* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Causes of Macro Instability
Nouriel Roubini wikipedia , lookup
Edmund Phelps wikipedia , lookup
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
International monetary systems wikipedia , lookup
Money supply wikipedia , lookup
Nominal rigidity wikipedia , lookup
Inflation targeting wikipedia , lookup
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Stagflation wikipedia , lookup
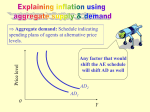
36 Current Issues in Macro Theory and Policy McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Causes of Macro Instability • Mainstream view • Held by most economists • Price stickiness • Unexpected demand shocks • Variable investment spending • Unexpected supply shocks LO1 36-2 Causes of Macro Instability • Monetarist view • Government interference is the problem • Equation of exchange MV = PQ • Stable velocity • Monetary causes of instability • Inappropriate monetary policy LO1 36-3 Causes of Macro Instability • Real-business-cycle view • Shifts in long-run aggregate supply Price Level ASLR2 ASLR1 P1 AD1 AD2 Q2 Q1 Real Domestic Output LO1 36-4 Causes of Macro Instability • Coordination failures • Fail to reach equilibrium because of lack of coordination mechanism • Limited information • Expectations and self-fulfilling prophecy • Unemployment equilibrium • Inflation equilibrium LO1 36-5 Does the Economy Self Correct? • New classical view • Rational expectations theory • Monetarists • Automatic correction will occur • Speed of adjustment • Unanticipated price-level changes • Fully anticipated price-level changes LO2 36-6 Does the Economy Self Correct? • New Classical View of Self-Correction ASLR AS2 Price Level AS1 c P3 b P2 P1 a AD2 AD1 Q1 Q2 Real Domestic Output LO3 36-7 Does the Economy Self Correct? • New Classical View of Self-Correction ASLR Price Level AS1 AS3 P1 P4 f a d P5 e AD1 AD3 Q 4 Q3 Q1 Real Domestic Output LO3 36-8 Does the Economy Self Correct? • Mainstream view • Downward wage inflexibility • Efficiency wage theory • Greater work effort • Lower supervision costs • Reduced job turnover • Insider-outsider relationships LO3 36-9 Rules or Discretion? • In support of policy rules • Reduce macro instability • Monetary rule • Shift AD to keep up with AS • Price stability achieved • Inflation targeting • Balanced budget LO4 36-10 Rules or Discretion? Price Level ASLR1 ASLR2 P1 AD2 P2 AD1 Q1 Q2 Real Domestic Output, GDP LO4 36-11 Rules or Discretion? • Defense of discretionary stabilization policy • Discretionary monetary policy • Velocity is not stable • Discretionary fiscal policy • Useful during recession • Policy successes LO4 36-12 Rules or Discretion? LO4 36-13 The Taylor Rule • Rules: Passive monetary policy • Discretion: Active monetary policy • Hybrid policy rule to dictate Fed • • • actions Policy responds to changes in real GDP and inflation Fed explains deviations from the rule Increase Fed credibility and reduce uncertainty 36-14