* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cytologist_an_endgered_species-BAC_13-09
Conservation biology wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Acute inhalation injury wikipedia , lookup
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Decline in amphibian populations wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
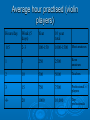
Cytologists - an endangered species? Behdad Shambayati Surrey Pathology Service An endangered species is a population of organisms which is facing a high risk of becoming extinct because it is either few in numbers, or threatened by changing environmental or predation parameters. “It is not the strongest of the species that survives, nor the most intelligent that survives. It is the one that is the most adaptable to change.” Charles Darwin Cytology “A Dinosaur Facing Extinction?” Behdad Shambayati Ashford and St.Peters HospitalChertsey, Surrey What Happened to Dinosaurs? Background extinction Slow decline in numbers leading to eventual extinction Sudden extinction Mass extinction theories Most likely- a slow decline followed by catastrophic event THE ALVAREZ ASTEROID IMPACT THEORY widely accepted theory (proposed in 1980 by physicist/geologist Luis Alvarez), is that an asteroid 4-9 miles (6-15 km) in diameter hit the Earth about 65 million years ago. The Alvarez asteroid impact theory “KT extinction” Cause of Cytologist Mass Extinction? Is cytology facing background extinction? 1960s- 1990s Golden age of cytology Exfoliative Cytology Respiratory cytology Urinary Bronchial samples Sputum Voided urine Washings Renal Pelvis brushings GI tract samples Oesophagus Stomach Duodenal, biliary ducts etc Skin scrapings Effusion Cytology CSF Synovial fluid Oral scrapings 1960s- 1990s Golden age of cytology FNA Cytology Breast Prostate Liver Lymph nodes Kidney & renal pelvis Lung Thyroid The carotid body Bone The Gonads Pancreas Salivary glands The eye Soft tissue tumours Current practice (2004) Exfoliative Cytology Respiratory cytology Urinary Bronchial samples Sputum Voided urine Washings Renal Pelvis brushings GI tract samples Oesophagus Stomach Duodenal, biliary ducts etc Skin scrapings Effusion Cytology CSF Synovial fluid Oral scrapings Current practice (2004) FNA Cytology Breast Prostate Liver Lymph nodes Kidney & renal pelvis Lung Thyroid The carotid body Bone The Gonads Pancreas Salivary glands The eye Soft tissue tumours ? Drivers for the decline in nongynae cytology Consultant staffing shortage Some consultant histopathologist apathy towards cytology /non-gynae Gynae backlogs Loss of technical expertise in the labs “Do a biopsy” recommendation Core biopsy and same day processing can give good TAT Fear of litigation Technical staffing shortage No support for FNA service Overuse of untrained MLAs Poor sample preparations ? Drivers for the decline in nongynae cytology No tissue architecture Eg Breast (insitu vs invasive carcinoma) Specific tumour subtyping not always possible Eg Poorly squamous carcinoma vs adnocarinoma in respiratory cytology Inadequate samples Requires practice Dabbling will not work eg bile duct brushings Small sample size ? Can not do ancillary test easily• Enough tissue EFGR, KRAS etc ? Drivers for the decline in gynae cytology Cytology numbers on the decrease due to fall in coverage and change in screening age range Automation (FocalPoint) and HPV testing (especially primary screening with HPV testing) will reduce (dramatically) the cytologists’ workload • Mergers & centralisation will result in some cytologists resigning / retiring / redundant! Who will prepare non-gynae samples? • • Hot lab cytology Histology department ? Drivers for the decline in gynae cytology- HPV primary screening May result in extended screening interval Will negate the requirement for ‘primary screening cytologists’ – we will only need ‘checkers’ & ‘reporters’ Molecular markers may replace cytology as the method of triage in HPV primary screening – what role will be left for cytologists? General factors Fewer, larger laboratories are inevitable. This limits the vocational geographic location of cytologists General factors “Cytology- not an attractive career” Absence of HSST in MSC Scientists unable to progress to highest level in MSC) will limit the desire for scientists to choose cytology as an option Lost opportunity as experienced BMS have wealth of transferable microscopy skills 10,000 hours or 10 year rule 10,000 hours of purposeful of practice in any subject to achieve mastery “The role of deliberate practice in the acquisition of expert performance” Ericsson etal Psychological review 100, no 3 (1993): 363-406 Average hour practised (violin players) Hours/day Week (5 days) Year 10 year total 0.5 2-3 100-150 1000-1500 Most amateurs 1 5 250 2500 Keen amateurs 2 10 500 5000 Teachers 3 15 750 7500 Professional players 4+ 20 1000 10,000 Top professionals Other examples • Andy Murray – 2003 started out on the Challenger and Futures circuit, 2012 wins first Grand Slam finals • Bill Gates drops out of Harvard and start a company… – By then he had exceeded 10,000 hours of computer programming in previous 7 years • Beatles – 10 years from founding until success of White album Conclusion Collaborative Working to harness existing experience and skills in BMS cytologists to maintain the current standards in cervical screening and help to develop diagnostic cytology and stop its path to extinction in near future Must practice EVIDENCE based medicine not EMINENCE based medicine Coelacanth ….living fossil The coelacanth has been nicknamed a “living fossil”, because it originally was known only through fossils. The coelacanth is thought to have evolved into roughly its current form approximately 400 million years ago Cytology needs to evolve