* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Machine Learning
Computer vision wikipedia , lookup
Existential risk from artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Human-Computer Interaction Institute wikipedia , lookup
Quantum machine learning wikipedia , lookup
Person of Interest (TV series) wikipedia , lookup
Philosophy of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Concept learning wikipedia , lookup
History of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
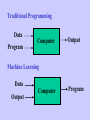
Artificial Intelligence and Applications School of Computer Science and Engineering Bai Xiao • • • • • Xiao Bai(Family name) Associate Professor,Ph.D. Supervisor B.S., Computer Science, Beihang University (BUAA) Ph. D. Computer Science, University of York, U.K. Research Interests: Computer Vision, Pattern Recognition, Image Processing, Remote Sensing Image Analysis, Machine Learning 公共邮箱: [email protected] FTP: ftp://219.224.169.249/ • • • • Artificial Intelligence is a broad area focus on how to let machines to have intelligence. It is also a modern research area. We will mainly learn machine learning especially learning algorithms, applications. Machine learning, pattern recognition, vision based learning and the corresponding applications. • • • Research based courses, not exam based. Teaching, Assignment(30%), Attendance(30%), Final report(40%). Assignment: Reading research documents, i.e. research papers, books; presentation; coding assignment; applications and etc. • Books: • R. Duda, P. Hart & D. Stork, Pattern Classification (2nd ed.), Wiley (Required) • T. Mitchell, Machine Learning, McGraw-Hill (Recommended) • Papers: Canonical Papers and Recent Papers on this area. • Reports: From Experts or Researcher about their recent research progress. Introduction to Machine Learning Bai Xiao A Few Quotes • “A breakthrough in machine learning would be worth ten Microsofts” (Bill Gates, Chairman, Microsoft) • “ Machine learning is the next Internet ” (Tony Tether, Director, DARPA) • Machine learning is the hot new thing ” (John Hennessy, President, Stanford) • “Web rankings today are mostly a matter of machine learning” (Prabhakar Raghavan, Dir. Research, Yahoo) • “Machine learning is going to result in a real revolution” (Greg Papadopoulos, CTO, Sun) • “ Machine learning is today ’ s discontinuity ” (Jerry Yang, CEO, Yahoo) What is “Machine Learning” • Machine learning is a subfield of computer science that evolved from the study of pattern recognition and computational learning theory in artificial intelligence. • Machine learning explores the study and construction of algorithms that can learn from and make predictions on data. • Such algorithms operate by building a model from example inputs in order to make data-driven predictions or decisions, rather than following strictly static program instructions. Traditional Programming Data Program Computer Output Machine Learning Data Output Computer Program Sample Applications • • • • • • • • • • Web search Computational biology Finance E-commerce Space exploration Robotics Information extraction Social networks Debugging [Your favorite area] • • • Machine Learning Algorithms: Decision Tree, Concept Learning, Neural Network, Support Vector Machine, Clustering, Bayesian Learning, Reinforcement Learning, Dictionary based Learning, Semi-supervised Learning Application: Image Classification, Image Recognition, Image Retrieval. Interesting Topics: some related ongoing research topics. ML in a Nutshell • Tens of thousands of machine learning algorithms • Hundreds new every year • Every machine learning algorithm has three components: – Representation – Evaluation – Optimization Representation • • • • • • • • Decision trees Sets of rules / Logic programs Instances Graphical models (Bayes/Markov nets) Neural networks Support vector machines Model ensembles Etc. Evaluation • • • • • • • • • • Accuracy Precision and recall Squared error Likelihood Posterior probability Cost / Utility Margin Entropy K-L divergence Etc. Optimization • Combinatorial optimization – E.g.: Greedy search • Convex optimization – E.g.: Gradient descent • Constrained optimization – E.g.: Linear programming