Directorate of Supervision The Role of International Financial Conglomerates in Emerging Markets Composition of the Brazilian Financial System – BFS (as % of total assets) 2001 1998 19% 26% 41% 46% 35% Government-ow ned 33% Domestic private Foreign private Government-ow ned Domestic private Foreign private 2004 Number of banks BFS 1998 2001 2004 21% 38% 41% Government-ow ned Domestic private Government-owned Domestic private Foreign private 23 122 58 16 96 70 14 82 58 Foreign private Directorate of Supervision The Role of International Financial Conglomerates in Emerging Markets Composition of the Brazilian Financial System - BFS • Overall reduction in the number of banks point to more concentration in the BFS • Private banks (domestic and foreign) occupy the space left by the reduction in the number of government-owned institutions, as a result of privatization • Foreign banks grab a greater share of the market in 2001, only to lose it to domestic banks in 2004 Directorate of Supervision The Role of International Financial Conglomerates in Emerging Markets Capital adequacy Basel capital ratio 20 10 2000 0 2004 2001 Year Government-ow ned Domestic private Foreign private Directorate of Supervision The Role of International Financial Conglomerates in Emerging Markets Capital adequacy • Private banks maintain their Basel capital ratio at good levels (above 15%), well above the required capital of 11% • No difference: Domestic X Foreign • Government banks show considerable improvement in theirs (doubling from 8 to 16% in the period) Directorate of Supervision The Role of International Financial Conglomerates in Emerging Markets Evolution of Intermediation Share in total volume of loans BFS Loans/Assets 50 40 30 (%) 20 10 0 100 % 50 0 1998 2001 2004 Year Government-ow ned Domestic private Foreign private 1998 2001 2004 Year Government-ow ned Domestic private Foreign private Directorate of Supervision The Role of International Financial Conglomerates in Emerging Markets Evolution of Intermediation • Considerable reduction in the loan portfolio of government banks (portfolio restructured ) and good increase in the loan portfolio of private domestic banks • Foreign banks also increased their credit portfolios, albeit less than domestic banks Directorate of Supervision The Role of International Financial Conglomerates in Emerging Markets Efficiency Operating costs* 80 60 (%) 40 20 0 2002 2003 2004 Year Government-ow ned Domestic private Foreign private * ratio between administrative outlays (including staff-related costs) and the sum of the net income of financial intermediation and fees Directorate of Supervision The Role of International Financial Conglomerates in Emerging Markets Efficiency • While government banks find difficulty in improving their efficiency, domestic private banks gradually improve theirs and foreign banks, inversely, see their efficiency deteriorating • The administrative expenses of both private domestic and foreign banks increased in the period but, in the case of the former, this was more than compensated by a comparatively higher increase in revenues Directorate of Supervision The Role of International Financial Conglomerates in Emerging Markets Earnings Return on equity (ROE) 30 20 (%) 10 0 -10 2000 2001 2004 Year Government-ow ned Domestic private Foreign private Directorate of Supervision The Role of International Financial Conglomerates in Emerging Markets Earnings • After a bad year in 2000, foreign banks recovered; the slight reduction in profitability from 2001 to 2004 being basically due to the appreciation of the Brazilian currency (Real) • Remaining government institutions were restructured and significantly improved their earnings performance • Domestic private banks confirm their good phase with a leap in profits from 2001 to 2004 (originating from higher earnings in both financial intermediation and services) Directorate of Supervision The Role of International Financial Conglomerates in Emerging Markets Some thoughts • No performance differences among domestic private and international financial conglomerates; • No financial innovation; • Support from home-supervisor • Lower concerns with capital adequacy; • International conglomerates interest tend to be unstable: • Market share depends on economic and political stability; • Strategic presence for market survey; • Strategy of speculative positions to arbitrage domestic gaps and fragilities; • Domestic private and government long term committed (no options). Directorate of Supervision The Role of International Financial Conglomerates in Emerging Markets Contact BANCO CENTRAL DO BRASIL Directorate of Supervision E-mail: [email protected] Phone: 55-61-414-2442 Fax: 55-61-321-4280 Directorate of Supervision