* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nov8 - Salamander Genome Project
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and archaeogenetics of South Asia wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
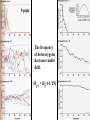
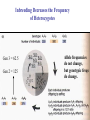
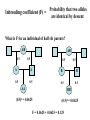
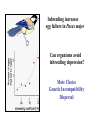
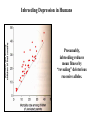
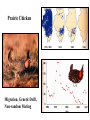
Box 9.1 History of Conservation Genetics Goals: (1) Preserved genetic diversity all levels (2) Promote the continuance of ecological and evolutionary processes that foster and sustain biodiversity. How can Molecular Markers Help Us? Molecular Markers Can be Used to Estimate Heterozygosity See Table 9.1 in Avise Many examples of reduced heterozygosity Limitations of Molecular Markers: Are they suited to detect past historical events? Are they suited to measure genome-wide heterozygosity? Are they likely to be associated or independent of phenotypic variation? 8 pops The frequency of heterozygotes decreases under drift. Hg+1 = Hg[1-1/2N] Inbreeding Decreases the Frequency of Heterozygotes Gen 3 = 62.5 Gen 2 = 125 Allele frequencies do not change, but genotypic freqs do change. Heterozygosity and Inbreeding Heterozygosity in an inbred population = Heterozygosity in a random mating population x Prob. not IBD H F = HO (1 - F) Anytime F is greater than 0, the frequency of heterozygotes is Lower in an inbred population than in a random mating population. Inbreeding coefficient (F) = Probability that two alleles are identical by descent What is F for an individual of half sib parents? AB 0.5 AB 0.5 0.5 0.5 A A B B 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 AA BB (0.5)4 = 0.0625 (0.5)4 = 0.0625 F = 0.0625 + 0.0625 = 0.125 Does genetic variation always determine the likelihood of extinction? 1) A number of studies have documented fitness affects associated with heterozygosity (Avise p. 487). 2) However, non-genetic aspects should also be considered in the formulation of species management plans. For example, a species may be endangered because mating and social behaviors are severely affected. Also, random changes in population size may be important irregardless of heterozygosity. Heterozygosity and Disease Resistance Cheetah are now genetically impoverished populations, especially at MHC loci. Feline infectious peritonitis (FIP) recently swept through several colonies killing 50-60% of the animals. However in domestic cats, the average mortality rate is only 1%. Also, there is growing evidence that disease is playing a major role in the current and ongoing world-wide amphibian declines. Inbreeding increases egg failure in Parus major Can organisms avoid inbreeding depression? Mate Choice Genetic Incompatibility Dispersal Inbreeding Depression in Humans Presumably, inbreeding reduces mean fitness by “revealing” deleterious recessive alleles. Prairie Chicken Migration, Genetic Drift, Non-random Mating Prairie chicken almost went extinct in the 1950’s. Why did fitness decrease after early efforts were implemented to conserve remnant populations? Average number of DNA alleles per locus Illinois pre-bottleneck 5.12 Illinois present 3.67 Other Pops in Midwest 5.33-5.88 An Extinction Vortex Loss of Habitat Extinction or reduced population sizes Gene Flow - reduced / eliminated Genetic Drift and Non-random Mating Loss of heterozygosity Deleterious alleles increase in frequency Inbreeding Depression -- lowered fitness Extinction or reduced population sizes