* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Aucun titre de diapositive
Federal takeover of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac wikipedia , lookup
Moral hazard wikipedia , lookup
Financial economics wikipedia , lookup
Financialization wikipedia , lookup
Interbank lending market wikipedia , lookup
Systemic risk wikipedia , lookup
Shadow banking system wikipedia , lookup
Fractional-reserve banking wikipedia , lookup
Securitization wikipedia , lookup
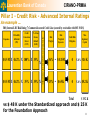
Déjeuner causerie Développements canadiens en gestion des risques The New Basel II Accord and Its Impact on the Banking Industry Alicia Zemanek Vice-présidente Relations avec les investisseurs Chef des Risques Gestion intégrée des risques Banque Laurentienne du Canada Laurentian Bank of Canada CIRANO-PRMIA Agenda • Evolution of Basel I into Basel II • Old vs New Basel Accord • The New Basel II Accord • Results of the QIS3 Exercise • Who is subject to the New Basel II Accord • Basel II Impact on the Banking Industry • Will we Have a New Accord by Spring 2004 ? 2 Laurentian Bank of Canada CIRANO-PRMIA Evolution of Basel I into Basel II 1988 Endorsement of Basel I Accord by G-10 central banks “The current accord is based on the concept of a capital ratio where the numerator represents the amount of capital a bank has available and the denominator is a measure of the risks faced by the bank and is referred to as risk-weighted assets” Risk Weights 0% Asset Categories Cash, Sovereign loans, Insured Residential Mortgages Calculation of Total Capital Ratio (as of oct 31st 2002 in $K) Available Capital 1 249 400 Risk Weighted Assets 9 276 528 Total Capital Ratio 20% Bank loans, Municipal loans 50% Uninsured Residential loans 100% All other loans and non-performing loans 13.5% Minimum Capital Requirements Tier 1 Total Basel I 4% 8% OSFI 7% 10% Problem with the accord: The Accord is insensitive to credit risk ratings. A General Electric loan (AAA rated), inder Basel I, generates more capital requirements than a sovereign debt to Mexico (BBB- rated) 3 Laurentian Bank of Canada CIRANO-PRMIA Old Vs New Basel Accord BASEL I BASEL II 1 Pillar (20 pages) (covers the quantification of minimum regulatory capital) 3 Pillars (216 pages) Pillar 1: Min. capital requirements Pillar 2: Supervisory review Pillar 3: Public disclosure 1 Methodology (approach) for calculating minimum capital 3 Methodologies (approaches) for calculating minimum capital Not very sensitive to risk Uses external or internal risk ratings to compute minimum capital requirements for credit risk All credit commitments are included Only credit commitments in the calculation ex. VISA, with maturity 1 year commitments (for LBC increases are included in the quantification capital between 6% & 17%) (explains 364 day revolving lines) Capital relates only to credit & market risk Capital relates to Credit, Market & Operational Risk (for LBC OP risk capital represents an additional 10%) 4 CIRANO-PRMIA Laurentian Bank of Canada The New Basel II Accord OR Regulatory Capital for Credit Risk Advanced Internal Ratings (AIRB) + = Basic Indicator Approach (BIA) OR Standardized OR Regulatory Capital for Operational Risk Advanced Measurement Approach (AMA) + Standardized OR Internal Model Approach Regulatory Capital for Market Risk PILLAR III (Public Disclosure) Corporate Governance RAROC Credit Risk Risk Mgmt & Reporting Mgmt Committee Struc-tural Risk Capital Mgmt + + = Board Product Pricing Operational Risk Strategic Planning Market Risk Internal Audit DISCLOSURE TO STAKEHOLDERS Foundation Internal Ratings (FIRB) TOTAL REGULATORY CAPITAL OR Capital Ratio (min. 8%) Standardized Stress Test Use Test = Measurement Total Book Capital less Deductions Total Regulatory Capital X 12.5 Methodology Min. Capital Ratio PILLAR II (Supervisory Review of Capital Adequacy) REGULATORY CAPITAL ADD-ON PILLAR I (Minimum Capital Requirements) Performance Measurement 5 CIRANO-PRMIA Laurentian Bank of Canada The New Basel II Accord Pillar I - Credit Risk - Standardized Approach Credit Risk Assessment X 100% of X exposure Credit Conversion Factor X 20% of X exposure (< or = 1 year), or else 50% Basel I AAA to AA- A+ BBB+ BB+ B+ Below Un Past to A- to BBB- to BB- to B- B- Rated Due Sovereign 0% 0% 20% 50% 100% 100% 150% 100% 150% Banks 20% 20% 50% 50% 100% 100% 150% 100% 150% Corporates 100% 20% 50% 100% 100% 150% 150% 100% 150% Residential Mortgages 50% 35% 100% Personal Lines of Credit 100% VISA 100% 75% 150% Small Business 100% 75% 150% Commercial 100% 100% 150% Commercial Mortgages 100% 100% 150% 75% Credit Risk Mitigation 150% = RISK WEIGHTED EXPOSURES Exposures drawn Commitments Basel II Financial Collateral LESS Guarantees Credit Derivatives On Balance Sheet Netting x 8% = MINIMUM REGULATORY CAPITAL RISK WEIGHTS SLOTTING Credit Conversion Factor less Haircuts 6 CIRANO-PRMIA Laurentian Bank of Canada Pillar I - Credit Risk - Standardized Approach An example... Exposure 1M$ Commercial secured Credit Line (secured by receivables with O/S amount at $0.5 M) Credit Conversion Factor Risk Weights Risk Weighted Exposure Credit Risk Mitigation Min. Regulatory Capital $ 0.5 M X 100% X 100% = $ 0.5 M LESS 0 X 8 % = $ 40 K $ 0.5 M X 20% X 100% = $ 0.1 M LESS 0 X8% = $8K Total $ 48 K OLD BASEL ACCORD = $ 40 K of Capital (CCF = 0% ) 7 CIRANO-PRMIA X 100% of exposure Unsecured Subordinated 75% Unsecured Senior 45% Receivables 35% Commercial Real Estate 35% X X Credit Conversion Factor X 75% of exposure Residential Real Estate 35% Other Physical 40% Gold 0% X = RISK WEIGHTED EXPOSURES 0.02% 0.05% 0.08% 0.15% 0.20% 0.30% 0.40% 0.60% 0.90% 1.50% 2.50% 4.00% 6.00% 9.00% 15.00% 20.00% 30.00% 100.00% % of Loss Given a Default (LGD) Credit Conversion Factor ADJUSTMENT FOR CORRELATION & MATURITY 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Average historical probability or default Commitments slotted by PD Risk Rating Exposures slotted by PD Pillar I - Credit Risk - Foundation Internal Rating For illustration only less X 8%= MINIMUM REGULATORY CAPITAL The New Basel II Accord CREDIT RISK MITIGATION (Credit derivatives, guarantees, on-balance sheet netting) Laurentian Bank of Canada Financial Collateral 0% 8 CIRANO-PRMIA Laurentian Bank of Canada Pillar I - Credit Risk - Foundation Internal Rating An example ... Exposures Probability of Default (PD) Credit Conversion Factor (CCF) % of Loss Given a Default (LGD) $ 0.5 M X 0.42% X 100% X 35% X $ 0.5 M X 0.42% X 75% X 35% X Adjustment for correlation and maturity 1M$ (Internal LBC Risk Rating 7) Commercial secured Credit Line (secured by receivables with $0.5 M O/S) Risk Weights Risk Weighted Exposure Min. Regulatory Capital Credit Risk Mitigation 36% = $ 0.18M 0 X8% $14 K 27% = $ 0.14M 0 X8% $11 K Total $ 25 K vs $ 48 K for the Standardized approach 9 CIRANO-PRMIA Laurentian Bank of Canada The New Basel II Accord X Unsecured Subor60% dinated Unsecured Senior Receivables Estimate of CCF X Corporate = 35% Sovereign = 35% Banks = 35% Commercial = 35% Res. Mortg.= 50% Credit lines+VISA= 61% Small Business = 35% 50% 35% Commercial Real Estate 25% Residential Real Estate 25% Other Physical 50% Financial Collateral 0% X X = less X 8%= MINIMUM REGULATORY CAPITAL 100% X % of Loss Given a Default (LGD) CREDIT RISK MITIGATION (Credit derivatives, guarantees, on-balance sheet netting) Credit Conversion Factor (CCF) ADJUSTMENT FOR CORRELATION & MATURITY 0.02% 0.05% 0.08% 0.15% 0.20% 0.30% 0.40% 0.60% 0.90% 1.50% 2.50% 4.00% 6.00% 9.00% 15.00% 20.00% 30.00% 100.00% Exposures slotted by PD 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Average historical probability or default Commitments slotted by PD Risk Rating RISK WEIGHTED EXPOSURES For illustration only Pillar I - Credit Risk - Advanced Internal Ratings 10 CIRANO-PRMIA Laurentian Bank of Canada Pillar I - Credit Risk - Advanced Internal Ratings An example ... Exposures Probability of Default (PD) Credit Conversion Factor (CCF) % of Loss Given a Default (LGD) $ 0.5 M X 0.42% X 100% X 35% X $ 0.5 M X 0.42% X 35% X 35% X Adjustment for correlation and maturity 1M$ (Internal LBC Risk Rating 7) Commercial secured Credit Line (secured by receivables with $0.5 M O/S) Risk Weights Risk Weighted Exposure Min. Regulatory Capital Credit Risk Mitigation 36% = $ 0.18M 0 X8% $14 K 13% = $ 65 K 0 X8% $5.2 K Total $ 19.2 K vs $ 48 K under the Standardized approach and $ 25 K for the Foundation Approach 11 CIRANO-PRMIA Laurentian Bank of Canada The New Basel II Accord Pillar I - Operational Risk - Basic Indicator AVERAGE OF BANKS’ ANNUAL ADJUSTED GROSS INCOME OVER LAST 3 YEARS x PRESCRIBED ALPHA FACTOR () OF 15% = MINIMUM REGULATORY CAPITAL 12 CIRANO-PRMIA Laurentian Bank of Canada The New Basel II Accord Pillar I - Operational Risk - Standardized Approach PRESCRIBED BETA Factor by Business Line Average of Bank’s annual gross income over last 3 years x Corporate finance Trading & Sales 18% 18% Retail Banking 12% Commercial Banking 15% Payment & Settlement 18% Agency Services 15% Asset Management 12% Retail Brokerage 12% = MINIMUM REGULATORY CAPITAL 13 CIRANO-PRMIA Laurentian Bank of Canada The New Basel II Accord Pillar I - Operational Risk - AMA Business Disruption and System Failures Execution, Delivery & Process Mgmt Damage to Physical Assets Employme nt Practices & Workplace safety Clients, Products ad Business Practices External Fraud Internal Fraud 7 Categories of Operational Losses 8 Business Lines Corporate Finance Trading & Sales Standardized Approach for 6 business lines Payment & Settlement Agency Services Asset Management Retail Brokerage AMA Approach for 2 businesses Commercial Banking Retail Banking Inputs Methodologies Outputs Statistical Models Statistical Distributions Regulatory Capital Self-Assessments Management Tools External Operational Loss Data Risk and Control Self-Assessment Workshops Internal Operational Loss Data Scenarios Scenario Analysis Reduction in Operational Losses 14 Laurentian Bank of Canada CIRANO-PRMIA Who is Subject to the New Basel II Accord ? In the US • Banks that are subject to the AIRB on a mandatory basis are those with total banking assets of $250 billion or more or total on-balance-sheet foreign exposure of $10 billion or more • Banks not subject to the AIRB on a mandatory basis can choose voluntarily to apply this approach. • Other banks would continue to apply the existing Basel I capital rules. Neither the standardized nor foundation approach will be permitted in the US. • Furthermore, all banks would continue to be subject to the existing capital ratio requirements. That is, a 10% total capital ratio, a 6% tier 1 capital ratio, and a 5% leverage ratio. 15 Laurentian Bank of Canada CIRANO-PRMIA Who is subject to the New Basel II Accord ? In Canada • OSFI expects implementation of AIRB by October 2006 for all material portfolios in Canada and the US by domestic banks that have total capital in excess of $5 billion Canadian, or that have greater than 10% of total assets or greater than 10% of total liabilities that are international. • For the other banks, OSFI’s guideline is less clear as there seemed to be legitimate questions about how or if the Accord should apply to other small domestic deposit-taking institutions in Canada. In other words, OSFI is debating whether smaller institutions should stay with Basel I (ex. Banks such as the recently incorporated Canadian Tire bank or Sears bank). • OSFI confirmed to Laurentian Bank that it may choose to apply voluntarily for approval from OSFI to use the AIRB approach, so long as it meets the same infrastructure requirements that other banks must satisfy. 16 Laurentian Bank of Canada CIRANO-PRMIA Results of the QIS3 Exercise For the Industry Contributions to change in capital % Change in Regulatory Capital from Current Accord (new CP3 basis) IRB Advanced Portfolio Group 1 Group 2 G10 Approach Group 1 Group 2 average minimum 11% -15% 3% -23% maximum 84% 81% Standardized IRB Foundation average minimum 3% -32% -19% -58% maximum 55% 41% IRB Advanced average minimum -2% -36% maximum 46% Corporate -4% n.a. Sovereign Bank 1% 0% n.a. n.a. Retail SME -9% -3% n.a. n.a. Securitization 0% n.a. Provisions Other portfolios -2% 2% n.a. n.a. Overall credit Risk -13% n.a. Operational Risk 11% n.a. Overall change -2% n.a. There’s considerable variation in the change in capital requirements from Basel I to Basel II. This reflects the relative risk insensitivity of the current accord 17 Laurentian Bank of Canada CIRANO-PRMIA Results of the QIS3 Exercise For the Laurentian Bank Current BIS approach 250 New Standardized Approach New IRB Foundation Approach New IRB Advanced Approach 200 150 100 50 0 Corporate Commercial Small Business Sovereign/Bank Res. Mortgages Personal Loans Line of credit & VISA The banks with the greatest reduction in capital requirements are those banks with a large proportion of retail activity” Basel May 5th, 2003 18 Laurentian Bank of Canada CIRANO-PRMIA Impact on the Industry • Banks will shift to more aggressive risk-based pricing such as in the already tightly squeezed mortgage market as these portfolios will require even less capital. Banks who do not choose to go towards the advanced approach will not be able to compete against the 6 big banks. • A bank that is highly concentrated in one or two of the businesses that will require more regulatory capital might face a crisis. An example: prime-based lending • Players in the card industry that have offered large limits as a marketing tool in their approach to customers might well have to shrink unused lines • Lending to high-quality credits will gain a strong beneficial effect and might hamper the credit offering for low quality credits. • There could be strategic implications for portfolios of construction lending, as they are classified as “high volatility” under Basel II with capital charges starting at 8% and rising as high as 28% for weaker credits 19 Laurentian Bank of Canada CIRANO-PRMIA Impact on the Industry (cont.) • Big capital markets players will face higher capital charges for securitization activities and be harder hit by operational risk charges, which are based on revenues • The potential for big banks to free up excess capital by buying a smaller bank non IRB Bank might foster mergers • Bank money management specialists will be at a disadvantage compared with non bank fund managers due to the operational risk capital they will now have to maintain • If a bank can structure a loan to reduce LGD by half, the capital requirement falls by half. Banks may respond by giving more emphasis to LGD. This is called “lending on collateral”. It has been a profitable lending activity for asset-based finance companies (e.g. Home Capital, GE Capital). Japan is an example of a lending system that over-emphasized collateral 20 Laurentian Bank of Canada CIRANO-PRMIA WILL WE HAVE AN ACCORD BY 2004? • There are sharp differences between 2 leading US Banking Supervisors. The FED is determined to reach agreement on Basel II by mid 2004 and still see the new rules come into force at the end of 2006. • On the other end, the OCC has strong reservations as it feels the rules are excessively complex and detailed making them difficult for banks to implement and supervisors to enforce. Furthermore, they would like to see a QIS4. • Following comments received by the banking industry, competitive effects of the New Accord are determined to be significant. Some of the big banks that are supposed to be the prime beneficiaries of Basel II have strong reserves and contend that the potential risks of the New Accord are too great. • In Canada, banks have requested a further delay of 1 year for implementation without support from US banks have indicated that they will be ready on time. 21