* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Regions of ancient Greece wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek architecture wikipedia , lookup
Pontic Greeks wikipedia , lookup
Thebes, Greece wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek religion wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek literature wikipedia , lookup
Greco-Persian Wars wikipedia , lookup
Spartan army wikipedia , lookup
Athenian democracy wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek cuisine wikipedia , lookup
Prostitution in ancient Greece wikipedia , lookup
First Persian invasion of Greece wikipedia , lookup
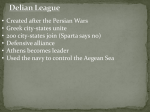
Ancient Civilizations City-state: Definition: a state that has its own government and consists of a city and the area around it Examples: Athens, Sparta, Delphi, Olympia, etc. 1. Did the ancient Greeks own slaves? 2. Could women vote in democratic Athens? 3. Were most city-states actually cities? 4. Did the ancient Greeks have nobles and aristocrats? 5. Was the secret of ancient Greece's success its rich, fertile land? 6. Did the ancient Greeks value wealth above all else? 1. Did the ancient Greeks own slaves? True 2. Could women vote in democratic Athens? 3. 4. 5. 6. False Were most city-states actually cities? False Did the ancient Greeks have nobles and aristocrats? True Was the secret of ancient Greece's success its rich, fertile land? False Did the ancient Greeks value wealth above all else? False Hellas or Eliada “Graecia” (Latin name given by the Romans which means “land of the Greeks) Athens: Direct Democracy everyone, not just politicians attended the Assembly Athens claims to be the "birthplace of democracy" Sparta: Oligarchy rule by a few Athens: Delian League (taxed and protect other city-states) Best navy Sparta: Peloponnesian League Best army Athens: Democracy (People rule! ) Civil participation They believed to be superior Value trade Sparta: Militaristic values Children were raised to be Spartans Respect Elders, women, and warriors Athens: Boys: reading, writing and mathematics, music, poetry, sports and gymnastics (based on wealth) Girls: Little formal education (less equal) Spartans: Boys: They were taken from parents at age seven and trained in the art of warfare choral dance, reading and writing Girls: Reading and writing, gymnastics, athletics and survival skills (more equal) Athens: Athenian women and girls were kept at home with no participation in sports or politics Property Sparta: Opposite to Athenian women The goal was to produce women who would produce strong healthy babies Athens: Art, architecture, drama and literature, philosophy, science, medicine, government, etc. Sparta: Military supremacy and simple lifestyle Athens: Athenians enjoyed luxuries and foods from all over their empire Sparta: Spartan Broth consisted of pork, blood, salt and vinegar