* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Financial Statements
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
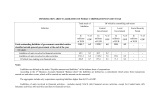
Module 2. Financial Statements Dr. Varadraj Bapat Financial Statements Introduction Balance Sheet Elements of Balance Sheet Dr. Varadraj Bapat Financial Statement Financial statements are records that provide an information of an individual’s, organization’s, or business’ financial status. They are normally prepared general or specific purposes. Dr. Varadraj Bapat General purpose Financial Statement examples Balance Sheet Profit and Loss A/c Cash Flow Statement Fund Flow Statement Segment Revenue Report Dr. Varadraj Bapat Specific purpose Financial Statement examples Departmental Budget Computation prepared for Income Tax Purpose Dr. Varadraj Bapat Balance Sheet Balance Sheet portrays value of economic resources controlled by an enterprises and the way they are financed. A balance sheet or statement of financial position is a summary of the financial balances of an entity on a particular point of time. i.e. summary of organization's assets, liabilities and equity as of a specific date. Dr. Varadraj Bapat Balance Sheet (Format) Liabilities Rs. Assets Rs. Owners Fund XX Fixed Assets XX Non Current Liabilities Current Liabilities XX Non current Investments XX Current Assets XX XX Every balance sheet shall give a true and fair view of state of affairs of the company as at the end of financial year. Dr. Varadraj Bapat Particulars (format as per revised Schedule VI) As at 31st Mar 2011 As at 31st Mar 2010 - - I. EQUITY AND LIABILITIES 1 Shareholder's Funds (a) Share Capital Dr. Varadraj Bapat (b) Reserves and Surplus (c) Money received against Share Warrants 2 Share Application Money pending allotment 3 Non-Current Liabilities (a) Long-Term Borrowings Dr. Varadraj Bapat - - - - - - - - (b) Deferred Tax Liabilities (Net) (c) Other Long Term Liabilities (d) Long-Term Provisions 4 Current Liabilities (a) Short-Term Borrowings (b) Trade Payables Dr. Varadraj Bapat - - - - - - - - - - (c) Other Current Liabilities - - (d) Short-Term Provisions - - TOTAL - - II. ASSETS 1 Non-Current Assets (a) Fixed Assets (i) Tangible Assets - - (ii) Intangible Assets - - Dr. Varadraj Bapat (iii) Capital work-in-progress (iv) Intangible assets under development (b) Non-Current Investments (c) Deferred Tax Assets (Net) (d) Long-Term Loans and Advances (e) Other Non-Current Assets Dr. Varadraj Bapat - - - - - - - - - - - - 2 Current Assets (a) Current Investments - - (b) Inventories - - (c) Trade Receivables - - (d) Cash and Cash Equivalents - - - - - - - - (e) Short-Term Loans and Advances (f) Other Current Assets TOTAL Dr. Varadraj Bapat Elements of Balance Sheet Assets Liabilities Owners Fund Dr. Varadraj Bapat Assets Probable future economic benefit What is owned or controlled Examples Cash Land and Building Investments Machinery Dr. Varadraj Bapat An asset is a resource controlled by the enterprise as a result of past events from which future economic benefits are expected to flow to the enterprise. Resource must have a cost or value that can be measured reliably Dr. Varadraj Bapat Types of assets •Fixed Assets •Current Assets •Investments Fixed Assets Tangible Intangible Dr. Varadraj Bapat Intangible Tangible Land & Building Goodwill Machinery TradeMarks Furniture Patents Dr. Varadraj Bapat Current Assets Monetary Non-Monetary Debtors RM Stock Bank FG Stock Dr. Varadraj Bapat Liabilities • A liability is a present obligation of the enterprise arising from past events, the settlement of which is expected to the result in an outflow of a resource embodying economic benefits. • A liability is an existing obligation based on the evidence available on balance sheet date. Dr. Varadraj Bapat •A liability is recognised when outflow of economic resources in settlement of present obligation can be anticipated and the value of outflow can be reliably measured. Dr. Varadraj Bapat Long-Term Liabilities Long-term liabilities are a company's debts or obligations that are to be repaid or performed beyond one year. Source of fund Examples: • Bank Loan • Loan from Financial Institution • Debentures Dr. Varadraj Bapat Current Liabilities • • Current liabilities are a company's debts or obligations that are to be repaid or performed within one year. Emerge from normal business Examples: • Creditors (Accounts Payable) • Outstanding Expenses Dr. Varadraj Bapat Current Liabilities Interest accrued but not due on Loan • Provision for Tax • Bank Overdraft • Dr. Varadraj Bapat Provision: Provision means any amount retained by way of providing for any known liability of which amount can not be determined with substantial accuracy. Provision refers to an amount set aside for meeting claims which are admissible but the amount whereof has not been confirmed. Dr. Varadraj Bapat Examples Provision for payment of electricity charges (but bill is not yet received). Provision for taxes (till final amount is assessed by authorities.) Provision for bonus Amount set aside for writing off bad debts. Dr. Varadraj Bapat Contingent Liability Contingent liability can be defined as a) a possible obligation that arises from past events and the existence of which will be confirmed only by occurrence or non-occurrence of one or more uncertain future events not wholly within the control of the enterprise Dr. Varadraj Bapat b) a present obligation that arises from past events but is not recognised because: i) it is not probable that an outflow of resources consisting economic benefits will be required to settle the obligation or ii)a reliable estimate of the amount of the obligation cannot be made. Dr. Varadraj Bapat Owners Fund Owners fund is defined as residual interest of an enterprises after deducting all its liabilities. Owners fund is the excess of aggregate assets of an enterprises over its aggregate liabilities. Dr. Varadraj Bapat Balance Sheet Equation Assets= Liabilities + Owners Fund Therefore, Owners Fund= Assets – Liabilities Owners Fund= Capital + Retained Earnings Dr. Varadraj Bapat Balance Sheet Equation A=L+O 1. Company borrows from bank + + (+ Bank, + Bank Loan Payable) 2. Issue of shares by company + + (+ Bank, + Equity Shares) Dr. Varadraj Bapat 3.(a) Cash purchase of equipment 3.(b) Collection of Debtors (+ Equipment, - Bank) (a) +, (b) +, - (+ Bank, - Debtors) 4.(a) Company repays bank loan 4.(b) Payment of Creditors / supplier (a) (b) - - (- Loan Payable, - Bank) (- Creditors, - Bank) Dr. Varadraj Bapat A=L+O 5. Company pays dividend to shareholders - - (- Bank, - Reserves) 6. Company purchases shares from shareholder, pays immediately (buy-back of shares) - - (- Bank, - Equity Capital) Dr. Varadraj Bapat A=L+O 7. Liability is converted into equity shares e.g., loan is converted into equity shares - + (- Loan Payable, + Equity shares) 8. Company incurs new liability to pay existing liability, e.g., Creditors are converted into long-term loan +,- (- Creditors, + Loan Payable) Dr. Varadraj Bapat A=L+O 9. Company distributes stock dividend to stockholders (Bonus Shares) +, (+ Equity Capital, - Reserves) - Dr. Varadraj Bapat Vertical Format of Balance Sheet Sources of Funds Owners Fund Borrowing Funds Rs. Secured Loan XX Unsecured Loan XX Total Capital Employed Dr. Varadraj Bapat Rs. XX XX XX Application of Fund Fixed Assets Rs. Investments Rs. XX XX Working Capital Current Assets XX Current Liabilities (XX) Net Working Capital XX Total Assets Employed XX Dr. Varadraj Bapat Every company has to prepare balance sheet in the form set out in Part I of Schedule VI of Companies Act. Dr. Varadraj Bapat Exercise 1 1. On January 2, owners invest Rs.15,000 in ShriRam Company to begin the business. 2. On January 3, ShriRam Company borrows Rs. 10,000 from DhanLakshmi Bank. 3. On January 5, ShriRam Company purchases Rs. 18,000 of inventory from suppliers. Payment due on Jan 8. Dr. Varadraj Bapat 4. On January 9, ShriRam Company sells inventory that cost Rs. 6,000 for Rs. 8,000 in cash. 5. On January 10, ShriRam Company pays for inventory purchased on January 5. 6. On January 12, ShriRam Company sells inventory that cost Rs. 5,000 for Rs. 6,000, on account. Payment will be received on January 31. Dr. Varadraj Bapat 7. On January 31, ShriRam Company collects the account receivable and puts in bank. Prepare Balance sheet of the concern after each transaction. Dr. Varadraj Bapat 1. On January 2, owners invest Rs.15,000 in ShriRam Company to begin the business. ShriRam Company Balance Sheet January 2, Year 1 Liabilities Assets Capital 15,000 Bank 15,000 Total 15,000 15,000 Total Dr. Varadraj Bapat 2. On January 3, ShriRam Company borrows Rs. 10,000 from DhanLakshmi Bank. ShriRam Company Balance Sheet January 3, Year 1 Liabilities Assets Paid-up 15,000 Bank 25,000 capital DhanLakshmi 10,000 Bank Loan Total 25,000 Total 25,000 Dr. Varadraj Bapat 3. On January 5, ShriRam Company purchases Rs. 18,000 of inventory from suppliers, on account Payment due on January 8 ShriRam Company Balance Sheet January 5, Year 1 Liabilities Assets Paid-up capital 15,000 Bank 25,000 DhanLakshmi 10,000 Inventory 18,000 Bank Loan Accounts 18,000 Payable/Creditors Dr. Varadraj Bapat Total 43,000 Total 43,000 4. On January 9, ShriRam Company sells inventory that cost Rs. 6,000 for Rs. 8,000 in cash.ShriRam Company Balance Sheet January 9, Year 1 Liabilities Assets Paid-up capital 15,000 Bank Reserves 2,000 Inventory 33,000 12,000 DhanLakshmi Bank Loan Creditors Total 45,000 10,000 18,000 45,000 Total Dr. Varadraj Bapat 5. On January 10, ShriRam Company pays for inventory purchased on January 5. ShriRam Company Balance Sheet January 10, Year 1 Liabilities Assets Paid-up capital 15,000 Bank 15,000 Reserves 2,000 Inventory 12,000 DhanLakshmi Bank Loan Creditors Total 10,000 Nil 27,000 Total Dr. Varadraj Bapat 27,000 6. On January 12, ShriRam Company sells inventory that cost Rs. 5,000 for Rs. 6,000, on account. Payment will be received on January 31 ShriRam Company Balance Sheet January 12, Year 1 Liabilities Assets Paid-up capital 15,000 Bank 15,000 Reserves 3,000 Inventory 7,000 DhanLakshmi 10,000 Debtors 6,000 Bank Loan Total 28,000 Total 28,000 Dr. Varadraj Bapat 7. On January 31, ShriRam Company collects the debtors and puts in bank. ShriRam Company Balance Sheet January 31, Year 1 Liabilities Assets Paid-up capital 15,000 Bank 21,000 Reserves 3,000 Inventory 7,000 DhanLakshmi Bank Loan Total 10,000 Debtors 28,000 Total Dr. Varadraj Bapat Nil 28,000 Exercise 2: Show the effect of each transaction on the balance sheet of M/s. Krishna Book Stores Shyam and Murlidhar set up a book stall M/s. Krishna Book Stores in their town. On 1 Jan 2010, Shyam opened new bank account in the name of their partnership by depositing Rs. 100000 cash and Murlidhar brought his own shop worth Rs. 200000 as capital. Dr. Varadraj Bapat On 2 January 2010, store purchased book of Rs. 75000 and Stationary of Rs. 10000 on immediate payment from SK International. On 5 January 2010, Stores supplies books of Rs. 90000 (costing 60000) to Saraswati Highschool. School paid cheque Rs. 45000 immediately and reaming amount will be paid on 10 January 2010. Dr. Varadraj Bapat On 9 January 2010, books costing 47000 purchased on credit from SSK and Associates. On 10 January 2010, Rs. 15000 received from Saraswati Highschool. On 15 January 2010, cheque of Rs. 47000 paid to creditors. Dr. Varadraj Bapat Balance Sheet as on 1 Jan 2010 Liabilities Capital Shyam Murlidhar Amount Assets 100000 Shop Premises 200000 Bank 300000 Dr. Varadraj Bapat Amount 200000 100000 300000 Balance Sheet as on 2 Jan 2010 Liabilities Capital Shyam Murlidhar Amount Assets 100000 Shop Premises 200000 Bank Inventory 300000 Dr. Varadraj Bapat Amount 200000 15000 85000 300000 Balance Sheet as on 5 Jan 2010 Liabilities Capital Shyam Murlidhar Profit and Loss A/c Amount Assets 100000 Shop Premises 200000 Bank 30000 Sundry Debtors Inventory 330000 Dr. Varadraj Bapat Amount 200000 60000 45000 25000 330000 Balance Sheet as on 9 Jan 2010 Liabilities Capital Shyam Murlidhar Profit and Loss A/c Sundry Creditors Amount Assets 100000 Shop Premises 200000 Bank 30000 Inventory 47000 Sundry Debtors 377000 Dr. Varadraj Bapat Amount 200000 60000 72000 45000 377000 Balance Sheet as on 10 Jan 2010 Liabilities Capital Shyam Murlidhar Profit and Loss A/c Sundry Creditors Amount Assets 100000 Shop Premises 200000 Bank 30000 Inventory 47000 Sundry Debtors 377000 Dr. Varadraj Bapat Amount 200000 75000 72000 30000 377000 Balance Sheet as on 15 Jan 2010 Liabilities Capital Shyam Murlidhar Profit and Loss A/c Amount Assets 100000 Shop Premises 200000 Bank 30000 Inventory Sundry Debtors 330000 Dr. Varadraj Bapat Amount 200000 28000 72000 30000 330000