* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Takes 50ms for ap to travel from SA to AV
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
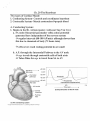
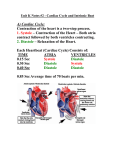
Ch. 20 The Heartbeat Two types of Cardiac Muscle 1. Conducting System- Controls and coordinates heartbeat 2. Contractile System- Muscle contraction^propels blood A. Conducting System: 1. Begins in the Rt. Atrium (poster, wall-near Sup Ven Cav) a. SA node (Sinoatrial-pacemaker cells) action potential generated here independent of the nervous system regular intervals (80-100 AP/min)- although slower than this due to chemicals of body (72 beats /min) cells never reach resting potential & are small b. A.P. through the Internodal Pathway to the AV node a.p. travels through contractile cells of both atria -> Takes 50ms for a.p. to travel from SA to AV +20 mV Sinoatriai (SA) node Internodal -20 mv pathways Threshold -40 mV ^ Prepotenttel Atriovenlriculaf JAV) n<Jde AV bundle Bundle branct^s Purklnje (a) The conducting system _ — (spontaneous depolarization) ^ Time (sec) _ —— (b) Depolarization at the SA node Rate of impulse slows down due to smaller cells and inefficient connections (40-60 AP/min) Delay important-allows vents to fill before contraction d. From AV node^ Bundle of HIS (the only electrical connection between the atria and ventricles) Bundle Branches (IV Septum)- right and left (larger) Purkinje fibers-^ moderator band-> papillary muscles e. Abnormalities- Bradychardia- heart rate slow Tachychardia- heart rate fast B. Contractile System- Ventricular Muscle Contraction 1. Action Potentials from the Purkinje fibers stimulate the contractile cells in the atrial and ventricular walls 2. A.P. leads to Ca binding to troponin, etc. etc. The Cardiac Cycle- the period between the start of one heartbeat and the start of the next - .8 seconds at rest Systole- Contraction Diastole- Relaxation The two atria contract while the two ventricles relax- Atrial Systole, Ventricular Diastole Then, the two atria relax while the two ventricles contractAtrial Diastole, Ventricular Systole Cardiac Cycle in 3 phases: 1. Relaxation Period (.4 seconds)- Ventricles start to relax (pressure falls- opening AY valves again) and all 4 chambers are in diastole 75% of ventricular filling occurs before the atria contract 2. Atrial Systole (.1 seconds-contraction)- Action potential from SA node causes atria to contract- forces the last 25% of blood into ventricles AY valves still open, semilunar closed 3. Ventricular Systole (.3 seconds-contraction)- Ventricles receive action potential/signal & contract closes AV valves, pressure increases forcing semilunars open ventricles begin to relax, pressure drops & semilunars close Exercise decreases the relaxation period Heart sounds: 1. First sound (lubb)- AV valves close 2. Second sound (dub)- Semilunar valves close 3. Pause between them during relaxation period