* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Math 7 Pre_AP
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical proof wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Secondary School Mathematics Curriculum Improvement Study wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics and architecture wikipedia , lookup
Philosophy of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Elementary mathematics wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematical notation wikipedia , lookup
Foundations of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Ethnomathematics wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics and art wikipedia , lookup
List of important publications in mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical model wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
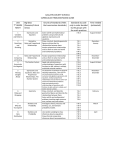
Test Code Year Form 1171 16 3 Last Revision Date: 04/29/2016 ACP Blueprint Mathematics 7 Pre-AP Semester 1, 2016-2017 Reporting Category TEKS/SE R or S No. of Items % of Test 1. Computational and Algebraic Relationships determine the constant of proportionality (k = y/x) within mathematical and real-world problems. 2 7.4C S 1 4% 2. Computational and Algebraic Relationships represent linear relationships using verbal descriptions, tables, graphs, and equations that simplify to the form y = mx + b. 2 7.7A R 2 7% 3. Number and operations. Order a set of real numbers arising from mathematical and real-world contexts. 1 8.2D R 2 7% 4. Proportionality. Graph proportional relationships, interpreting the unit rate as the slope of the line that models the relationship. 2 8.4B R 2 7% 5. Proportionality. Use data from a table or graph to determine the rate of change or slope and y-intercept in mathematical and real-world problems. 2 8.4C R 3 11% 6. Proportionality. Represent linear proportional situations with tables, graphs, and equations in the form of y = kx. 2 8.5A S 3 11% 7. Proportionality. Represent linear non-proportional situations with tables, graphs, and equations in the form of y = mx + b, where b does not equal 0. 2 8.5B S 3 11% 8. Proportionality. Use a trend line that approximates the linear relationship between bivariate sets of data to make predictions. 4 8.5D R 2 7% 9. Proportionality. Solve problems involving direct variation. 2 8.5E S 2 7% 10. Proportionality. Identify functions using sets of ordered pairs, tables, mappings, and graphs. 2 8.5G R 2 7% 11. Proportionality. Write an equation in the form y = mx + b to model a linear relationship between two quantities using verbal, numerical, tabular, and graphical representations. 2 8.5I R 3 11% SE Descriptions SE Descriptions 12. Expressions, equations, and relationships. The student applies mathematical process standards to use multiple representations to develop foundational concepts of simultaneous linear equations. The student is expected to identify and verify the values of x and y that simultaneously satisfy two linear equations in the form y = mx + b from the intersections of the graphed equations. Reporting Category TEKS/SE R or S No. of Items % of Test 2 8.9 S 3 11% R 16 57% S 12 43% All 28 Total Note: R = Readiness Standard, S = Supporting Standard. A copy of the Grade 7 and Grade 8 Mathematics STAAR Reference Chart is printed in each booklet. This assessment is consumable. A graphing calculator must be provided for each student. CAS calculators are NOT permitted. Percentages are rounded to the nearest whole number. Reporting Categories: 1. Numerical Representations and Relationships 2. Computations and Algebraic Relationships 3. Geometry and Measurement 4. Data Analysis and Personal Financial Literacy Mathematical Process Standards Description: SE 1. Apply mathematics to problems arising in everyday life, society, and the workplace. 1A 2. Use a problem-solving model that incorporates analyzing given information, formulating a plan or strategy, determining a solution, justifying the solution, and evaluating the problem-solving process and the reasonableness of the solution. 1B 3. Select tools, including real objects, manipulative, paper and pencil, and technology as appropriate, and techniques, including mental math, estimation, and number sense as appropriate, to solve problems. 1C 4. Communicate mathematical ideas, reasoning, and their implications using multiple representations, including symbols, diagrams, graphs, and language as appropriate. 1D 5. Create and use representations to organize, record, and communicate mathematical ideas. 1E 6. Analyze mathematical relationships to connect and communicate mathematical ideas. 1F 7. Display, explain, and justify mathematical ideas and arguments using precise mathematical language in written or oral communication. 1G