* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Supplementary Methods
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Real-time polymerase chain reaction wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
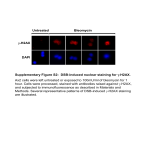
Supplementary Methods Construction of HEYL expression vectors, preparation of viral supernatant and infection of cells For the construction of HEYL expression vectors, the PCR product of Myc-tagged full-length HEYL was cloned into pcDNA3.1 (Invitrogen), retroviral vector pLPCX (Clontech) or another retroviral vector MSCV2.2-IRES-GFP. The Myc-tagged deletion constructs were made through ligation of two PCR products following the deletion of the selected domains. Retroviral shRNA vectors targeting HEYL (shRNA1: ATGGGTCTCTGAAATCACTGAA, shRNA2: AGACTTGCATCTTGTGTTTCTA) were purchased from Open Biosystems. These vectors and the corresponding control vectors were introduced into cells through transfection using lipofectamine 2000 or by retroviral transduction. For virus production, 293T cells were cotransfected with the viral and packaging vectors, and the media was collected 48 hours later. The viral supernatants, after filtration and in the presence of 4ul/ml lipofectamine 2000, were used to infect HaCaT, MCF-10A and MDA-MB-231 cells. After transfection or viral transduction, the cells were cultured in normal growth media. Forty eight hours later, cells were selected by cell sorting for GFP, or antibiotic selection (2ug/ml puromycin), and selected clones were pooled before use. Generation of anti-HEYL rabbit antibody and immunohistochemical staining and Immunofluorescence analysis A synthetic peptide corresponding to a peptide sequence (EPSGSDGESDGPID) in the Nterminus of HEYL was conjugated to keyhole limpet hemocyanin (the carrier protein), and was injected into rabbits. Anti-HEYL polyclonal antibody from sera was affinity-purified using the Aminolink Immobilization kit (Pierce). The efficacy of the antibody was measured by ELISA. The IHC staining of Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections and tissue microarrays were performed. Sections were incubated with polyclonal anti-HEYL Ab at a 1:250 dilution overnight. Diluted biotinylated anti-rabbit IgG (Vectastain kit) was added to the sections and incubated for 30 minutes. Vectastain ABC reagent (Vector) and 3, 30-diaminobenzamidine (DAB) was then used for staining color development. HEYL nuclear staining intensity was scored as 0 (negative staining), 1 (intermediate staining) and 2 (strong staining). Only a score of 2 was considered as positive staining. Immunofluorescence staining Cells on 24 well plates were fixed in 10% Formalin and permeabilized in 0.5% Triton-X. After 1 hour block in 20 mg/ml bovine serum albumin, anti-Smad3 rabbit Ab at 1:100 dilution or antiHEYL mouse Ab at 1:100 was then added to the cells and incubated at 40C for overnight. Cells were then incubated with secondary antibody conjugated to Alexafluor 488 or 568 (Molecular Probes) for 1 hour at room temperature. The cell nuclei were stained using DAPI. The fluorescence was then observed under a confocal microscope. Whole mount staining, RT-PCR and immunostaining of mouse mammary glands For whole mount staining, the mammary glands were put on slides and fixed with 10% Formalin overnight. The fat tissues of glands were removed using acetone, and the glands were stained with Carmine Alum solution overnight after hydration. Finally, the glands were destained, rehydrated and mounted. To quantify mammary gland ductal branches, 4 random fields of each whole mount were examined under 10x magnification and the primary, secondary and tertiary ducts were counted. 4-6 whole mounts were examined in each group. For H&E and immunohistochemical staining, the glands were fixed with 10% Formalin overnight and embedded in paraffin. The slides were stained with anti-Ki67 antibody at 1:300 dilution overnight. To quantify ki-67 staining, 8 random fields of each slide were examined under 20x magnification and the ratio of Ki67 positive versus negative staining cells was calculated. 4-6 mouse slides were examined in each group. The wildtype or HeyL transgenic mice were bred three times. When the wildtype or HeyL transgenic mice were aged, the mammary glands were examined weekly to detect tumor formation. The Inguinal mammary fad pads or the palpable tumors were excised and used in H&E staining as mentioned above. Gene expression analysis in mouse mammary tissue Frozen mammary gland chunks embedded in OCT were cut into 15um slices, which were mixed with 70% ethanol to dissolve OCT. After spinning, the tissue pellets were lysed with Trizol (Invitrogen) to extract RNA, which was used in RT-PCR. The primers used to detect the HeyL transgene expression in mammary glands in the PCR are: F: GAAGCGCAGAGGGATCATAG, R: CCCAATACTCCGGAAGTCAA. To extract proteins from mouse mammary glands, the frozen tissues were homogenized on dry ice and lysed with RIPA buffer. Western blot analysis was performed to analyze protein expression. Immunoprecipitation and western blotting Transfected cells in T25 flasks were lysed in 250ul 1x lysis buffer (1% Triton-X, 150 nM NaCl, 10mM Tris, 1mM EDTA and EGTA and 0.5% NP-40) with protease inhibitor on ice for 30 minutes. The lysates were centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 5 minutes. The supernatant was collected and quantified by BCA assay. 600 ug of cell lysate at a concentration of 1ug/ul was incubated with 3ul anti-Flag Ab or 1ul anti-Myc Ab for 3 hours. 20ul Protein G plus Agarose beads were then added and incubated for 2 hours. The beads with protein complex were washed with 1x lysis buffer 4 times and loaded onto an SDS-PAGE gel after being heated. The proteins were then transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. After being blocked in 5% milk for 30 minutes, the membranes were blotted with anti-Flag (1:1000) or anti-Myc (1:1000) overnight and with secondary Horseradish peroxidase-conjugated Ab for 1 hour. The membranes were developed using chemiluminescence (Amersham). Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR RNA from clinical samples or cell lines was extracted using either Trizol (Invitrogen) or RNeasy mini kit (Qiagen) and treated with DNaseI. Superscript II cDNA synthesis kit (Invitrogen) was used for RT-PCR and 1ug total RNA was used as templates. Quantitect SYBR Green PCR kit (Qiagen) was used for the quantitative PCR according to the manufacturer’s protocol. PCR Primers were: HEYL 5'- CAACTCCTCCTCCTCCTCCT-3' (Forward) and 5'- TTGCAACGTGGAAATGTGTT-3' (Reverse); 36B4, a “housekeeping” ribosomal protein gene used as a loading control, 5'-GATTGGCTACCCAACTGTTGCA-3' (Forward) and 5'CAGGGGCAGCAGCCACAAAGGC-3' (Forward) and PAI 5'-AGGCAGCTCGGATTCAACTA-3' 5'-AGAGACGGGGGTCTTGGTAT-3' TCCATTTTCGAAGCCACCT-3' (Reverse); (Reverse); Smad7 (Forward) and (Reverse); p15 5'- 5'-TTTTGCATGTATCCTTCAAAGTG-3' 5'-TGCTCCCATCCTGTGTGTTA-3' (Forward) and 5'- TGGGTTATGACGGACCAAAT-3' (Reverse); mouse PAI-1 5'-TTTCCTAGCAGGCCACTCTG-3' (Forward) and 5'-GTACACGGTGTGTGGCTGTC-3' GGCCCTCTACCTTTCAGGAC-3' (Forward) and (Reverse); mouse P15 5'- 5'-TTTCAGTTCACAGGGGAAGG-3' (Reverse). 1ul cDNA was used in quantitative PCR. The quantitative PCR reaction was performed in a 96-well plate as follows: 95°C for 15 minutes and 40 cycles of 94°C for 15 seconds, 56°C for 30 seconds, and 72°C for 30 seconds. The relative expression of target genes to loading control was calculated based on the differences of their CT values. BrdU Cell Proliferation Assay Five thousand MCF-10A control or HEYL expressing cells were seeded on a 96-well plate and treated the next day with TGF-β for 12 hours. Bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) was added into cell media and incubated for 4 hours. The cells were then fixed and denatured for 30 minutes at room temperature. 100ul anti-BrdU antibody was added into each well and incubated for 1 hour at room temperature. After washing 3 times, 100ul Peroxidase Goat anti-Mouse IgG was added and incubated for 30 minutes at room temperature.The tetra-methylbenzidine substrate was incubated with the cells for 15 minutes in the dark at room temperature. 100μl of Stop Solution was then added and the measured absorbance representing BrdU incorporation in each well was read at dual wavelengths of 450-540 nm.