* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Morning Report - LSU School of Medicine
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
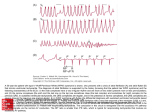
Morning Report September 23, 2010 ECG Rate Rhythm What do you think? What do you want to do? SA node SA node Cardiac pacemaker Upper wall of the RA Sinus Rhythm Normal heart rhythm controlled by SA node p-wave before every QRS PR – 120-200 msec SA node Sinus Arrhythmia Healthy children Decrease in SA node firing due to activation of the vagus nerve by exhalation HR varies with respiration Normal sinus rhythm with prolongation of RR during exhalation The Atria Premature Atrial Contractions (PACs) Ectopic focus stimulates the atria without input from the SA node Causes Drug use, caffeine, electrolyte imbalance, mostly unknown Symptoms (Usually asymptomatic) Skipped beat, pause followed by strong beat ECG Premature, inverted or oddly shaped P waves, sharp inflections in T waves May have narrow, wide or no QRS depending on focus Treatment Reassurance, avoidance The Atria Atrial Flutter 250-400 bpm Newborns or children with structural heart disease Reentrant circuit confined to RA Symptoms CHF (infants), dizziness, syncope, CP, SOB ECG Inverted “saw-tooth” Ventricular conduction - 1:1 (300bpm), 1:2 (150-200bpm) Treatment Urgent cardiac eval and treatment The Atria Atrial fibrillation Uncommon in young children Rapid fibrillation of the atrial muscle without coordinated contraction Causes Structural heart disease Stretching of atria Symptoms Palpitations, CP, syncope ECG Irregularly irregular rhythm Absent or low voltage p-waves Treatment Urgent referral to cards Clot formation >24h The AV node Supraventricular Tachycardia Rapid tachycardia originating above the bundle of His 1/250 children 3 categories Reentrant tachycardia with accessory pathway WPW Reentrant AV nodal tachycardia Atrial ectopic tachycardia SVT Heart rates 220-270bpm Symptoms Infants prolonged Poor feeding, pallor, irritability, lethargy, HD compromise 24-48h School age “beeping in chest”, heart pounding, CP, SOB, sweating, exercise intolerance HR may be 180 ECG Narrow complex tachycardia P waves difficult to see Finding vary with cause Treatment Cardiac referral EP study and ablation The Ventricles Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs) Ectopic firings within the ventricle 25% of healthy children Symptoms Asymptomatic, chest fullness, dizziness, “heart skips” ECG Premature, bizarre, wide QRS complex not preceded by a p-wave Often followed by a compensatory pause Treatment Benign if single, suppressed by exercise and no family history of death Referral to cardiology if history is suspicious The Ventricles Long QTc Syndrome Associated with a potentially dangerous arrhythmia, torsades de pointes QTc = QT/√previous RR QTc >450 msec is suggestive FH of sudden death, deafness Symptoms Syncope, seizures, palpitations, cardiac arrest (10%) Fainting while swimming, playing sports or exercising Treatment Refer if symptoms or if ECG is abnormal Ventricular Tachycardia Tachycardia of at least 3 successive ventricular beats <30 sec – nonsustained >30 sec – sustained Causes Drugs, caffeine, decongestants, electrolyte imbalances Symptoms Abnormal hearts, asymptomatic, pallor, fatigue, palpitations, feeding intolerance Ventricular Tachycardia ECG Bizarre, wide QRS complex (>120 msec), tachycardia May or may not see p-waves T waves are opposite polarization to QRS Treatment ABCs Cardiac Evaluation Ventricular Fibrillation Rare cardiac emergency Uncoordinated activity of the cardiac muscle fibers Often results in cardiac arrest Nonpalpable pulses ECG Bizarre, random waveform without clearly identifiable P waves or QRS complexes and a roaming baseline Treatment ABCs Defibrillation