* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The New Imperialism Section 5
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
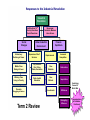
History of the Modern World Imperialism in the Industrial Age Mrs. McArthur Walsingham Academy Room 111 Images: "Postkarte: Der Krieg in China" website of German Historical Museum, Berlin Assignment: due Wed., 12/8 1. Read section summaries 1-4 (photocopies) 2. Complete Reading Check, Vocabulary Strategy, Reading Skill and Review questions 3. View PP slides #4-15 (Consult notes in the Notes View.) Optional Film: Wed.,12/8 from 3-5 PM. (This is an opportunity for those unable to attend Amazing Grace at Emily’s house.) The New Imperialism Section 1 Summary: Building Overseas Empires Witness History Audio: The White Man’s Burden Witness History Audio: Empire Builders Motives Driving the New Imperialism European Imperialism grew out of a number of causes. The Industrial Revolution required natural resources not available in the home countries; the need for naval bases around the world and for prestige also furthered imperialism; missionaries sought to convert more souls; and social Darwinism made the idea of conquering other peoples more acceptable. Note Taking Transparency 160 The Rapid Spread of Western Imperialism Although a small group of Westerners were against colonialism, most were willing to take advantage of its perks, and conquering other lands proved quite easy. Several older civilizations were in decline during the time of Imperialism, and European powers had powerful armies and navies with technical advances such as the Maxim machine gun. Color Transparency 144: Responsibilities of Powerful Nations Forms of Imperial Rule There were several kinds of colonial rule. Direct rule involved sending soldiers from the home country to control the population of the colony. Indirect rule used sultans, chiefs, or other local rulers to oversee operations in the colony. In a protectorate, local rulers followed the advice of their European advisors on issues of trade or missionary activity. Progress Monitoring Transparency Note Taking Transparency 160 Color Transparency 144: Responsibilities of Powerful Nations 5 of 6 Progress Monitoring Transparency The New Imperialism Section 2 Summary: The Partition of Africa Witness History Audio: Resisting Imperialism Africa in the Early 1800s When imperialists arrived in Africa, they met many different peoples who spoke hundreds of languages and had many different forms of government. Muslims had conquered or influenced much of North, East, and West Africa, but the Ottoman empire was in decline. In southern Africa the Zulus had expanded their control, but they in turn came to be dominated by the technology of the Boers. Color Transparency 145: European Explorations of Africa Note Taking Transparency 161 1 of 8 European Contact Increases African resistance, difficult terrain, and diseases kept Europeans from much of the interior regions of the continent in the early stages of imperialism. Explorers finally pushed into the interior, followed soon after by missionaries. Dr. David Livingstone was both an explorer and missionary who wrote about Africa’s people and opposed the slave trade. A modern re-creation of Livington’s 4,000Km trek. 2 of 8 A Scramble for Colonies King Leopold II arranged trade treaties with African leaders and soon monopolized the Congo. This started the scramble for colonies by other European nations. An agreement about the process of colonizing Africa was reached at the Berlin Conference in 1884. Color Transparency 149: The Scramble for Africa Witness History Video: The Scramble for African Colonies Africans Resist Imperialism The colonizers often met with armed resistance. Ethiopia managed to resist European colonization altogether. In this Age of Imperialism, some Western-educated Africans developed an elite status, while others formed nationalist movements to pursue independence. Progress Monitoring Transparency 3 of 8 Color Transparency 145: European Explorations of Africa 5 of 8 Note Taking Transparency 161 6 of 8 Color Transparency 149: The Scramble for Africa Progress Monitoring Transparency Assignment: due Monday, 12/14 1. Read section summary 5 (photocopy) 2. Complete Reading Check, Vocabulary Strategy, Reading Skill and Review questions. 3. Identify: concession, protectorate, sphere of influence 4. View PP slides #17-22 (Consult notes in the Notes View.) The New Imperialism Section 5 Summary: China and the New Imperialism Witness History Audio: Trading Opium for Tea Trade Between Britain and China China moved from having a trade surplus with Western countries to having a trade deficit. When British merchants were getting rich from selling opium to the Chinese, China’s demands to shop the trade led to war. British warships had the latest technology and China was defeated. Britain then forced China to open more ports to trade and to give Britain the port of Hong Kong. The Taiping Rebellion Weakens China The peasant revolt known as the Taiping Rebellion nearly toppled the Qing dynasty and led to the deaths of 20–30 million Chinese. As a result, the Qing government had to share power with regional commanders. The New Imperialism Section 5: China and the New Imperialism Geography Interactive: Imperialism in China Launching Reform Efforts When it became obvious that China was no match for Western powers or a modernized Japan, imperialists rushed to carve out spheres of influence along the coast. The U.S. introduced an Open Door Policy to keep Chinese trade open. In 1898, emperor Guang Xu began a reform program to modernize China called the Hundred Days of Reform, but the Conservatives soon retook control. Color Transparency 148: The Great Powers Divide China Note Taking Transparency 164 The Qing Dynasty Falls The Qing dynasty once again had to contend with foreign guns and demands after the Boxer Uprising brought in forces of the Western powers and Japan. A Chinese nationalist movement was growing and led to the birth of a republic after the empress Ci Xi died. Progress Monitoring Transparency Empress Ci Xi Note Taking Transparency 164 Color Transparency 148: The Great Powers Divide China Assignment: due Tues. 12/14 Review for Semester Exam • Be sure that you have consulted the study guide that is on SPA. • Organize your study materials/ • Draw up questions you would like to pose. • Study the graphic organizer on the next slide. (Term 2) Progress Monitoring Transparency Industrial Revolution Justifications: 19th Century Liberalism Social Darwinism Social Changes Aristocracy Declining in Power Responses: Socialism, Marxism Labor Unions Finance Capitalism Urban Industrial Environment Expansion of Gov't Services Requirements Increased Competition Middle Class Rising in Power City Services: Fire, Police, Water, Sanitation Raw Materials Nationalism Working Class Living in Poverty Public Health Education New Markets Imperialism Peasants Struggling to Survive Term 2 Review Investments Militarism Entangling Alliances Underlying Causes of World War Assassination of Archduke Ferdinand