* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ws: Enzymes as Catalyst review
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
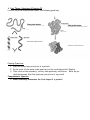
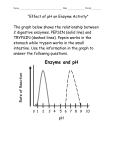
Biology Jones/Marsters Enzymes as Catalysts Review A catalyst is something that can cause something else to change, without being changed themselves. Enzymes are considered organic catalysts. Catalysts, because they cause something to change (a chemical reaction) without being changed by the reaction. Organic, because they are carbon based molecules. For each section within this assignment there are “planning questions” designed to help you write your answer to the “comprehensive question” (in bold). - Answer the planning questions with very brief answers. - Include all the information in your answers from the planning questions to thoroughly answer the comprehensive question with logic and complete sentences in a small paragraph. 15 5 Time 10 5 Lactose 10 Glucose and Galactose 15 Energy (kcal) With the enzyme Lactase Glucose and Galactose Without the enzyme Lactase Lactose Energy (kcal) Part One: The Reaction Look at the two graphs below and answer the following questions. Time Planning questions: 1. What are the reactants and products in this reaction? 2. Looking at the second graph, what is the enzyme in this reaction? 3. How much energy does this reaction require with the enzyme? 4. How much energy does this reaction require without the enzyme? Comprehensive question: 5. Using the term activation energy, explain what the enzyme does to this reaction. Be specific and use supporting examples from your answers in #1 & #4. Part Two: Enzymes and Their Environment Look at the following graphs regarding pH and answer the questions below. Planning Questions: 1. At what pH level does the enzyme Pepsin work best? 2. At what pH level does the enzyme Trypsin work best? 3. What do you think would happen to Pepsin if it were in a solution with a pH of 7? 4. What do you think would happen to Trypsin if it were in a solution with a pH of 2? Now look at the next two graphs regarding temperature and answer the questions below. Catalase Reaction Rate Reaction Rate Lactase 10 30 60 90 120 Temp. F 10 30 60 90 120 Temp. F 5. What happens to Catalase when it is exposed to high temperatures? 6. What happens to Lactase when it is exposed to high temperatures? Comprehensive Question: 7. What do these two graphs tell you about enzymes, their environments, and their function? In your answer be sure to explain how temperature and pH changes can denature a protein. Why does a protein lose its ability to function if it becomes denatured? Be specific and use supporting examples from your answers in #1 & #6. Part Three: Structure & Function II Look at the pictures below and answer the following questions. Planning Questions: 1. Describe the primary structure of a protein. 2. Is the order of the amino acids important to the resulting protein? Explain 3. Take a look at the secondary, tertiary and quaternary structures. What do you think determines this final quaternary structure of a protein? Comprehensive Question: 4. What ultimately determines the final shape of a protein?