* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Antibiotics - Noadswood Science
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae wikipedia , lookup
Staphylococcus aureus wikipedia , lookup
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus wikipedia , lookup
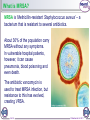
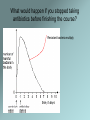
MRSA L.O: To understand how bacteria can develop resistance to antibiotics What is MRSA? MRSA is ‘Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus’ – a bacterium that is resistant to several antibiotics. About 30% of the population carry MRSA without any symptoms. In vulnerable hospital patients, however, it can cause pneumonia, blood poisoning and even death. The antibiotic vancomycin is used to treat MRSA infection, but resistance to this has evolved, creating VRSA. 2 of 26 © Boardworks Ltd 2011 The evolution of superbugs 3 of 26 © Boardworks Ltd 2011 Antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria 4 of 26 © Boardworks Ltd 2011 How do bacteria become resistant? Although vaccinations an, bacteria and virii can mutate to form a new, resistant “strain”:d antibiotics are useful in the fight against pathogens Bacteria 1) Variation – some strains of bacteria are resistant and some aren’t. 2) Competition – The non-resistant bacteria are killed by the penicillin. 3) Survival of the fittest – the resistant bacteria survive. Penicillin 03/05/2017 4) Passing on of genes – the resistant bacteria reproduce and pass on their adaptations to their offspring. This is how the bird flu virus developed. What would happen if you stopped taking antibiotics before finishing the course? Resistant bacteria multiply Read through the MRSA information and answer the questions. 1. What is MRSA? 2. What symptoms would a sufferer have? 3. Why are antibiotics a problem to harmless strains of bacteria? 4. Why are hospital patients at risk? 5. How can you prevent MRSA? 6. How can you treat MRSA? MRSA – Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus How can we control the spread of antibiotic resistant bacteria in hospitals? Could you stop using antibiotics? Why / Why not? Bacterial and Viral infections There are two types of outbreaks: An epidemic (local outbreak) A pandemic (global outbreak) Antibiotic overuse advert Are Flesh Eating Superbugs Really a Threat? What you think is happening (your hypothesis) Why do you think this? (your theory) What is the evidence? Antibiotics Advantages • Cures a lot of diseases • Usually relieves symptoms in a few days • Reduces deaths from diseases Disadvantages • Resistant bacteria can develop • Diseases become more difficult to treat • Not taking the full course causes more resistant bacteria to survive • Increases likelihood of them working when you need Is there disease causing life on venus? Does this data support the claim? Sun Venus Venus’s inferior conjuncture Earth Is there disease causing life on venus? Does this data support the claim? Be prepared to report back on: 1. Is their any scientific logic to this argument? 2. Does the data support the claim? 3. What questions would you like to ask to further investigate this claim? Is there life on venus? Does this data support the claim?