* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Definition - KhmerDocs
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Relative clause wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
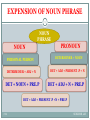
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
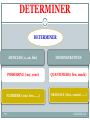
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
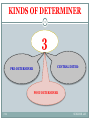
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Vietnamese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Determiner phrase wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
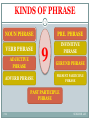
Phrases, Clauses and Sentences 1 PREPARED BY SENGHOR LAY CUE SENGHOR LAY What is a phrase? 2 Definition: A phrase is a small group of words that adds meaning to a word. A phrase is not a sentence because it is not a complete idea with a subject and a predicate. CUE SENGHOR LAY KINDS OF PHRASE 3 PRE. PHRASE NOUN PHRASE VERB PHRASE ADJECTIVE PHRASE ADVERB PHRASE 9 INFINITIVE PHRASE GERUND PHRASE PRESENT PARTICIPLE PHRASE PAST PARTICIPLE PHRASE CUE SENGHOR LAY What is a noun phrase? 4 Definition: A noun phrase is a group of words that does the work of noun. A noun phrase is either a pronoun or any group of words that can be replaced by a pronoun. CUE SENGHOR LAY STRUCTURES OF NOUN PHRASE 5 Noun pre-modifier Modifiers before the noun are called premodifiers. ( modify means to limit, restrict, characterize, or otherwise focus meaning ) All of pre-modifiers that are present and noun together form A NOUN PHRASE. CUE SENGHOR LAY 6 Noun post-modifier Modifiers coming after a noun are called postmodifiers. NOUN PHRASE PRE-MODIFIER + NOUN Ex- white house, the three old democratic legislators… CUE SENGHOR LAY 7 NOUN PHRASE NOUN + POST-MODIFIER The most common post- modifier is Prepositional phrase Ex- The glass on the table, the boy in the store…………. CUE SENGHOR LAY 8 NOUN PHRASE Pre-modifier + noun + post-modifier Ex- The boy on the top of the house……………. The overhead projector on the ceiling…… The teacher next to the window…………… CUE SENGHOR LAY EXPENSION OF NOUN PHRASE 9 NOUN PHRASE NOUN PERSONAL PERSON DETERMINER + ADJ + N DET + NOUN + PRE.P PRONOUN DETERMINER + NOUN DET + ADJ + PRESENT .P + N DET + ADJ + N + PRE.P DET + ADJ + PRESENT .P +N + PRE.P CUE SENGHOR LAY What is a determiner? 10 Definition: Determiner is a word that is used to clarify the noun. To define something or someone To state the amount of people, things or other nouns To state possessive To state something or someone is specific To state how things or people are distributed To state the difference between noun To state someone or something is not specific CUE SENGHOR LAY DETERMINER 11 DETERMINER ARTICLES ( a, an, the) DEMONSTRATIVES POSSESSIVE ( my, your) QUANTIFIERS ( few, much) NUMBERS ( one, two…...) ORDINALS ( first, second…….) CUE SENGHOR LAY KINDS OF DETERMINER 12 3 PRE-DETERMINER CENTRAL DETER- POST-DETERMINER CUE SENGHOR LAY What is a pre-determiner? 13 Definition: A pre-determiner is a word that is used to put in front of other determiners in noun phrase. Pre-determiner can be The subset ( all, both, half…..) Ex- all the children, both the boys, half the children CUE SENGHOR LAY 14 Multipliers that consisting of ( once, twice, thrice ) Ex- once a day, twice a day, thrice a day…………… Fraction other than half ( one-tenth, two-third…) Ex- one-tenth the speed, two-third the time………….. CUE SENGHOR LAY 15 The subset ( double, treble, quadruple…) Ex- They now earn double their previous salary. Multiplying expression headed by times Ex- ten times the fatalities, three times a day four times each month……………………….. CUE SENGHOR LAY 16 Exclamation ( what which ) can precede the indefinite article Ex- what a day, what a happy occasion, such a friend CUE SENGHOR LAY What is a central determiner? 17 Definition: A central determiner is a word that is used to put after pre-determiner ( not all). Ex- four time a day, two- third the time…….. CUE SENGHOR LAY CENTRAL DETERMINERS 18 CENTRAL DETERMINERS ARE ARTICLES DEMONSTRATIVES POSSESSIVE DETERMINERS INTERROGATIVE DETERMINERS RELATIVE DETERMINERS NOMINAL RELATIVE DETERMINERS ( WHICH) WH-CONDITIONAL DETERMINER ( WHAT) INDEFINITE DETERMINER ( some, any) CUE SENGHOR LAY What is a post-determiner? 19 Definition: A post-determiner is a word that is used to put after pre-determiner and central determiner. Cardinals Ex- all my six children, all my two brothers…………. CUE SENGHOR LAY 20 Primary ordinals Ex- her twenty-first birthday……………………….. General ordinals Ex- both her other daughter………………………….. Primary quantifiers Ex- all your few suggestions…………………………… CUE SENGHOR LAY What is a modifier? 21 Definition: A modifier is a word or sentence element that is used to limit or qualify another word, a phrase or a clause. FORMS OF MODIFIER ADJECTIVE CUE ADVERB SENGHOR LAY KINDS OF MODIFIER 22 MODIFIER PRE-MODIFIER CUE POST-MODIFIER SENGHOR LAY What is a pre-modifier of noun? 23 Definition: A pre-modifier of noun is a word that is used to put before noun and modify noun. PRE-MODIFIER OF NOUN CAN BE ADJECTIVE OR ADJECTIVE PHRASE Ex- one single blood-pressure measurement………… CUE SENGHOR LAY 24 NOUN OR NOUN PHRASE Ex- It is a hundred and fifty pound job…………… -ING PARTICIPLE Ex- the coming weeks…………………………………….. -ED PARTICIPLE Ex- wasted natural resources…………………………… CUE SENGHOR LAY 25 GENITIVE NOUN PHRASE Ex- the old soldier’s way…………………………… NUMERAL Ex- six essays…………………………………………… ADVERB Ex- the then managing editor…………………….. CUE SENGHOR LAY 26 PREPOSITIONAL PHRASE Ex- behind- the- scenes negotiation………………….. CLAUSE Ex- It is required to allow updating and track entries by data from several sensors using a read and lock procedure call. CUE SENGHOR LAY What is a post-modifier of noun? 27 Definition: A post-modifier of noun is a word that is used to put after noun. Post-modifier of noun can be PREPOSITIONAL PHRASE Ex- It is just a question of which is the more efficient approach. CUE SENGHOR LAY 28 FINITE RELATIVE CLAUSE Ex- We don’t have a constitution which stops government from legislating certain things. RELATIVE -ING PARTICIPLE CLAUSE Ex- The air mass bringing the coldest temperatures is the polar continental mass which comes in from the Soviet Union. CUE SENGHOR LAY 29 RELATIVE -ED PARTICIPLE CLAUSE Ex- It is a school project planned for mine. RELATIVE INFINITIVE CLAUSE Ex- And again Fred when is the time to do it. CUE SENGHOR LAY 30 APPOSITIVE FINITE CLAUSE Ex- It is really shorthand for the view that well-being depends on more than the absence of the disease. ADVERB Ex- ………………….so you arrived the day before did you. CUE SENGHOR LAY 31 ADJECTIVE Ex- Ohm let me fine you something ethnic. NOUN PHRASE Ex- He is in his address this morning. CUE SENGHOR LAY FUNCTION OF NOUN PHRASE 32 NOUN PHRASE CAN BE USED 1- SUBJECT Ex- My old laptop is not working now. CUE SENGHOR LAY 33 2- DIRECTIVE OBJECT Ex- …………………..sign your name there. 3- INDIRECT OBJECT Ex- I always tell people the truth when I was young. CUE SENGHOR LAY 34 4- SUBJECTIVE PREDICATE Ex- Uh faith has been a gift for you. 5- OBJECTIVE PREDICATE Ex- I called this little talk a survey of global economic crisis. CUE SENGHOR LAY 35 6- COMPLEMENT OF PREPOSITION Ex- Ohm but why isn’t it in French. 7- PRE-MODIFIER OF A NOUN OR NOUN PHRASE Ex- Simon is on this revision course. CUE SENGHOR LAY 36 8- VOCATIVE Ex- You are a teacher of English, Dad. 9- ADVERBIAL Ex- The flag goes up far side. CUE SENGHOR LAY 37 10- PRE-MODIFIER OF ADJECTIVE Ex- The plane was 4 hours late. 11- PRE- MODIFIER OF PREPOSITION Ex- He revealed Washington had informed Pakistan an hour before the start of assault. CUE SENGHOR LAY 38 12- PRE-MODIFIER OF ADVERB Ex- Now Mercedes have always been good at insulting their car but they are gone a stage further with this. 13- POST-MODIFIER OF NOUN Ex- Women may suffer from lack of acceptable because too many of men their ages are dead. CUE SENGHOR LAY 39 14- POST-MODIFIER OF ADJECTIVE Ex- We are short fifteen dollars. Ex- Students are short two hundred dollars. CUE SENGHOR LAY What is an adjective? 40 Definition: An adjective is a word that is used to modify or to describe a noun or pronoun. ADJECTIVE ANSWERS Which…..? CUE What kind…? How many..? SENGHOR LAY What is an adjective phrase? 41 Definition: An adjective phrase is a group of words that does the work of an adjective. The adjective phrase has its head as an adjective, which may preceded by premodifiers and followed by post-modifiers. Sometimes only one adjective is also an adjective phrase. CUE SENGHOR LAY STRUCTURES OF ADJECTIVE PHRASE 42 ADJECTIVE PHRASES ARE PRE-MODIFIER + ADJECTIVE PRE-MODIFIER + ADJECTIVE + POST-MODIFIER ADJECTIVE CUE SENGHOR LAY What is a pre-modifier of adjective? 43 Definition: A pre-modifier of adjective is a word that is used to put before an adjective. Generally, the pre-modifier is an intensifier. Ex- This is a perfectly good conversation as far as I am concerned. Ex- That is a bit premature, isn’t it. CUE SENGHOR LAY What is a post-modifier of adjective? 44 Definition: A post-modifier of adjective is a word that is used to put after an adjective. Adjectives are typically post-modified by prepositional phrases and various kinds of clause. CUE SENGHOR LAY POST-MODIFIERS ARE 45 1-PREPOSITIONAL PHRASE Ex- I was afraid of him, didn’t really know him. 2-THAT- CLAUSE Ex- I expect you are glad you are not a vegetarian. CUE SENGHOR LAY 46 3- WH -CLAUSE Ex- Yes, you have to be careful what is available in what color. 4- TO INFINITIVE CLAUSE Ex- If you have any questions then I would be happy to hear from you, but would you please allow me until 7 May. CUE SENGHOR LAY 47 5- ING- PARTICIPLE CLAUSE Ex- But police were busy handling out letters about operation to residents and Bush was happy with the result. 6- COMPARATIVE CLAUSE Ex- No I am sure it is easier than they say. CUE SENGHOR LAY 48 7- ADVERB Ex- It certainly tasted strong enough. CUE SENGHOR LAY FUNCTIONS OF ADJECTIVE PHRASE 49 ADJECTIVE PHRASE CAN BE USED 1- PRE-MODIFIER OF A NOUN Ex- Well, it is a much less popular route. 2- SUBJECTIVE PREDICATE Ex- No I mean Palin was extraordinary ugly. CUE SENGHOR LAY 50 3- OBJECTIVE PREDICATE Ex- He is opening his mouth very wide just now. 4- POST-MODIFIER OF A PRONOUN Ex- There would still be eyes watching and wondering from a distance but, briefly there was no one close. CUE SENGHOR LAY 51 5- POST-MODIFIER OF NOUN Ex- To outsider London seems one of the most vibrant culture capitals of the world, a city bright with theaters ballet galleries. CUE SENGHOR LAY 52 6- NOMINAL ADJECTIVE Ex- Tonight I hope you will not mind if I eschew the academic. 7- COMPLEMENT OF A PREPOSITION Ex- Kaye doesn’t finish till late. CUE SENGHOR LAY What is an adverb? 53 Definition: An adverb is a word that is used to modify or describe a verb, an adjective or another adverbs. ADVERB ANSWERS WHEN….? WHERE…? CUE HOW MUCH..? HOW..? TO WHAT DEGREE…? SENGHOR LAY What is an adverb phrase? 54 Definition: An adverb phrase is a group of words that does the work as an adverb. An adverb phrase has its head an adverb, which may be preceded by pre-modifier and sometimes followed by post- modifier. CUE SENGHOR LAY What is a pre-modifier of adverb? 55 Definition: A pre-modifier of adverb is a word that is used to put before adverb. The most common pre-modifier is ( very ). Ex- I wear this occasionally but very rarely. CUE SENGHOR LAY What is a post-modifier of adverb? 56 Definition: A post-modifier of adverb is a word that is used to put after adverb. Two adverb intensifiers- enough and indeed are commonly post-modified adverb. Ex- It was quoted often enough in the recent debate in the other place. CUE SENGHOR LAY STRUCTURES OF ADVERB PHRASE 57 ADVERB PHRASE PRE-MODIFIER + ADVERB CUE PRE-MODIFIER +ADVERB + POST-MODIFIER SENGHOR LAY FUNCTIONS OF ADVERB PHRASE 58 1- PRE-MODIFIER OF AN ADJECTIVE Ex- We are far too close to it. 2- PRE-MODIFIER OF AN ADVERB Ex- I am going to give you a prescription to clear up the infection, then you need to have your teeth extremely cleaned, as soon as possible. CUE SENGHOR LAY 59 3- ADVERBIAL Ex- Refunds of fee are not normally available. 4- SUBJECTIVE PREDICATE Ex- I thought he was here. CUE SENGHOR LAY 60 5- PRE-MODIFIER OF A PREPOSITION Ex-But I have a feeling they might be right by the door. 6- PRE-MODIFIER OF A PRONOUN Ex- When I look around my friends, virtually all of them seem to have got job careers. CUE SENGHOR LAY 61 7- PRE-MODIFIER OF A DETERMINER Ex- Everybody knows that the results in fact have absolutely no meaning and can be interpreted any way you like. 8- PRE-MODIFIER OF A NUMERAL Ex- The chap around forty is called Obama. CUE SENGHOR LAY 62 9- PRE-MODIFIER OF A NOUN PHRASE Ex- This is really quite a problem I imagine. 10- POST-MODIFIER OF A NOUN PHRASE Ex- Your friend here speaks English well. CUE SENGHOR LAY 63 11- POST-MODIFIER OF AN ADJECTIVE OR ADVERB Ex- Well right that is fair enough then. 12- OBJECTIVE PREDICATE Ex- Shall I move these way? CUE SENGHOR LAY 64 13- SUBJECTIVE PREDICATE Ex- At least we are outside. 14- COMPLEMENT OF PREPOSITION Ex- Oh I should have thought he have had before now. CUE SENGHOR LAY 65 CUE SENGHOR LAY What is a preposition? 66 Definition: A preposition is a part of speech that shows a relationship between two things. PREPOSITION CAN BE ABOUT LOCATION (ON, UNDER, IN..) CUE TIMING (BEFORE, AFTER, DURING………..) DIRECTION (FROM, TOWARD, TO…………………..) SENGHOR LAY 67 CUE SENGHOR LAY What is a prepositional phrase? 68 Definition: A prepositional phrase is a group of words that consists of a preposition and followed by noun phrase that serves as the object of the preposition. A prepositional phrase is composed of the preposition and a following noun phrase. CUE SENGHOR LAY FORMS OF PREPOSITIONAL PHRASE 69 PREPOSITIONAL PHRASE PREPOSITION + NOUN ( PHRASE) CUE PREPOSITION + DETERMINER + NOUN ( PHRASE ) SENGHOR LAY 70 Prepositional phrases are used either adjectively to modify noun or adverbially to modify verbs, adjectives, or clause. Ex- The man in the house rented it. Ex- He went in the arena. Ex- Obama was happy about the goal. Ex- On reflection, I believe that Palin was a good nominee to be named. CUE SENGHOR LAY FUNCTIONS OF PREPOSITIONAL PHRASE 71 1- POST-MODIFIER OF NOUN Ex- Everybody questions the significance of the result. 2- POST-MODIFIER OF AN ADJECTIVE Ex- He was happy with his results. CUE SENGHOR LAY 72 3- SUBJECTIVE PREDICATE Ex- Yesterday, the sun was just as it is in India. 4- OBJECTIVE PREDICATE Ex- From the time I bought her out of hospital she never slept. CUE SENGHOR LAY 73 CUE SENGHOR LAY What is a verb? 74 Definition: A verb is a word that expresses action or otherwise helps to make a statement. CUE SENGHOR LAY 75 CUE SENGHOR LAY What is a verb phrase? 76 Definition: A verb phrase is composed of the verb of the sentence and any modifiers of verb, including adverb, prepositional phrase or object. A verb phrase is a group of verbs that consists of one or two helping verb (s) and one main verb. CUE SENGHOR LAY What is a helping verb? 77 Definition: A helping verb is a kind of verbs that is used to help other verbs make negative, interrogative sentence and make tenses or aspects. Definition: A main verb is a kind of verbs that is used to state the action of subject. ( Main verb can’t be omitted ) CUE SENGHOR LAY FORMS OF VERB PHRASE 78 VERB PHRASE MAIN VERB CUE HELPING VERB + MAIN VERB AUX + AUX + MAIN VERB SENGHOR LAY What is an infinitive? 79 Definition: An infinitive is the name of certain verb forms that exists in many language. In the usual description of English, the infinitive of a verb is its basic form with or without the particle ( to): therefore, do and to do, be and to be and so on are infinitives. CUE SENGHOR LAY FORMS OF INFINITIVE VERB 80 INFINITIVE VERB CAN BE VERB CUE TO + VERB TO + ADVERB + VERB SENGHOR LAY KINDS OF INFINITIVE VERB 81 INFINITIVE BARE INFINITIVE CUE FULL INFINITIVE CLEFT INFINITIVE SENGHOR LAY HOW TO USE BARE INFINITIVE 82 Bare infinitive is used as the main verb after dummy auxiliary verb ( do or most modal auxiliary verbs ( will, can……….) Ex- Obama will give an official speech to his great citizens after he is nominated. CUE SENGHOR LAY 83 Bare infinitive is used after several verbs of perception ( see, watch, hear, and sense take a direct object and a bare infinitive). Ex- I heard Cambodian prime minister speak in the conference yesterday. Ex- Sarah Palin watches her speech be broadcast on CNN. CUE SENGHOR LAY 84 Bare infinitive is used after several verbs of permission or causation including ( make, bid, let, and have………………………………) Ex- She always makes me cry everyday. Ex- Hillary lets Mc cain give a speech to his supporters in the white house. CUE SENGHOR LAY 85 Bare infinitive is used as present subjunctive form and imperative form Ex- PAD always demands Thai prime minister be punished after he declined to solve economic downturn for his nations. CUE SENGHOR LAY HOW TO USE FULL INFINITTIVE 86 Full infinitive is used like a noun phrase to be a subject of a verb. Ex- To speak is very difficult for people who do not want to speak. Ex- To study seems uncomfortable. CUE SENGHOR LAY 87 Full infinitive is used like an adjective or adverb, expressing purpose or intent. Ex- Obama is the man to talk to in the meeting. Ex- Clinton is the former president to be named. CUE SENGHOR LAY 88 Full infinitive is used as an object of a verb. Ex- She wants to speak English with Palin. Full infinitive is used after the direct object of many transitive verbs. Ex- I asked her to make his case on his behalf. CUE SENGHOR LAY 89 Full infinitive is used after an intransitive verb, together with a subject using the preposition ( for ). Ex- I arranged for him to accompany me or I waited for summer to arrive. CUE SENGHOR LAY HOW TO USE CLEFT INFINITIVE 90 Cleft infinitive is used to emphasize subject. Ex- He wants me to strongly shout. Ex- Hillary wants Obama to strictly reform the USA after election. CUE SENGHOR LAY What is an infinitive phrase? 91 Definition: An infinitive phrase is composed of an infinitive verb and any modifying adverbs or prepositional phrase. The infinitive phrase has three functions NOUN CUE ADJECTIVE ADVERB SENGHOR LAY EXAMPLES 92 Ex- My duty as a coach is to teach skills. Ex- My sister wanted a cat to love. Ex- Bill is eager to work on his skating. CUE SENGHOR LAY What is a gerund? 93 Definition: A gerund is a verbal that ends in – ing and functions in a sentence as a noun. VERB + ING CUE SENGHOR LAY HOW TO USE GERUND 94 1- GERUND AS SUBJECT Ex- Travelling might satisfy your desire for new new experiences. 2- GERUND AS DIRECT OBJECT Ex- They do not appreciate singing at concert. CUE SENGHOR LAY 95 3- GERUND AS SUBJECT COMPLEMENT Ex- My cat’s favorite activity is sleeping. 4- GERUND AS OBJECT OF PREPOSITION Ex- The police arrested him for kissing an 80-year old woman in the garden during water festival. CUE SENGHOR LAY 96 5- GERUND AFTER VERB PATTERN CUE admit avoid Carry on consider delay deny dislike enjoy finish imagine involve practise SENGHOR LAY 97 6- GERUND AFTER SPECIAL PHRASE CUE To be busy Couldn’t help Don’t mind How about It is no good There is no What about Spend on time It is no use There is no point Worth… Feel like SENGHOR LAY 98 7- GERUND AFTER PREPOSITION Ex- After having a shower, I waited for Palin. 8-GERUND IN PASSIVE Ex- I have three shirts that need washing. ( need, require, want……………………..) CUE SENGHOR LAY What is a gerund phrase? 99 Definition: A gerund phrase is a group of words that consists of a gerund and the modifiers ( pronoun, noun phrase, prepositional phrase, to infinitive phrase (adverb). GERUND PHRASE GERUND + DIRECT OBJECT CUE GER + D.O + PRE.P GER + D.O + TO INFI.P SENGHOR LAY HOW TO USE GERUND PHRASE 100 1- GERUND PHRASE AS SUBJECT Ex- Finding a good teacher needs time. 2- GERUND PHRASE AS DIRECT OBJECT Ex- I hope that you appreciate my offering you this opportunity. CUE SENGHOR LAY 101 3- GERUND PHRASE AS SUBJECT COMPLEMENT Ex- Obama’s strategy has been lying to his supporters. 4- GERUND PHRASE AS OBJECT OF PREPOSITION ( FOR) Ex- You might get in trouble for taking an illness to avoid work. CUE SENGHOR LAY What is a present participle? 102 Definition: A present participle verb is a kind of verbs that ends in – ing form and functions as verb and as attributive verb. VERB + ING CUE SENGHOR LAY HOW TO USE PRESENT PARTICIPLE VERB 103 1- PRESENT PARTICIPLE VERB is used to form the present action or present progressive. Ex- Susanna is learning English at CUE now. 2- PRESENT PARTICIPLE is used as adjective to modify noun. Ex- The watering can that is used by Obama is mine. CUE SENGHOR LAY 104 3- PRESENT PARTICIPLE is used to modify verb or sentence. Ex- Broadly speaking, the project was successful. Ex- Running for office, the senator tried to ignore the fact he took bribes. CUE SENGHOR LAY What is a past participle verb? 105 Definition: A past participle verb is a kind of verbs that is finished by ( -ed ) or changed to the other form that depends on verbs. VERB + ED CUE SENGHOR LAY HOW TO USE PAST PARTICIPLE 106 1- PAST PARTICIPLE is used to form the present perfect aspect. Ex- He has studied English since he was 12. 2- PAST PARTICIPLE is used to form passive voice. Ex- The chicken was eaten after cook. CUE SENGHOR LAY 107 3- PAST PARTICIPLE is used to modify a noun, active sense. Ex- Our fallen comrades will suffer at night. 4- PAST PARTICIPLE is used to modify a noun , passive sense. Ex-Our arrested hero will speak to his supporters at 12. CUE SENGHOR LAY 108 4- PAST PARTICIPLE is used to modify a verb or sentence. Ex- Given a wonderful handkerchief, Serey Mon smiles and says thank you to his audience. CUE SENGHOR LAY What is a clause? 109 Definition: A clause is a unit containing a lexical verb. A clause is a unit that consists of a subject and followed by a predicate. CUE SENGHOR LAY KINDS OF CLAUSE 110 CLAUSE UPSTAIRS CLAUSE CUE DOWNSTAIRS CLAUSE SENGHOR LAY What is an upstairs clause? 111 Definition: An upstairs clause is a group of words that contains a subject and a predicate and expresses a complete thought. SUBJECT + PREDICATE (COMPLETE IDEA ) CUE SENGHOR LAY What is a downstairs clause? 112 Definition: A downstairs clause is a group of words that contains a subject and a predicate, but doesn’t express a complete thought. A downstairs clause is often marked by a dependent marker word. CUE SENGHOR LAY KINDS OF DOWNSTAIRS CLAUSE 113 DOWNSTAIRS CLAUSE NOUN CLAUSE CUE ADJECTIVE CLAUSE ADVERB CLAUSE SENGHOR LAY What is a noun clause? 114 Definition: A noun clause is a downstairs clause that functions as a noun within upstairs clause. NOUN CLAUSE USUALLY BEGINES WITH How , Why, What, Where, When, Who, That, Which, Whose, Whether…. CUE SENGHOR LAY KINDS OF NOUN CLAUSE 115 NOUN CLAUSE THAT WHCLAUSE CLAUSE CUE INFINITIVE -CLAUSE INGCLAUSE SENGHOR LAY EXAMPLES 116 Ex- Everyone believes that Koy is the most handsome in Phnom Penh. Ex- What Obama believes is not very important. Ex- My plan is to marry Brad Pitt. Ex- I am scared of losing Brad I don’t move to Hollywood. CUE SENGHOR LAY FUNCTIONS OF NOUN CLAUSE 117 1- NOUN CLAUSE is used as subject. Ex- That Bush left early surprised us. 2- NOUN CLAUSE is used as complements Ex-The problem is that Cambodia is not a rich country. CUE SENGHOR LAY 118 3- NOUN CLAUSE is used as an object of a verb. Ex- We didn’t realize that Obama can resolve problem. 4- NOUN LAUSE is used as an object of a gerund. Ex- Finding out that Sok cried makes us bored. CUE SENGHOR LAY 119 5- NOUN CLAUSE is used as an object of an infinitive. Ex- He needs to know that she was arrested yesterday. 6- NOUN CLAUSE is used as an object of a preposition. Ex- The gossip was about why was arrested yesterday. CUE SENGHOR LAY 120 7- NOUN CLAUSE is used as an object of a participle. Ex- Realizing that she was killed, we ran to Paris. 8- NOUN CLAUSE is used as a complement of an adjective. Ex- Are you sure that she was accused of killing? CUE SENGHOR LAY What is an adjective clause? 121 Definition: An adjective clause, also called relative clause, is a group of words that contains a subject and a predicate of its own and does the work of an adjective. An adjective clause is a downstairs clause that does the work as an adjective. CUE SENGHOR LAY 122 Adjective clause or relative clause always begins with relative pronouns. Who Whom Whose CUE Where Which That When SENGHOR LAY 123 We use adjective clause, also called relative clause, to identify or give additional information about nouns (people, places, or things…….). CUE SENGHOR LAY 124 Who and Whom Are used only for person or people. (Who) is the subject of the clause. After ( who) you should see a verb. ( whom) is the object of the clause. After ( whom) you should see a subject (noun, pronoun). CUE SENGHOR LAY 125 Sentence with adjective clause Can be seen as combination of two sentences. I have a friend. She loves to shop. Ex- I have a friend who loves to shop. CUE SENGHOR LAY 126 who The man is playing baseball. The man is holding a bat. Ex- The man who is holding a bat is playing baseball. CUE SENGHOR LAY 127 Whom I see the doctor in the room. The doctor is my father. Ex- The doctor whom you see in the room is my father. CUE SENGHOR LAY 128 Which Is used only for things which can be both subject and object of the clause. The telephone is in your room. The telephone is ringing. Ex- The telephone which is in your room is ringing. CUE SENGHOR LAY 129 That Is used for both people and things ( less formal than whom and which ) That can be both subject and object of the clause. I see the flowers. The flowers are in the pond. Ex- The flowers that you see are in the pond. CUE SENGHOR LAY 130 Whose Is the possessive and is used for both people and things and must be followed by a noun. Whose + noun CUE can be subject or obj. SENGHOR LAY 131 Ex- I heard the scientist whose work is attracting interesting. Ex- I met the scientist whose work I admire. Whose The girl is crying. Her cat is sick. Ex- The girl whose cat is sick is crying. CUE SENGHOR LAY 132 The verb in the adjective clause is singular if the subject relative clause refers to a singular noun. It is plural if it refers to a plural noun. Ex- Ben is my friend who lives in Boston. Ex- John and Alex are my friends who live in Paris. CUE SENGHOR LAY 133 Who, whom, which, that, (o) Can be the subject of the preposition in its clause. If the preposition is at the beginning of the clause, whom or which must be used. CUE SENGHOR LAY 134 In formal English, we put the preposition at the beginning of the clause. Also, we use only whom not who or that to refer to people, and which not that to refer to things. Ex- He is the writer who I work for. He is the writer for whom I work. CUE SENGHOR LAY 135 Where Modifies the noun place ( country, city, building, house, room, street, and so on ). Ex- I want to know the name of city where you you were born. CUE SENGHOR LAY 136 When Modifies the noun time ( century, year, …). Ex- Obama wants to know the date when you were born. Ex- I will tell her the time when I am free. CUE SENGHOR LAY ADJECTIVE CLAUSE 137 ADJECTIVE CLAUSE RESTRICTIVE ADJECTIVE CLAUSE CUE NONRESTRICTIVE ADJECTIVE CLAUSE SENGHOR LAY 138 RESTRICTIVE ADJECTIVE CLAUSE Identify the noun or pronoun modified. It gives information needed in order to know who or what the pronoun refers to. Ex- The car that has broken headlights belongs to my teacher of English. CUE SENGHOR LAY 139 NON-RESTRICTIVE ADJECTIVE CLAUSE Give extra information about the noun or pronoun but is not needed to identify it. Ex- The Eiffel Tower has an elevator, which I rode to the top. CUE SENGHOR LAY 140 NON-RESTRICTIVE ADJECTIVE CLAUSE Use CUE Who, which, whom, whose, where, when SENGHOR LAY 141 IN NON-RESTRICTIVE CLAUSE Do not use the relative pronoun ( that). Do not omit the objective relative pronoun. Always put commas around a nonrestrictive adjective clause. CUE SENGHOR LAY 142 If an adjective clause is a restrictive adjective clause, the adjective phrase is a restrictive adjective phrase. If an adjective clause is a non- restrictive adjective clause, the adjective phrase is a non-restrictive adjective phrase. CUE SENGHOR LAY What is an adverb clause? 143 Definition: An adverb clause is a subordinate clause that functions as an adverb within main clause. CUE SENGHOR LAY KINDS OF ADVERB CLAUSE 144 ADVERB CLAUSE OF 1- TIME 2- REASON 3- CONCESSION 4- CONTRAST 5- RESULT 6- PURPOSE 7- PLACE 8- MANNER CUE SENGHOR LAY What is an adverb of time? 145 Definition: An adverb clause of time is an adverb clause that is introduced by When, whenever, while, as, before, after, till, until, since, and as soon as. CUE SENGHOR LAY EXAMPLES 146 When he arrives, he will tell us the truth. Mary was dancing while Bush was singing. The train left as we arrived. CUE SENGHOR LAY What is an adverb clause of reason? 147 Definition: An adverb clause of reason is an adverb clause that is introduced by Because, since, for, and as …. CUE SENGHOR LAY EXAMPLES 148 I was late because I could not catch the bus. The manager dismissed Mary for she was very lazy. As the weather was bad, we cancelled the picnic. CUE SENGHOR LAY What is an adverb of concession? 149 Definition: An adverb of concession is an adverb clause that is introduced by Though, although, even though, no matter how, no matter what, and as,….. CUE SENGHOR LAY EXAMPLES 150 Although he is small, he is very strong. No matter how smart they are, they are required to do the revision. No matter what the doctor did, the girl was dead. CUE SENGHOR LAY What is an adverb clause of contrast? 151 Definition: An adverb clause of contrast is an adverb clause that is introduced by Whereas, and while… CUE SENGHOR LAY EXAMPLES 152 We took the train whereas Peter drove. While Obama is a good math student, we do well in English. CUE SENGHOR LAY What is an adverb clause of result? 153 Definition: An adverb clause of result is an adverb clause that always linked with So that, so+ adjective/ adverb + that and such + a + noun + that,….. CUE SENGHOR LAY EXAMPLES 154 Tom was so weak that he could not run. It was such a strange story that no one believe it. CUE SENGHOR LAY What is an adverb clause of purpose? 155 Definition: An adverb clause of purpose is an adverb clause that always linked with So that, in order that, for fear that, in case,…. CUE SENGHOR LAY EXAMPLES 156 He arrived earlier so that he would not late. They brought a lot of food for fear that they would be hungry during the trip. She brought the credit card in case she did not have enough cash. CUE SENGHOR LAY What is an adverb clause of place? 157 Definition: An adverb clause of place is an adverb clause that is introduced by Where, and wherever Ex- Nobody knows where he has been. Ex- He travels wherever he like. CUE SENGHOR LAY What is an adverb clause of manner? 158 Definition: An adverb clause of manner is an adverb clause that is introduced by As, as if, and as though…. CUE SENGHOR LAY EXAMPLES 159 Please do as I have told you. note He cries as if he were mad. He speaks as though he were the boss. The subjunctive is used after as if, as though. CUE SENGHOR LAY COMPLETE 160 IDEA SUBJECT CUE PREDICATE SENGHOR LAY What is a sentence? 161 Definition: A sentence is a group of words that beginning with a capital letter and ending with a full stop, exclamation, or question mark . In written language, containing a main verb. A sentence is a group of words that usually contains a subject and a predicate and expresses a complete idea. CUE SENGHOR LAY What is a sentence? 162 Definition: A sentence is a group of words that expresses a complete thought. Sentence has two parts SUBJECT CUE PREDICATE SENGHOR LAY KINDS OF SENTENCE 163 SENTENCE CUE 1- SIMPLE SENTENCE 2- COMPOUND SENTENCE 3- COMPLEX SENTENCE 4- COMPOUND COMPLEX SENTENCE SENGHOR LAY What is a simple sentence? 164 Definition: A simple sentence, also called as an independent clause, is a group of words that contains a subject and a predicate. It expresses a complete thought. Ex- My teacher is a Cambodian. CUE SENGHOR LAY What is a compound sentence? 165 Definition: A compound sentence is a sentence that contains two independent clauses joined by coordinators. Coordinators are also called FANBOYS CUE SENGHOR LAY What is a complex sentence? 166 Definition: A complex sentence is a sentence that has one independent clause and joined by one or more dependent clause (s). Ex- Palin will work with Obama after she is nominated. CUE SENGHOR LAY What is a compound complex sentence? 167 Definition: A compound complex sentence is a sentence that is composed of two independent clauses and one or more dependent clause (s). Ex- She wants to be an educator, but Susanna doesn’t want to do after she graduates. CUE SENGHOR LAY SOME ADDITIONAL SENTENCES 168 CLEFT SEENTENCE Definition: A cleft sentence is a sentence formed by a main clause and a subordinate clause, which together express a meaning that could be expressed by a simple sentence. Ex- It was from John that she heard the news. CUE SENGHOR LAY What is a universal sentence? 169 Definition: A universal sentence is the sentence in the present tense sometime refers to a state which holds at all times or at every time in the existence of the referent of the subject. Ex- The sun rises in the east. Ex- The earth is round. CUE SENGHOR LAY What is an imperative sentence? 170 Definition: An imperative sentence is a kind of sentences that is used to give a command. An imperative sentence sometime subject is understood. Ex- Please, have a look at handsome man. CUE SENGHOR LAY What is a matrix sentence? 171 Definition: A matrix sentence is a sentence that has been embedded as a constituent. Ex- After eating the raw fish, the cat died. CUE SENGHOR LAY