* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Surgical Treatment of Urge Incontinence
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
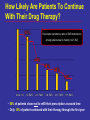
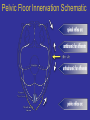
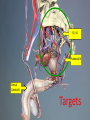
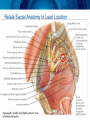
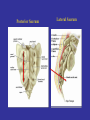
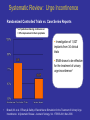
Neuromodulation for Genito-Urinary Disorders Steven W. Siegel, MD Centers for Continence Care and Female Urology Metropolitan Urologic Specialists Saint Paul, Minnesota 1 Disclosure – Medtronic, AMS, Uroplasty, Allergan • Consultant, lecturer, proctor, grant/research support – Medical Advisor, Board Member or Equity Partner • Uroplasty, Allergan, GT Medical, QIG – Off Label Usage: • Interstim for pelvic pain, neurogenic disorders • BoNT for OAB Neuromodulation in Urology • • • • Sacral (InterStim) Tibial (Urgent PC) Spinal (VoCare) Chemodenervation (Botox) Neuromodulation for GU Disorders • Refractory OAB – Failed drugs and behavioral therapy • Urinary Retention – Idiopathic non-obstructive • Non-neurogenic etiology • Fecal Incontinence Current treatments for Overactive Bladder • • • • Behavioral therapies & Physical Therapy Drugs, anitcholinergic Intravesical Botox Neuromodulation – Sacral – PTNS • Surgery – Augmentaton cystoplasty – Urinary diversion How Likely Are Patients To Continue With Their Drug Therapy? Prescription persistency rates of OAB medications among patients new to market (n=21,362) • 56% of patients chose not to refill their prescription a second time • Only 15% of patient continued with their therapy through the first year History of Sacral Neuromodulation 1981 1994 1997 1999 2002 2002 2006 2011 Tanagho and Schmidt UCSF European CE Mark FDA approves for Urge Incontinence FDA approves for UF and NOUR FDA approves for OAB Wide use of fluoro, staged implant/tined lead Small stimulator FDA approval for bowel indication (in 1,000s) Number of Patients InterStim Therapy Cumulative Use Worldwide Technique Change – 2002 Percutaneous Tined Lead Placement 100,000 patients have received InterStim Therapy Additional SNM Applications • • • – Pediatric patients/Dysfunctional elimination syndrome IC/Pelvic pain Bowel Dysfunction Present indications* » Fecal incontinence » Fecal urgency-frequency (IBS) » Idiopathic chronic constipation – Many patients have both GU/GI symptoms – Often GI improvements most meaningful to patients Siegel S, JOU 2001 Comiter C, JOU 2003 Feler C, Anesth Clin NA 2003 Peters K, BJU 2004 Everaert K, Eur Urol 2004 Hoebeke P, JOU 2004 De Gennaro M, JOU 2004 Humphreys M, JOU 2006 Roth abstract 823, AUA 2007 Mechanism of Action • Not a bladder specific therapy • Central afferent modulation – Targets reflex centers in cord and pons • Treats both OAB and retention – Blocks ascending sensory pathway inputs • Turns on voiding reflexes by suppressing the guarding reflex pathways • ‘Human Software’ Analogy Leng WW - Urol Clin North Am - 01-FEB-2005; 32(1): 11-8 Peripheral Neuroanatomy • Parasympathetic – S2 – S4 afferent and efferent (Pelvic Nerve) – Excites bladder, inhibits urethra • Sympathetic – T12 – L1 afferent and efferent (Hypogastric Nerve) – Excites urethra, inhibits bladder • Somatic – S2 – S4 afferent and efferent (Pudendal Nerve) – Excites external urethral sphincter Pelvic Floor Innervation Schematic OAB Response (ITT and As Treated) S3, S4 Pudendal N Dorsal Genital N Targets Anatomy: Sacral Canal Relate Sacral Anatomy to Lead Location Posterior Sacrum Lateral Sacrum Trial Stimulation: PNE • Insulated Needle with exposed tip placed at S3 – nerve location & function • Sensory Response – Genital/anal sensation – Patient comfort • Motor Response – Bellows & toe Trial Period Criteria Success equals > 50% improvement • number of leaks/day • number of voids/day • voided volume/void • degree of urgency Implantable Pulse Generator IPG Implantation • • • • • Based on success of trial Outpatient procedure under local/sedation Patient unchanged if therapy denied/discontinued Can modulate stimulation parameters externally Permanent devices last up to 10 years (Interstim I) Patient Selection • Abnormal Voiding – May include other symptoms • Pain • Bowel dysfunction • Younger (typical age 45-55) • Non-neurogenic • High tone pelvic floor muscle dysfunction Poor Candidates for SNM • Nerve damage – Peripheral neuropathy – Future need for MRI • Pelvic malignancy • Intrinsic abnormality of bladder – XRT – Fibrosis – Decompensation • Pain without voiding complaints • Very elderly SNM: Clinical Efficacy Urge Incontinence1 45% completely dry 34% experienced > 50% reduction in leaking episodes Urgency Frequency2 31% returned to normal voids (4 to 7 voids/day) 33% experienced > 50% reduction in voids Retention3 61% eliminated use of catheters 16% experienced > 50% amount of urine emptied from catheter usage N=38 N=33 N=38 SNS Study Group 1JOU 1999;162 ,2JOU 2000;163, 3JOU 2001;165 Systematic Review: Urge Incontinence Randomized Controlled Trials vs. Case Series Reports % of patients achieving continence or > 50% improvement in their symptoms Investigation of 1,827 implants from 34 clinical trials SNM shown to be effective for the treatment of urinary urge incontinence1 • Brazelli, M. et al. Efficacy & Safety of Sacral Nerve Stimulation for the Treatment of Urinary Urge Incontinence: A Systematic Review. Journal of Urology. Vol. 175 835-841, Mar. 2006 Results of a prospective, randomized, multicenter study evaluating the safety and efficacy of InterStim Therapy at 6-month follow-up in subjects with symptoms of overactive bladder Urge Incontinence Frequency-Urgency Siegel, et al AUGS 2012 Urgency-Frequency Improvement in Quality of Life, 6-Month SF-36 Scores % of Patients 100 75 50 25 0 PF - Physical Functioning BP - Bodily Pain RP - Role Physical GH - General Health V - Vitality RE - Role Emotional SF - Social Functioning MH - Mental Health PF RP BP GH V SF RE MH P < 0.0001P = 0.01 P = 0.01P = 0.003P = 0.01P = 0.002P = 0.17 P = 0.01 Control (n=20) Implant (n=23) US Norm Janknegt RA, Hassouna MM, Siegel SW, Schmidt RA, Gajewski JB, Rivas DA: Patient satisfaction and complications following sacral nerve stimulation for urinary retention, urge incontinence and perineal pain: A multicenter evaluation. Int Urogynaecol J, 11: 231, 2000 Five year results of SNM for voiding dysfunction: Outcomes of a prospective, worldwide clinical study • 17 centers – 163 patients, mean age 44.7, 87% females • Success rate 5 years post implant – 68% UI – 56% UF – 71% Retention • If success at 1 year, rate of success at 5 years – 89% UI – 71% UF – 78% Retention Van Kerrebroeck et al, JOU 2007 Complications • Reoperation rate <20% – Loss of efficacy – Pain at lead or IPG site – Infection * Starkman, NUU 2007; van Voskuilen, BJU 2007; Kessler, Eur. Urol 2006 How Should We Treat OAB Patients? BoNT, Other surgery PTNS, SNM Drugs PFM Rehab Behavioral Discussion





























![Welcome [www.mnwcare.com]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008705630_1-47e653144b7bc85f4c911ec652c0a12e-150x150.png)



