* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
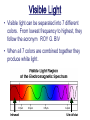
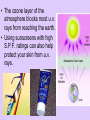
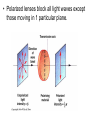
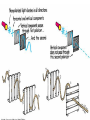
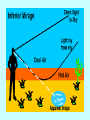
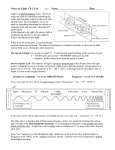
Physical Science Ch. 12 & 13: Electromagnetic Waves and Light Electromagnetic Radiation • Electromagnetic waves (E.M.) are transverse waves produced by the motion of electrically charged particles (photons). • E.M. waves do not require a medium, and are therefore able to travel at 186,000 mi/s (300,000 km/s), the speed of light (which is an E.M. wave). Does Light Have Mass? • Well…….maybe. Electromagnetic Spectrum • The different electromagnetic waves are arranged in the electromagnetic spectrum in order of increasing frequency and decreasing wavelength. • The higher the frequency, the more photons (energy) per wave, and the more potentially harmful the wave is. Low energy High energy Radio Waves • Radio waves are the lowest frequency E.M. wave. • They are used primarily for communications, such as cell phones, t.v. and radio transmissions, and cordless devices such as phones, speakers, etc. Microwaves • Microwaves are a type of radio wave. They are used in cell phones and microwave ovens. • At normal levels, microwaves are harmless. • Why shouldn’t you put metal objects (or CD’s) in a microwave? • • • • Metal foil CD Bulb Chips Infrared Radiation • Infrared radiation transfers energy in the form of heat. • Examples include heat lamps and the warmth from the sun. Special types of film and cameras can show infrared radiation. This is called thermography. Visible Light • Visible light can be separated into 7 different colors. From lowest frequency to highest, they follow the acronym ROY G. BIV • When all 7 colors are combined together they produce white light. • When all 7 colors of the spectrum are absent, then the “color” black is produced. • What is a “black” light and how does it work? Colors • When an object appears a certain color, it is because that is the color which is being reflected back to your eye, just like a mirror. • A white object reflects all colors, a black object reflects no color. Visible Light Spectrum • A prism can separate visible light into the 7 different colors. • Drops of moisture in the atmosphere can act as a prism, and form a rainbow. • A pigment is a colored material which is used to change the color of other materials. • The 3 primary pigments are magenta, cyan, and yellow (pg. 393). These colors can be combined to produce any other color of pigment. • So if you go to the store and pick out a certain color of paint, odds are they will not have that color on the shelf. But they will mix the correct proportions of the primary pigments together to create your color. • Visible light can also cause certain chemical reactions to occur. • Examples: photosynthesis, milk spoiling, H2O2 breakdown Is it possible to see in the dark? Ultraviolet Light (U.V.) • U.V. rays are potentially dangerous at high levels or with prolonged exposure. • U.V. rays can cause sunburns and skin cancer, and kill bacteria and healthy cells. • The ozone layer of the atmosphere blocks most u.v. rays from reaching the earth. • Using sunscreens with high S.P.F. ratings can also help protect your skin from u.v. rays. X-Rays • X-rays are high frequency e.m. waves which are potentially dangerous at moderate levels. • X-rays can penetrate many materials such as skin, muscle, and many fabrics. • X-rays are used in dental and medical procedures, and can cause cancer and decrease a persons life expectancy with prolonged exposure. Gamma Radiation • Gamma radiation is high frequency waves which can be extremely dangerous. • Potentially dangerous gamma rays may be given off from radioactive materials, and are present everywhere on earth at low safe levels. • Gamma radiation can kill healthy cells, but can also be used to kill cancerous cells. This is called radiation therapy. Classifications of Materials • Different materials can be classified by how they allow waves (usually light) to pass through them. • These classifications are opaque, translucent, and transparent. • Transparent materials allow almost all visible light to pass through. Ex.: glass, plastic wrap • Translucent materials allow a partial amount of visible light to pass through. Ex.: wax paper, shower doors, plastic milk jugs • Opaque materials stop almost all visible light from passing through. Ex.: drywall, thick curtains Types of Lighting • There are 2 main types of artificial lighting. 1. Incandescent – a heated filament excites the gases inside an enclosed bulb. 2. Fluorescent – an electric current is transferred through a glass tube filled with a conductive gas. A small amount of mercury inside emits u.v. rays when energized. These rays excite phosphors on the inside of the tube, producing light. Polarized Light Normal light will produce waves which vibrate in many different planes. Polarized light is light which vibrates in only 1 plane. This is created by passing normal light through a polarized lens. • Polarized lenses block all light waves except those moving in 1 particular plane. • Think of polarized lenses like tines on a comb. Normal light that passes through the lens, like tangled hair through a comb, will align in the same plane. • Polarized glass and lenses are effective at blocking out glare from the sun. As a result they are used in car windshields, sunglasses, and camera lenses. Lasers & Coherent Light • Coherent light is visible light traveling at only 1 specific wavelength (resulting in 1 color). This wave has all of it’s crests and troughs aligned and travels in only 1 direction. A laser is an example of coherent light. • A laser is a device used to create a beam of coherent light. Lasers In a laser, an electric current excites a material (like neon) and causes it to emit photons. These photons are enclosed inside the laser device where they bounce back and forth between 2 mirrors and becomes perfectly aligned (coherent light). Some of these photons, if they are aligned correctly, escape through a small portion of one of the mirrors. This is the laser beam. • Think of it like a piggy bank. If you want to get some money out through the top slit, the coins have to line up perfectly before they will come out. • Since laser beams are perfectly aligned and move in the same exact direction, they spread out very little. Total Internal Reflections • Normally, when a wave enters a medium it is either reflected or re-emitted out of the medium. However, when a wave entering a medium is completely reflected back into the material instead of out of it, this is called a total internal reflection. • Optical fibers (Fiber optics) produce a total internal reflection. Such fibers can be used for communications, entertainment, and surgeries. Certain “fluorescent” plastics produce internal reflections which may make them appear to glow. • A mirage is a visual distortion produced by the refraction of light. • Some mirages produce a mirror or a watery image, and others may make an object appear larger or smaller, nearer or further away. • This device produces a false image, but not a true mirage. • Paul bought a very bright LED flashlight. He showed Dave how bright it was by shining a regular light in his eyes, and then the LED. After viewing the LED for a few seconds, the room suddenly appeared darker to Dave. Why? • Not to be outdone, Dave then pulls out a laser pointer which he had and said, “Well just look at how bright this one is.” Bad idea. Why? • I cdnuolt blveiee taht I cluod aulaclty uesdnatnrd waht I was rdanieg. The phaonmneal pweor of the hmuan mnid. Aoccdrnig to rscheearch at Cmabrigde Uinervtisy, it deosn't mttaer in waht oredr the ltteers in a wrod are, the olny iprmoatnt tihng is taht the frist and lsat ltteer be in the rghit pclae. The rset can be a taotl mses and you can sitll raed it wouthit a porbelm. Tihs is bcuseae the huamn mnid deos not raed ervey lteter by istlef, but the wrod as a wlohe. Amzanig huh? • How do you suppose they were able to etch the image into the middle of the glass cube? • Todd was showing a friend how his black light worked, when his white cat walked in the room. What color did the cat appear under the black light, and why? • Les spilled a little bit of oil into the water as he was working on his boat. This caused a rainbow effect to appear. Why do you think this occurred? • Karen went to the beach last week, and because it was a cloudy day she did not use any sunscreen. To her dismay, she came back with a slight sunburn. How is this possible? • How is one universal remote able to control all of the components in your entertainment system (tv, DVD, cable box, etc.) by itself) » = • In art class, Andy was mixing watercolors together to obtain the right shades for his project. He found that using the 3 primary pigment colors, there were only 2 main “colors” which he could not produce. What were they? • When asked what he was doing outside on the ground, Beaman replied, “Creating constructive interference by simultaneous refraction of mid-level electromagnetic radiation through a convex lens, in order to harness their combined energies and thermally terminate formicidae hymenoptera with extreme prejudice.” What was he doing?