* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download nouns - University of Maryland, Baltimore
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Grammatical gender wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ojibwe grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Literary Welsh morphology wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Archaic Dutch declension wikipedia , lookup
Grammatical number wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Vietnamese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Classifier (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latvian declension wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic nouns and adjectives wikipedia , lookup
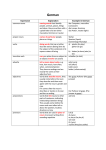
nouns Nouns are one of the basic parts of speech. This handout will help you identify and use different types of nouns. General Rules Definition and Function A noun refers to a person, place, idea, or thing. Nouns function as subjects and objects within sentences. Example: The dog ate the food in the bowl. Note: “Dog” is the subject. “Food” is a direct object. “Bowl” is the object of the preposition “in.” Plurals For a complete discussion of making nouns plural, please see our “Plurals” handout. Nouns and Articles For a complete discussion of using articles with nouns, please see our “Articles” handout. Noun Phrases A noun phrase is a group of words that functions together with a noun. The noun is said to be the head of the phrase. Example: The girl in the yellow dress is my daughter. Note: “The girl in the yellow dress” is a noun phrase. “Girl” is the head of the phrase. Proper and Common Nouns Proper nouns refer to specific and unique persons, places, or things. They are usually capitalized. Examples: Barack Obama Baltimore University of Maryland Common nouns refer to ordinary or general persons, places, or things. They are usually not capitalized. Examples: president city university Note: For more information on when to capitalize different words, please see our “Capitalization” handout. Writing Center Version 3.0 1 SMC Campus Center 621 W. Lombard St. Room 307 www.umaryland.edu/writing 410-706-7725 Concrete and Abstract Nouns Concrete nouns are persons, places, and things that you can perceive with your senses. Examples: rocks papers scissors Abstract nouns are persons, places, and things that you cannot perceive with your senses. They are usually ideas or concepts. Examples: tenacity hope bliss Collective Nouns Collective nouns are groups of persons, places, or things that function as a single unit. Examples: family government team When emphasis is placed on the noun as a single unit, it functions as a singular noun. Example: The audience is small. It only has nine members. When emphasis is placed on the noun as a group of individuals, it functions as a plural noun. Example: The audience would not turn off their phones during the movie. Count and Non-count Nouns Count Nouns Count nouns can be counted and expressed in the plural. Examples: two oranges three chairs five countries Non-count Nouns Non-count nouns, also known as mass nouns, cannot be quantified and lack a plural form. They usually fall into one of the following categories: Non-count Nouns Gases Oxygen Pollution Air Smoke Liquids Water Coffee Blood Milk Metals Gold Aluminum Zinc Iron Phenomena Electricity Gravity Fire Weather Abstractions Truth Beauty Peace Greed Languages English Arabic French Chinese Sets of Items Furniture Garbage Equipment Fruit Particles Salt Sand Flour Sugar Food Cheese Bread Veal Pork There is a way to express quantity with non-count nouns, but it is not by using a number and making the Writing Center 2 SMC Campus Center 621 W. Lombard St. Room 307 www.umaryland.edu/writing 410-706-7725 noun plural. Examples: three peaces two veals seventy oxygens Instead, you would use a countable unit of measurement before the non-count noun. Examples: two cups of sugar five liters of water two pieces of furniture Exceptions Many nouns have a count and non-count sense. Example: There are five hairs on my pillow. My husband has a full head of hair. Note: “Five hairs” refers to individual, countable hairs. “Head of hair” refers to a mass of hair. Additionally, most non-count nouns can be used as count nouns when referring to types, varieties, or classes of things. Example: There will be fifteen cheeses at the party. Note: What this sentence is really saying is that there will be fifteen different “types of cheese” at the party. Exceptions (But Not Really) There are times when native speakers use non-count nouns as if they were count nouns. These instances can be confusing for those learning English. Example: I will have five coffees. Note: What this sentence is really saying is that the speaker would like “five cups of coffee.” Less and Fewer Use “less” with non-count nouns and “fewer” with count nouns. Example: She had less water than her sister. Example: She had fewer cookies than her brother. Much and Many Use “much” with non-count nouns and “many” with count nouns. Example: How much salt did you put on this taco? Example: How many tacos did you eat? Compound Nouns Compound nouns are made up of a small collection of words separated by hyphens. Examples: sister-in-law runner-up Gerunds Gerunds are not technically nouns: they are verb forms that function as nouns. They end in “–ing.” Writing Center 3 SMC Campus Center 621 W. Lombard St. Room 307 www.umaryland.edu/writing 410-706-7725 Example: Running is fun. Note: “Running” is a gerund that functions as the subject of the sentence. Note: For more information on gerunds, please see our “Verbs” handout. Substantive Adjectives Sometimes adjectives can be used as nouns. These sorts of adjectives are called substantive adjectives. They are preceded by the word “the” and are grammatically plural. Example: We should help the poor. Note: “Poor” is technically an adjective, but in this sentence it acts as a noun and stands in for “poor people.” Example: The meek shall inherit the earth. Note: “Meek” is technically an adjective, but in this sentence it acts as a noun and stands in for “meek people.” References Azar, B. S., & Hagen, S. A. (2009). Understanding and using English grammar. White Plains, NY: Pearson Longman. Faigley, L. (2009). The little penguin handbook. New York, NY: Longman. Howard, R.M. (2011). Writing matters. Boston, MA: McGraw-Hill. Writing Center 4 SMC Campus Center 621 W. Lombard St. Room 307 www.umaryland.edu/writing 410-706-7725